Abstract
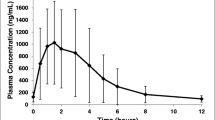
Six healthy subjects between the ages of 21 and 31 years received diazepam tablets orally at a dose of 5 mg t.i.d. atO, 5, and 10hr on days 1–13. On day 14, the dose was 5 mg at 0 and 5 hr and 15 mg at 10 hr. Subsequently, the dose was 15 mg once daily on days 15–24. Numerous plasma samples were obtained during the multiple-dose regimen, and appropriate equations were fitted to all the multiple-dose data. Diazepam absorption was satisfactorily described by a first-order process, with disposition characterized by a linear two-compartment open model. The harmonic mean absorption half-life was 32 min, and the harmonic mean terminal exponential half-life was 57hr. The mean apparent oral total drug plasma clearance was 22.7ml/hr/kg. Steady-state plasma levels of the primary metabolite, desmethyldiazepam, were reached after 5–8 days of dosing. Steady-state diazepam plasma concentration-time profiles suggested that once daily administration of the total daily dose at bedtime might be a satisfactory dosing regimen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Physicians' Desk Reference, 30th ed., Medical Economics Co., Oradell, N.J., 1976, p. 1307.
I. A. Zingales. Diazepam metabolism during chronic medication: Unbound fraction in plasma, erythrocytes and urine.J. Chromatog. 75:55–78 (1973).
E. Van der Kleijn, J. M. van Rossum, E. T. J. M. Muskens, and N. V. M. Rijntjes. Pharmacokinetics of diazepam in dogs, mice and humans.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 31:109–127 (1972).
H. H. Dashberg, E. van der Kleijn, P. J. R. Guelen, and H. M. van Praag. Plasma concentrations of diazepam and of its metabolite N-desmethyldiazepam in relation to anxiolytic effect.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 15:473–483 (1974).
A. Berlin, B. Siwers, S. Agurell, å. Hiort, F. Sjöqvist, and S. Strom. Determination of bioavailability of diazepam in various formulations from steady state plasma concentration data.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 13:733–744 (1972).
S. Agurell, A. Berlin, H. Ferngren, and B. Hellström. Plasma levels of diazepam after parenteral and rectal administration in children.Epilepsia 16:277–283 (1975).
S. A. Kaplan, M. L. Jack, K. Alexander, and R. E. Weinfeld. Pharmacokinetic profile of diazepam in man following single intravenous and oral and chronic oral administrations.J. Pharm. Sci. 62:1789–1796 (1973).
L. Hillestad, T. Hansen, H. Melsom, and A. Drivenes. Diazepam metabolism in normal man. I. Serum concentrations and clinical effects after intravenous, intramuscular, and oral administration.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16:479–484 (1974).
L. Hillestad, T. Hansen, and H. Melsom. Diazepam metabolism in normal man. II. Serum concentration and clinical effect after oral administration and cumulation.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16:485–489 (1974).
J. Kanto, E. Iisalo, V. Lehtinen, and J. Salminen. The concentrations of diazepam and its metabolites in the plasma after an acute and chronic administration.Psychopharmacologia 36:123–131 (1974).
R. Sellman, J. Kanto, E. Raijola, and A. Pekkarinen. Induction effect of diazepam on its own metabolism.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37:345–351 (1975).
J. Kanto. Plasma concentrations of diazepam and its metabolites after peroral, intramuscular, and rectal administration: Correlation between plasma concentration and sedatory effect of diazepam.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 12:427–432 (1975).
M. Linnoila, K. Korttila, and M. J. Mattila. Effect of food and repeated injections on serum diazepam levels.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 36:181–186 (1975).
U. Klotz, G. R. Avant, A. Hoyumpa, S. Schenker, and G. R. Wilkinson. The effects of age and liver disease on the disposition and elimination of diazepam in adult man.J. Clin. Invest. 55:347–359 (1975).
U. Klotz, K. H. Antonin, and P. R. Brieck. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of diazepam after single and subchronic doses.Eur.J. Clin. Pharmacol. 10:121–126 (1976).
J. G. Wagner and coworkers. Pharmacokinetic parameters estimated from intravenous data by uniform methods.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:161–182 (1977).
P. B. Andreasen, J. Hendel, G. Greisen, and E. F. Hvidberg. Pharmacokinetics of diazepam in disordered liver function.Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 10:115–120 (1976).
R. E. Weinfeld, H. N. Posmanter, K. C. Khoo, and C. V. Puglisi. Rapid determination of diazepam and nordiazepam in plasma by electron capture gas-liquid chromatography: Application in clinical pharmacokinetic studies.J. Chromatog. (in press).
J. G. Wagner.Biopharmaceutics and Relevant Pharmacokinetics, Drug Intelligence Publications, Hamulton, Ill., 1971, p. 295.
W. A. Colburn, D. Shen, and M. Gibaldi. Pharmacokinetic analysis of drug concentration data obtained during repetitive drug administration.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 4:469–486 (1976).
C. M. Metzler.A User's Manual for NONLIN, Technical Report 7292/69/7292/005, Upjohn Co., Kalamazoo, Mich., November 25, 1969.
R. Ronfeld and H. G. Boxenbaum. In preparation, programs available upon request.
C. M. Metzler, G. L. Elfring, and A. J. McEwen.A User's Manual for NONLIN and Associated Program, Upjohn Co., Kalamazoo, Mich., April 20, 1974.
J. G. Wagner, E. Novak, L. G. Leslie, and C. M. Metzler. Absorption, distribution, and elimination of spectinomycin dihydrochloride in man.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1:261–285 (1968).
H. G. Boxenbaum, S. Riegelman, and R. M. Elashoff. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2:123–148 (1974).
H. G. Boxenbaum, K. A. Geitner, M. L. Jack, W. R. Dixon, and S. A. Kaplan. Pharmacokinetic and biopharmaceutic profile of chlordiazepoxide HCl in healthy subjects: Multiple dose oral administration.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:25–39 (1977).
J. G. Wagner. Model-independent linear pharmacokinetics.Drug Intelligence 10:179–180 (1976).
G. R. Wilkinson and D. G. Shand. A physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 18:377–390 (1975).
S. Huck, G. Stacher, G. Gogolák, and C. Stumpf. Action of six commonly used benzodiazepines on isolated guinea-pig ileum preparation.Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 218:77–83 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eatman, F.B., Colburn, W.A., Boxenbaum, H.G. et al. Pharmacokinetics of diazepam following multiple-dose oral administration to healthy human subjects. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 5, 481–494 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061729
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061729