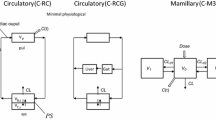
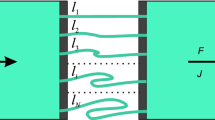
Abstract
The residence time distributions of sucrose and taurocholate have been determined from the outflow concentration-time profiles after bolus input into an in situperfused rat liver preparation. The normalized variance (and the dispersion number) appeared to be independent of perfusate flow rate (10 to 37ml/mm) and perfusate albumin concentration (0–5%). The apparent volume of distribution for sucrose appeared to increase with flow rate but was unaffected by the concentration of albumin (0–5%) present in the perfusate. The changes in taurocholate availability with flow rate were adequately accounted for by the dispersion model, whereas taurocholate availabilityprotein binding changes required an albumin-mediated transport model to be used in conjunction with the dispersion model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs: I. Theoretical considerations of a “well-stirred” model and a “parallel tube” model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding and hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:625–653 (1977).
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs: II. Experimental evidence for acceptance of the “well-stirred” model over the “parallel tube” model using lidocaine in the perfused ratin situ preparation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:655–680 (1977).
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs: III. Additional experimental evidence supporting the “well-stirred” model, using metabolite (MEGX) generated from lidocaine under varying hepatic blood flow rates and linear conditions in the perfused liverin situ preparation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:681–699 (1977).
A. B. Ahmad, P. N. Bennett, and M. Rowland. Models of hepatic drug clearance: Discrimination between the “well-stirred” and “parallel tube” models.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 35:219–224 (1983).
D. B. Jones, D. J. Morgan, G. W. Mihaly, L. K. Webster, and R. A. Smallwood. Discrimination between the venous equilibrium and sinusoidal models of hepatic drug elimination in the isolated perfused rat liver by perturbation of propranolol protein binding.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 229:522–526 (1984).
W. Colburn. Albumin does not mediate the removal of taurocholate by rat liver.J. Pharm. Sci. 71:373–374 (1982).
K. S. Pang and J. R. Gillette. Kinetics of metabolite formation and elimination in the perfused rat liver preparation: Differences between the elimination of preformed acetaminophen and acetaminophen formed from phenacetin.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 207:178–194 (1978).
S. Keiding and E. Chiarantini. Effect of sinusoidal perfusion on galactose elimination in perfused rat liver.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 205:465–470 (1978).
M. Rowland, K. Leitch, G. Fleming, and B. Smith. Protein binding and hepatic clearance: Discrimination between models of hepatic clearance with diazepam, a drug of high intrinsic clearance, in the isolated perfused rat liver preparation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 12:129–147 (1984).
S. Keiding and E. Steiness. Flow dependence of propranolol elimination in perfused rat liver.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 230:474–477 (1984).
L. Bass, P. J. Robinson, and A. J. Bracken. Hepatic elimination of flowing substances: The distributed model.J. Theoret. Biol. 72:161–184 (1978).
E. L. Forker and B. Luxon. Hepatic transport kinetics and plasma disappearance curves. Distributed modelling versus conventional approach.Am. J. Physiol. 235:E648-E660 (1978).
L. Bass. Saturation kinetics in hepatic drug removal: A statistical approach to functional heterogeneity.Am. J. Physiol. 244:G583-G589 (1983).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. Hepatic elimination-dispersion model.J. Pharm. Sci. 74:585–587 (1985).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. A dispersion model of hepatic elimination. 1. Formulation of the model and bolus considerations.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:227–260 (1986).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. A dispersion model of hepatic elimination: 2. Steady-state considerations. Influence of blood flow, protein binding and hepatocellular enzymatic activity.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:261–288 (1986).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. A dispersion model of hepatic elimination: 3. Application to metabolite formation and elimination kinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:289–308 (1986).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. Correlation between in vitro microsomal enzyme activity and whole organ hepatic elimination kinetics: Analysis with a dispersion model.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 38:117–181 (1986).
M. S. Roberts, J. D. Donaldson, and M. Rowland. Models of hepatic elimination: Comparison of stochastic models to describe residence time distributions and to predict the influence of drug distribution, enzyme heterogeneity and systemic recycling or hepatic elimination.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 16:41–84 (1988).
M. Gibaldi and G. Perrier.Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed., Marcel Dekker, New York, 1982, pp. 409–417.
A. W. Woikoff, C. A. Goresky, J. Selkin, Z. Gatmaiten, and I. M. Arias. Role of ligandin in the transfer of bilirubin from plasma into liver.Am. J. Physiol. 236:E638-E648 (1979).
C. A. Goresky, A linear method for determining liver sinusoidal and extravascular volume.Am. J. Physiol. 204:626–640 (1963).
C. A. Goresky. Kinetic interpretation of hepatic multiple-indicator studies.Am. J. Physiol. 245:G1-G12 (1983).
E. L. Forker and B. A. Luxon. Albumin helps moderate removal of taurocholate by rat liver.J. Clin. Invest. 67:1517–1522 (1981).
J. M. Pries, A. B. Staples, and R. F. Hanson. The effect of hepatic blood flow on taurocholate extraction by the isolated perfused rat liver.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 97:412–417 (1981).
L. Bass, M. S. Roberts, and P. J. Robinson. On the relation between extended forms of the sinusoidal perfusion and of the convection-dispersion models of hepatic elimination.J. Theoret. Biol. 126:457–482 (1987).
R. H. Smallwood, D. J. Morgan, G. W. Mihaly, and R. A. Smallwood. Lack of linear correlation between hepatic ligand uptake rate and unbound ligand concentration does not necessarily imply receptor mediated uptake.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 16:397–411 (1988).
R. H. Smallwood, D. J. Morgan, D. B. Jones, G. W. Mihaly, and R. A. Smailwood. Effect of plama protein binding on elimination of taurocholate by isolated perfused rat liver—comparison of venous equilibrium undistributed and distributed sinusoidal and dispersion models.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 16:377–396 (1988).
R. Weisiger, J. Gollen, and R. Ockner. Receptor for albumin on the liver cell surface may mediate uptake of fatty acids and other albumin-bound substances.Science 211:1048–1051 (1981).
L. Bass and S. Keiding. Physiologically based models and strategic experiments in hepatic pharmacology.Biochem. Pharmacol. 37:1425–1431 (1988).
L. Schwarz, R. Burr, M. Schwark, E. Pfaff, and H. Greim. Uptake of taurocholate acid into isolated rat liver cells.Em. J. Biochem. 55:617–623 (1975).
T. Iga and C. D. Klaassen. Uptake of bile acids by isolated rat hepatocytes.Biochem. Pharmacol. 31:211–216 (1982).
P. V. Dippe and D. Levy. Characterisation of the bile acid transport system in normal transformed hepatocytes: photoaffinity labelling of the taurocholate carrier protein.J. Biol. Chem. 258:8896–8901 (1983).
G. M. M. Groothuis, M. J. Hardonk, K. P. T. Keulemans, P. Nieuwenhuis, and D. K. M. Meijer. Autoradiographic and kinetic demonstration of acinar heterogeneity of taurocholate transport.Am. J. Physiol. 243:G455-G462 (1982).
N. E. Huffman, J. H. Iser, and R. A. Smallwood. Hepatic bile transport: effect of conjugation and position of hydroxyl groups.Am. J. Physiol. 229:298–302 (1975).
R. A. Weisiger, C. M. Zacks, N. D. Smith, and J. L. Boyer. Effect of albumin binding on extraction of sulfobromophthalin by perfused elasmobranch liver: evidence for dissociation limited uptake.Hepatology 4:492–501 (1984).
R. A. Weisiger. Dissociation from albumin: A potentially rate-limiting step in the clearance of substances by the liver.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82:1563–1567 (1985).
P. V. Sluijs, B. Postema, and D. K. F. Meijer. Lactosylation of albumin reduced uptake rate of dibromosulfophthalein in perfused rat liver and dissociation rate from albumin in vitro.Hepatology 7:688–695 (1987).
A. W. Wolkoff. The role of an albumin receptor in hepatic organic anion uptake: the controversy continues.Hepatology 7:777–779 (1987).
P. D. I. Richardson and P. G. Withrington. Liver blood flow. I. Intrinsic and nervous control of liver blood flow.Gastroenterology 81:159–173 (1981).
P. D. I. Richardson and P. G. Withrington. Liver blood flow. II. Effects of drugs and hormones on liver blood flow.Gastroenterology 81:356–375 (1981).
J. L. Campra and T. B. Reynolds. The hepatic circulation. In I. Arias, D. Popper, D. Schatchter, and D. A. Shafritz (eds.),The Liver Biology and Pathobiology, Raven, NY, chap. 37, pp. 627–645 (1982).
A. M. Thompson, H. M. Cavert, and N. Lifson. Kinetics of distribution of D2O and antipyrine in isolated perfused rat liver.Am. J. Physiol. 192:531–537 (1958).
A. M. Thompson, H. M. Cavert, N. Lifson, and R. L. Evans. Regional tissue uptake of D2O in perfused organs: rat liver, dog heart and gastocnemius.Am. J. Physiol. 197:897–902 (1959).
W. O. Griffen, D. G. Levitt, C. J. Ellis, and N. Lifson. Intrahepatic distribution of hepatic blood flow: single-input studies.Am. J. Physiol. 218:1474–1479 (1970).
N. Lifson, D. G. Levitt, W. O. Griffen, and C. J. Ellis. Intrahepatic distribution of hepatic blood flow: double-input studies.Am. J. Physiol. 218:1480–1488 (1970).
M. S. Roberts, J. D. Donaldson, and D. R. Jackett. Availability predictions by hepatic elimination models for Michaelis-Menten kinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharmaceut. 17:687–719 (1989).
B. C. Sherrill and J. M. Dietschy. Characterisation of the sinusoidal transport process responsible for uptake of chylomicrons by the liver.J. Biol. Chem. 253:1859–1867 (1978).
D. B. Jones, G. W. Mihaly, R. A. Smallwood, L. K. Webster, D. J. Morgan, and N. P. Madsen. Differential effects of hypoxia on the disposition of propranol and sodium taurocholate by the isolated perfused rat liver.Hepatology 4:461–466 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Dean's MRC (NZ) Fund.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, M.S., Fraser, S., Wagner, A. et al. Residence time distributions of solutes in the perfused rat liver using a dispersion model of hepatic elimination: 1. Effect of changes in perfusate flow and albumin concentration on sucrose and taurocholate. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 18, 209–234 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062200
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062200