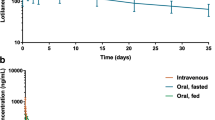
Abstract
Studies are reported which describe the effects of formulation, animal species, and route of administration on the pharmacokinetics of ivermectin. Biological half-life t1/2 increases in the order: swine (0.5 day) > dogs (1.8 day) > cattle ≌ sheep (2.8 day). Formulation modifications, based upon the solubility properties of the drug, have been directed towards the development of a nonaqueous injectable formulation for cattle and an aqueous vehicle for horses. Bioavailability following subcutaneous injection in cattle can be regulated by control of injection solvent composition: a vehicle composed of a mixed aqueous-organic solvent exhibits pharmacokinetic properties (i.e., Cp, t1/2, AUC, and F) intermediate between those furnished by an aqueous formulation and via a purely nonaqueous solvent. The longer apparent biological half-life from this latter vehicle (t1/2=8.3 days) confirms that a slow absorption process dominates the pharmacokinetics in the nonaqueous injectable product to produce an effective controlled-release formulation. These bioavailability results illustrate the increase in the concentration of an organic solvent and a concomitant decrease in surfactant concentration in a micellar aqueous system for prolonged drug delivery via injection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers-Schönberg, G., Arison, B. H., Chabala, J. C., Douglas, A. W., Eskola, P., Fisher, M. H., Lusi, A., Mrozik, H., Smith, J. L. and Tolman, R. L., 1981. Avermectins. Structure determination. Journal of the American Chemical Societv, 103: 4216–4221.
Anderson, D. L. and Roberson, E. L., 1982. Activity of ivermectins against canine intestinal helminths. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 43: 1681–1683.
Armour, J., Bairden, K. and Preston, J. M., 1982. Anthelmintic efficiency of iveragainst naturally occurring gastrointestinal nematodes of sheep. Veterinary Record, 111: 80–81.
Campbell, W. C. 1982. Efficacy of the avermectins against filarial parasites: A short review. Veterinary Research Communications, 5: 251–262.
Campbell, W. C. and Benz, G. W., 1984. Ivermectin: a review of efficacy and safety. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 7: 1–16.
Campbell, W. C., Fisher, M. H., Stapley, E. O., Albers-Schönberg, G. and Jacob, T. A., 1983. Ivermectin: A potent new antiparasitic agent. Science, 221: 823–828.
Chabala, J. C., Mrozik, H., Tolman, R. L., Eskola, P., Lusi, A., Peterson, L. H., Woods, M. F. and Fisher, M. H., 1980. Ivermectin, a new broad-spectrum antiparasitic agent. Journal of Medical Chemistry, 23: 1134–1136.
Courtnev, C. H., Ingals, W. L., and Stitzlein, S. L. 1983. Ivermectin for the control of swine scabies: Relative values of prefarrowing treatment of sows and weaning treatment of pigs. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 44: 1220–1223.
Hibbert, H. and Carter, N. M., 1928. Studies on the reactions relating to carbohydrates and polysaccharides. XVII. Structure of the isomeric methylidene glycerols. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 50: 3120–3127.
Leo, A., Hansch, C. and Elkins, D., 1971. Partition coefficients and their uses. Chemical Reviews, 71: 525–555.
Lo, P.-K. A. and Williams, J. B., 1983. Solubilization of ivermectin in water. U. S. Patent 4,389,397. Chemical Abstracts, 99:76906q.
Meleney, W. P. 1982. Control of psorootic scabies on calves with ivermectin. American Journal of Veterinary Research, 43: 329–331.
Mirck, M. H. and vanMeurs, G. K., 1982. The efficacy of ivermectin against strongyloides westeri in foals. Veterinary Quarterly, 4: 89–91.
Notari, R. E., 1980. Biopharmaceutics and clinical pharmacokinetics. An Introduction. Third Edition, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, p. 127.
Pivnichny, J. V., Shim, J.-S.K. and Zimmerman, L. A. 1983. Direct determination of avermectins in plasma at nanogram levels by high-performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 72: 1447–1450.
Tolan, J. W., Eskola, P., Fink, D. W., Mrozik, H. and Zimmerman, L. A., 1980. Determination of avermectins in plasma at nanogram levels using highperformance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Journal of Chromatography, 190: 367–376.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albert Lo, PK., Fink, D.W., Williams, J.B. et al. Pharmacokinetic studies of ivermectin: Effects of formulation. Vet Res Commun 9, 251–268 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02215150
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02215150