Abstract
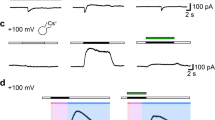
High pH is known to be associated with normal cell growth and neoplastic transformation. We observed that Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells grown under sustained alkaline stress (pH 7.7) develop “foci” composed of spindle-shaped cells lacking contact inhibition and exhibiting only poor adhesion to the culture support. Foci-developing (F) cells were cloned and grown in control medium (pH 7.4), where they maintained their neoplastic features indicating a stable pH-induced genetic transformation. After F cells had been fused to giant cells with polyethylene glycol, the cell membrane potential (V m) was measured by means of microelectrodes. In contrast to non-transformed MDCK cells, V M of F cells showed spontaneous biorhythmicity caused by periodic opening of Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Spiking activity was blunted by the Ca2+ channel blocker nifedipine, by the K+ channel blocker Ba2+, by the Na+/H+ exchange blocker amiloride and its analogue ethylisopropylamiloride, and by an extracellular pH of 7.6 and 6.8. We conclude that MDCK cells transformed by sustained alkaline stress have lost their stable plasma membrane potential but, instead, exhibit endogenous Ca2+- and pH-sensitive oscillations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge MJ (1988) Inositol trisphosphate-induced membrane potential oscillations in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 403:589–599
Berridge MJ, Galione A (1988) Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J 2:3074–3082
Borle AB, Borle CJ, Dobransky P, Gorecka-Tisera AM, Bender C, Swain K (1990) Effect of low extracellular Ca2+ on cytosolic free Ca2+, Na+, and pH of MDCK cells. Am J Physiol 259:C19-C25
Chang D, Kushman NL, Dawson DC (1991) Intracellular pH regulates basolateral K+ and Cl− conductances in colonic epithelial cells by modulating Ca2+ activation. J Gen Physiol 98:183–196
Gillies RJ, Martinez-Zaguilan R, Martinez GM, Serrano R, Perona R (1990) Tumorigenic 3T3 cells maintain an alkaline pH under physiological conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7414–7418
Goldbeter A, Dupont G, Berridge MJ (1990) Minimal model for signal-induced Ca2+ oscillations and for their frequency encoding through protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1461–1465
Grandin N, Charbonneau M (1990) Cycling of intracellular pH during cell division of Xenopus embryos is a cytoplasmic activity depending on protein synthesis and phosphorylation. J Cell Biol 111:523–532
Grandin N, Charbonneau M (1991) Intracellular free calcium oscillates during cell division of Xenopus embryos. J Cell Biol 112:711–718
Hesketh TR, Smith GA, Moore JP, Taylor MV, Metcalfe JC (1983) Free cytoplasmic calcium concentration and the mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Biol chem 258:4876–4882
Igusa Y, Miyazaki S-I (1983) Effects of altered extracellular and intracellular calcium concentration on hyperpolarizing responses of the hamster egg. J Physiol (Lond) 340:611–632
Igusa Y, Miyazaki S-I (1986) Periodic increase of cytoplasmic free calcium in fertilized hamster eggs measured with calcium-sensitive electrodes. J Physiol (Lond) 377:193–205
Ince C, Leijh PCJ, Meijer J, van Bavel E, Ypey DL (1984) Oscillatory hyperpolarizations and resting membrane potentials of mouse fibroblast and macrophage cell lines. J Physiol (Lond) 352:625–635
Kersting U, Joha H, Steigner W, Gaßner B, Gstraunthaler G, Pfaller W, Oberleithner H (1989) Fusion of cultured dog kidney (MDCK) cells: I. Technique, fate of plasma membranes and of cell nuclei. J Membr Biol 111:37–48
Kimura M, Gardner JP, Aviv A (1990) Agonist-evoked alkaline shift in the cytosolic pH set point for activation of Na+/H+ antiport in human platelets. J Biol Chem 265:21068–21074
Kitamura K, Sakai T, Kajioka S, Kuriyama H (1989) Activations of the Ca dependent K channel by Ca released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of mammalian smooth muscles. Biomed Biochim Acta 48:8364–3369
Kuba K (1980) Release of calcium ions linked to the activation of potassium conductance in a caffeine-treated sympathetic neurone. J Physiol (Lond) 298:251–269
Lang F, Friedrich F, Kahn E, Wöll E, Hammerer M, Waldegger S, Maly K, Grunicke H (1991) Bradykinin-induced oscillations of cell membrane potential in cells expressing the Ha-ras-oncogene. J Biol Chem 266:4938–4942
Libenson L, Jena M (1974) Extracellular pH and neoplastic transformations. Cancer Res 34:953–957
Meyer T, Stryer L (1988) Molecular model for receptor-stimulated calcium spiking. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5051–5055
Oberleithner H, Kersting U, Hunter M (1988) Cytoplasmic pH determines K+ conductance in fused renal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8345–8349
Oberleithner H, Kersting U, Silbernagl S, Steigner W, Vogel U (1989) Fusion of cultured dog kidney (MDCK) cells: II. Relationship between cell pH and K+ conductance in response to aldosterone. J Membr Biol 111:49–56
Oberleithner H, Westphale H-J, Gaßner B (1991) Alkaline stress transforms Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Pflügers Arch 419:418–420
Orchard CH, Houser SR, Kort AA, Bahinski A, Capogrossi MC, Lakatta EG (1987) Acidosis facilitates spontaneous sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release in rat myocardium. J. Gen Physiol 90:145–165
Peres A, Giovannardi S (1990) Mitogen-induced oscillations of membrane potential and Ca2+ in human fibroblasts. FEBS Lett 261:35–38
Pucéat M, Clément O, Scamps F, Vassort G (1991) Extracellular ATP-induced acidification leads to cytosolic calcium transient rise in single rat cardiac myocytes. Biochem J 274:55–62
Sauvé R, Simoneau C, Parent L, Monette R, Roy G (1987) Oscillatory activation of calcium-dependent potassium channels in HeLa cells induced by histamine H, receptor stimulation: a single-channel study. J. Membr Biol 96:199–208
Sauvé R, Diarra A, Chahine M, Simoneau C, Garneau L, Roy G (1990) Single-channel and fura-2 analysis of internal Ca2+ oscillations in HeLA cells: contribution of the receptor-evoked Ca2+ influx and effect of internal pH. Pflügers Arch 416:43–52
Sauvé R, Diarra A, Chahine M, Simoneau C, Morier N, Roy G (1991) Ca2+ oscillations induced by histamine H1 receptor stimulation in HeLa cells: fura-2 and patch clamp analysis. Cell Calcium 12:165–176
Sperelakis N, Schneider MF, Harris EJ (1967) Decreased K+-conductance produced by Ba2+ in frog sartorius fibres. J Gen Physiol 50:1565–1583
Thornton JR (1981) High colonic pH promotes colorectal cancer. Lancet 1:1081–1083
Tsunoda Y (1990) Cytosolic free calcium spiking affected by intracellular pH change. Exp Cell Res 188:294–301
Tsunoda Y, Matsuno K, Tashiro Y (1991) Cytosolic acidification leads to Ca2+ mobilization from intracellular stores in single and populational parietal cells and platelets. Exp Cell Res 193:356–363
Ueda S, Oiki S, Okada Y (1986) Oscillations of cytoplasmic concentrations of Ca2+ and K+ in fused L cells. J Membr Biol 91:65–72
Yada T, Oiki S, Ueda S, Okada Y (1986) Synchronous oscillation of the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration and membrane potential in cultured epithelial cells (intestine 407). Biochim Biophys Acta 887:105–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westphale, H.J., Wojnowski, L., Schwab, A. et al. Spontaneous membrane potential oscillations in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells transformed by alkaline stress. Pflügers Arch 421, 218–223 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374830
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374830