Abstract
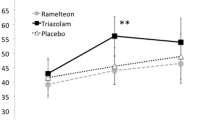
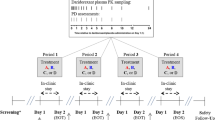
In a double-blind, six-way crossover study the effects on psychomotor performance and memory of single doses of Ro 41-3696 (1, 3, 5 and 10 mg), a novel non-benzodiazepine partial agonist at the benzodiazepine receptor, zolpidem (10 mg) and placebo were compared after night-time administration to 12 healthy young male subjects. Psychomotor performance tests (tracking and attention as part of a standardized task battery) were conducted just before and at 1.5 and 8 h after drug intake. The memory test consisted of the recall of a list of 15 words at 8 h after drug intake which had been learned at 1.5 h after intake. At 1.5 h after drug intake 10 mg zolpidem induced markedly larger psychomotor effects than any dose of Ro 41-3696. The effects of 5 and 10 mg Ro 41-3696 and zolpidem were significantly greater than those of placebo (P < 0.05). The following morning, 8 h after drug intake, the slight residual effects of 5 and 10 mg Ro 41-3696 were statistically significantly greater than placebo, whereas zolpidem effects did not differ from placebo. The results of the memory test showed that learning as well as recall were most clearly impaired by zolpidem. An influence of Ro 41-3696 on these variables was not observed for doses up to 5 mg. In conclusion, Ro 41-3696 at all doses tested induced less effects on psychomotor performance and memory than 10 mg zolpidem at 1.5 h after intake. However, the effects of Ro 41-3696 appeared to be of longer duration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton H (1994) Guidelines for the rational use of benzodiazepines — when and what to use. Drugs 48:25–40
Balkin TJ, O'Donnell VM, Wesensten N, McCann U, Belenky G (1992) Comparison of the daytime sleep and performance effects of zolpidem versus triazolam. Psychopharmacology 107:83–88
Berlin I, Warot D, Hergueta T, Molinier P, Bagot C, Puech AJ (1993) Comparison of the effects of zolpidem and triazolam on memory functions, psychomotor performances, and postural sway in healthy subjects. J Clin Psychopharmacol 13:100–106
Boer LC, Wientjes CJE (1988) Assessment of psychological fitness. In: Aschenbrenner H (ed) Proceedings of the workshop on psychological fitness. NATO DS/A/DR 89:107, pp 1–11
Dingemanse J (1995) Pharmacotherapy of insomnia: practice and prospects. Pharm World Sci: 17:67–75
Dingemanse J, Bury M, Roncari G, Zell M, Gieschke R, Gaillard AWK, Odink J, Van Brummelen P (1995) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Ro 41-3696, a novel non-benzodiazepine hypnotic. J Clin Pharmacol: (in press)
ECSC-EEC-EAEC (1994) Guidelines on psychotropic drugs for the EC. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 4:61–77
Fairweather DB, Kerr JS, Hindmarch I (1992) The effects of acute and repeated doses of zolpidem on subjective sleep, psychomotor performance and cognitive function in elderly volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 43:597–601
Gaillard AWK, Gruisen A, de Jong R (1988) The influence of antihistamines on human performance. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 35:249–253
Ghoneim MM, Mewaldt SP (1990) Benzodiazepines and human memory: a review. Anesthesiology 72:926–938
Gieschke R, Cluydts R, Dingemanse J, de Cock W (1994) Effects of bretazenil vs. zolpidem and placebo on experimentally-induced sleep disturbance in healthy volunteers. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 16:667–675
Hindmarch I (1991) Residual effects of hypnotics: an update. J Clin Psychiatry 52 [Suppl]: 14–15
Johnson LC, Chernik DA (1982) Sedative-hypnotics and human performance. Psychopharmacology 76:101–113
Jonas JM, Coleman BS, Sheridan AQ, Kalinske RW (1992) Comparative clinical profiles of triazolam versus other shorteracting hypnotics. J Clin Psychiatry 53 [12 Suppl.]: 19–31
Langer SZ, Arbilla S, Scatton B, Niddam R, Dubois A (1988) Receptors involved in the mechanism of action of zolpidem. In: Sauvanet JP, Langer SZ, Morselli PL (eds) Imidazopyridines in sleep disorders. Raven Press, New York, pp 55–80
Langtry HD, Benfield P (1990) Zolpidem: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic potential. Drugs 40:291–313
Lorizio A, Terzano MG, Parrino L, Cesana BM, Priore P (1990) Zolpidem: a double-blind comparison of the hypnotic activity and safety of a 10-mg versus 20-mg dose. Curr Ther Res 47:889–898
Maczaj M (1993) Pharmacological treatment of insomnia. Drugs 45:44–55
Martin JR, Moreau J-L, Jenck F, Widmer U (1994) Pharmacological profile of several quinolizinones acting as partial agonists at the benzodiazepine receptor. Neuropsychopharmacology 10, 3S [Part 2]: 170S
Roehrs T, Merlotti L, Zorick F, Roth R (1994) Sedative, memory, and performance effects of hypnotics. Psychopharmacology 116:130–134
Scherschlicht R (1994) The quinolizinone hypnotic Ro 41-3696, a partial agonist at the flumazenil binding site, induces EEG sleep in rabbits but lacks sedative side effects in rodents. 8. Biennial IPEG meeting, Berlin, Germany
Schoch P, Moreau JL, Martin JR, Haefely WE (1993) Aspects of benzodiazepine receptor structure and function with relevance to drug tolerance and dependence. Biochem Soc Symp 59:121–134
Shiffrin RM, Schneider W (1977) Controlled and automatic human information processing. II. Perceptual learning, automatic attending, and a general theory. Psychol Rev 84:127–190
Sternberg S (1969) Mental processes revealed by reaction time experiments. Am Sci 4:421–457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dingemanse, J., Bury, M., Joubert, P. et al. Comparative pharmacodynamics of Ro 41-3696, a new hypnotic, and zolpidem after night-time administration to healthy subjects. Psychopharmacology 122, 169–174 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246091
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246091