Summary
-
1.
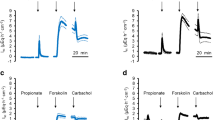
In the tied off colon of the anaesthetized rat in situ, the effect of diphenolic laxatives (bisacodyl and phenolphthalein) and of osmotic laxatives (mannitol, sodium sulfate and lactulose) on water net flux was studied. All the laxatives reduced water net flux from lumen to blood or reversed it into water net flux from blood to lumen. Pretreatment with indomethacin reduced or abolished the effect of the diphenolic laxatives on water net flux but did not change the effect of the osmotic laxatives.
-
2.
In the perfused colon of the rat in situ, the effect of the diphenolic and the osmotic laxatives on water net flux and on PGE-release into the colonic lumen was investigated. All laxatives reduced water net flux from lumen to blood in this preparation, too.
PGE-release into the lumen during perfusion with osmotic laxatives was not different from the control. The diphenolic lexatives increased PGE-release dosedependently about 2-fold.
-
3.
Intraluminal perfusion of the jejunal loop of the rat in situ with bisacodyl increased intestinal blood flow by about 50%. Addition of indomethacin to the perfusion fluid abolished this increase.
-
4.
It is concluded that diphenolic laxatives exert their laxative action at least partially via stimulation of intestinal PGE-biosynthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamic, S., Bihler, I.: Inhibition of intestinal sugar transport by phenolphthalein. Mol. Pharmacol. 3, 188–194 (1967)
Beubler, E., Juan, H.: The function of prostaglandins in transmucosal water movement and blood flow in the rat jejunum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 299, 89–94 (1977)
Beubler, E., Juan, H.: Is the effect of diphenolic laxatives mediated via release of prostagladin E? Experientia 34, 386–387 (1978a)
Beubler, E., Juan, H.: PGE-release, blood flow and transmucosal water movement after mechanical stimulation of the rat jejunal mucosa. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 305, 91–95 (1978b)
Beubler, E., Lembeck, F.: Methylxanthines and intestinal drug absorption. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 292, 73–77 (1976)
Beubler, E., Lembeck, F., Schweditsch, M.: Effects of PGE2 and colchicine on the intestinal fluid volume. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 301, 195–199 (1978)
Chignell, C. F., Titus, E. O.: The inhibition of rat small intestinal (Na++K+-ATPase by phenolphthalein and other purgative drugs. Fed. Proc. 27, 831 (1968)
Collier, H. O. J., McDonald-Gibson, W. J., Saeed, S. A.: Stimulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis by drugs: effects in vitro of some drugs affecting gut function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 58, 193–199 (1976)
Coupar, I. M., McColl, I.: Stimulation of water and sodium secretion and inhibition of glucose absorption from the rat jejunum during intraarterial infusions of prostaglandins. Gut 16, 759–765 (1975)
Duncan, D. B.: Multiple range and multiple F-tests. Biometrics 11, 1–42 (1955)
Ferreira, S. H., Moncada, S., Vane, J. R.: Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nature New Biol. 231, 237–239 (1951)
Fingl, E.: Laxatives and cathartics. In: The pharmacological basis of therapeutics (Goodman, L. S., Gilman, A., eds.). Fifth ed., p. 983. New York: MacMillan Publishing 1975
Forth, W., Rummel, W.: Activation and inhibition of intestinal absorption by drugs. In: IEPT — Pharmacology of intestinal absorption of drugs. Section 39B, Vol. I (W. Forth and W. Rummel, eds.). Oxford: Pergamon Press 1975
Forth, W., Rummel, W., Baldauf, J.: Wasser- und Elektrolytbewegung am Dünn- und Dickdarm unter dem Einfluß von Laxantien, ein Beitrag zur Klärung ihres Wirkungsmechanismus. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmak. Exp. Path. 254, 18–32 (1966)
Goodfriend, T. L., Levine, L., Fasman, G. D.: Antibodies to bradykinin and angiotensin: A use of carbodiimides in immunology. Science 144, 1344–1346 (1964)
Matuchansky, C., Bernier, J. J.: Effect of prostaglandin E1 on glucose, water, and electrolyte absorption in the human jejunum. Gastroenterology 64, 1111–1118 (1973)
Nell, G., Overhoff, H., Forth, W., Rummel, W.: The influence of water gradients and oxyphenisatin on the net transfer of sodium and water in the rat colon. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 277, 363–372 (1973a)
Nell, G., Rummel, W., Forth, W., Wanitschke, R.: Abolition of the apparent Na+-impermeability of the colon mucosa. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 274, R81 (1972)
Nell, G., Forth, W., Overhoff, H., Pfleger, K., Rummel, W.: Ein-und Ausstrom von Natrium an Dünn-und Dickdarm. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 269, 423–424 (1971)
Nell, G., Forth, W., Rummel, W., Wanitschke, R.: Pathway of sodium moving from blood to intestinal lumen under the influence of oxyphenisatin and deoxycholate. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 293, 31–37 (1976)
Nell, G., Overhoff, H., Forth, W., Kulenkampff, H., Specht, W., Rummel, W.: Influx and efflux of sodium in jejunal and colonic segments of rats under influence of oxyphenisatin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 277, 53–60 (1973b)
Pace-Asciak, C.: Prostaglandin synthetase activity in the rat stomach fundus: activation by l-norepinephrine and related compounds. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 280, 161–171 (1972)
Peskar, B., Hertting, G.: Release of prostaglandins from isolated cat spleen by angiotensin and vasopressin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 279, 227–234 (1973)
Pierce, N. F., Carpenter, C. C. J., Elliott, H. L., Greenough, W. B.: Effects of prostaglandins, theophylline, and cholera exotoxin upon transmucosal water and electrolyte movement in the canine jejunum. Gastroenterology 60, 22–32 (1971)
Robert, A.: Antisecretory, antiulcer, cytoprotective and diarrheogenic properties of prostaglandins. In: Advances in prostaglandin and thromboxane research (Samuelsson, B., Paoletti, R., eds.). pp. 507–520. New York: Raven Press 1976
Smith, J. B., Willis, A. L.: Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nature New Biol. 231, 235–237 (1971)
Vane, J. R.: Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nature New Biol. 231, 232–235 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beubler, E., Juan, H. PGE-Mediated laxative effect of diphenolic laxatives. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 305, 241–246 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498817
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498817