Abstract
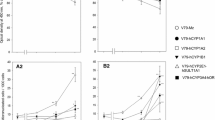
The toxicities of the coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl (TCB), 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PeCB) and 3,3′,4,4′,5,5′hexachlorobiphenyl (HCB) were compared in a 72-h study on chick embryos. The substances were injected into the air sacs of hens' eggs preincubated for 7 days. Mortality was measured 72 h later and corresponding LD50 values were calculated. The rank order of toxicity was PeCB> TCB>HCB. Using the same injection procedure, the potencies of these chlorobiphenyls with regard to their induction of hepatic 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase activity were compared. The ranking order of the substances as inducers was the same as their order when ranked according to toxicity. The three coplanar chlorobiphenyls were considerably more toxic and potent as inducers than the nonplanar 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl. In a 2-week toxicity study, PeCB and HCB were injected into the yolks of hens' eggs preincubated for 4 days. PeCB was about 50-fold more potent than HCB in causing embryonic death. Both substances caused abnormalities, including edema, liver lesions, microphthalmia and beak deformities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandiera S, Safe S, Okey AB (1982) Binding of polychlorinated biphenyls classified as either phenobarbitone-methylcholanthrene- or mixed-type inducers to cytosolic Ah receptor. Chem Biol Interact 39: 259–277
Brunström B (1986) Activities in chick embryos of 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase and aryl hydrocarbon (benzo[a]pyrene) hydroxylase and their induction by 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl in early embryos. Xenobiotica 16: 865–872
Brunström B (1988) Sensitivity of embryos from duck, goose, herring gull, and various chicken breeds to 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl. Poultry Sci 67: 52–57
Brunström B, Darnerud PO (1983) Toxicity and distribution in chick embryos of 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl injected into the eggs. Toxicology 27: 103–110
Brunström B, Örberg J (1982) A method for studying embryotoxicity of lipophilic substances experimentally introduced into hens' eggs. Ambio 11: 209–211
Hamilton JW, Dension MS, Bloom SE (1983) Development of basal and induced aryl hydrocarbon (benzo[a]pyrene) hydroxylase activity in the chicken embryo in ovo. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 80: 3371–3376
Higginbotham GR, Huang A, Firestone D, Verrett J, Ress J, Campbell AD (1968) Chemical and toxicological evaluations of isolated and synthetic chloro derivatives of dibenzo-p-dioxin. Nature 220: 702–703
Jensen S (1966) Report of a new chemical hazard. New Sci 32: 612
Kannan N, Tanabe S, Wakimoto T, Tatsukawa R (1987) Coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls in Aroclor and Kanechlor mixtures. J Assoc Off Anal Chem 70: 451–454
McKinney JD, Chae K, McConnell EE, Birnbaum LS (1985) Structure-induction versus structure-toxicity relationships for polychlorinated biphenyls and related aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Health Perspect 60: 57–68
McKinney JD, Chae K, Gupta BN, Moore JA, Goldstein JA (1976) Toxicological assessment of hexachlorobiphenyl isomers and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in chicks. I. Relationship of chemical parameters. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 36: 65–80
Millis CD, Mills RA, Sleight SD, Aust SD (1985) Toxicity of 3,4,5,3′,4′,5′-hexabrominated biphenyl and 3,4,3′,4′-tetrabrominated biphenyl. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 78: 88–95
Nebert DW, Jensen NM (1979) The Ah locus: genetic regulation of the metabolism of carcinogens, drugs, and other environmental chemicals by cytochrome P-450-mediated monooxygenases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 6: 401–437
Phillipson CE, Godden PMM, Lum PY, Ioannides C, Parke DV (1984) Determination of cytochrome P-448 activity in biological tissues. Biochem J 221: 81–88
Pohl RJ, Fouts JR (1980) A rapid method for assaying the metabolism of 7-ethoxyresorufin by microsomal subcellular fractions. Anal Biochem 107: 150–155
Poland A, Glover E (1977) Chlorinated biphenyl induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity: a study of the structure-activity relationship. Mol Pharmacol 13: 924–938
Poland A, Knutson JC (1982) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 22: 517–554
Safe S (1984) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs): biochemistry, toxicology and mechanism of action. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol 13: 319–395
Schrankel KR, Kreamer BL, Hsia MTS (1982) Embryotoxicity of 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachloroazobenzene and 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachloroazoxybenzene in the chick embryo. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 11: 195–202
Shimada T (1987) Lack of correlation between formation of reactive metabolites and thymic atrophy caused by 3,4,3′,4′tetrachlorobiphenyl in C57B1/6N mice. Arch Toxicol 59: 301–306
Shimada T, Sawabe Y (1983) Activation of 3,4,3′,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl to protein-bound metabolites by rat liver microsomal cytochrome P-448-containing monooxygenase system. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 70: 486–493
Silkworth JB, Grabstein EM (1982) Polychlorinated biphenyl immunotoxicity: dependence on isomer planarity and the Ah gene complex. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 65: 109–115
Tanabe S, Kannan N, Subramanian An, Watanabe S, Ono M, Tatsukawa R (1986) Potentially significant residues of highly toxic non-ortho substituted PCBs in human adipose tissues and in terrestrial and marine animals. Dioxin 86: 6th International Symposium on Chlorinated Dioxins and Related Compounds. September 16–19, 1986, Fukuoka, Japan. Abstract, p 132
Yoshimura H, Yoshihara S, Ozawa N, Miki M (1979) Possible correlation between induction modes of hepatic enzymes by PCBs and their toxicity in rats. Ann NY Acad Sci 320: 179–192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunström, B., Andersson, L. Toxicity and 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase-inducing potency of coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in chick embryos. Arch Toxicol 62, 263–266 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00332485
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00332485