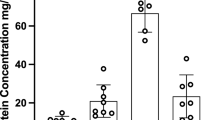
Summary
The binding to human plasma proteins of ampicillin, α-azidobenzylpenicillin, benzylpenicillin, phenobarbital and diphenylhydantoin was studied by equilibrium dialysis of labelled compounds. Human foetal and neonatal plasma had very low binding capacities for all five drugs as compared with plasma from adults. Hyperbilirubinemia in the neonatal period further decreased the binding capacity. The age dependence of drug binding activity should be taken into account when analysing pharmacological effects in foetuses and newborn children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boréus, L.O.: Placental transfer of ampicillin. To be published in Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1971.
Ganshorn, A., Kurz, H.: Unterschiede zwischen der Proteinbindung Neugeborener und Erwachsener und ihre Bedeutung für die pharmakologische Wirkung. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak.260, 117–118 (1968).
Gornall, A.G., Bardawill, J. David, M.M.: Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J. biol. Chem.177, 751–766 (1949).
Grunbaum, B.W., Zec, J., Durrum, E.L.: Application of an improved microelectrophoresis technique and immunoelectrophoresis of the serum proteins on cellulose acetate. Microchem. J.7, 41–53 (1963).
Jalling, B., Boréus, L.O., Rane, A., Sjöqvist, F.: Plasma concentrations of diphenylhydantoin in young infants. Pharmacol. Clin. (Berl.)2, 198–200 (1970).
Keen, P.M.: The binding of penicillins to bovine serum albumin. Biochem. Pharmacol15, 447–463 (1966).
Lous, P.: Plasma levels and urinary excretion of three barbituric acids after oral administration to man. Acta pharmacol. (Købh.)10, 147–165 (1954).
Lunde, P.K.M., Rane, A., Yaffe, S.J., Lund, L., Sjöqvist, F.: Plasma protein binding of diphenylhydantoin in man: Interaction with other drugs and the effect of temperature and plasma dilution. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.11, 846–855 (1970).
Nosslin, B.: The direct diazo reaction of bile pigments in serum. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.12, Suppl. 49 (1960).
Rane, A., Lunde, P.K.M., Jalling, B., Yaffe, S.J., Sjöqvist, F.: Plasma protein binding of diphenylhydantoin in normal and hyperbilirubinemic infants. J. Pediat.78, 877–882 (1971).
Scholtan, W.: Die Bindung der Penicilline an die Eiweißkörper des Plasmas und der Gewebsflüssigkeit. Antibiot. Chemother. (Basel)14, 55–93 (1968).
Sjöberg, B., Ekström, B., Forsgren, U.: α-Azidobenzylpenicillin. I. Chemistry, bacteriology, and experimental chemotherapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1967, 560 – 567.
Svensmark, O., Buchtal, F.: Dosage of phenytoin and phenobarbital in children. Dan. med. Bull.10, 234–235 (1963).
Thalme, B.: A system of microliter methods suitable for routine clinical work. Acta med. scand.174, Suppl. 403, 1–16 (1963).
Warren, G.H.: The prognostic significance of penicillin serum levels and protein binding in clinical medicine. A review of current studies. Chemotherapia (Basel)10, 339–358 (1965/66).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehrnebo, M., Agurell, S., Jalling, B. et al. Age differences in drug binding by plasma proteins: Studies on human foetuses, neonates and adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 3, 189–193 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00565004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00565004