Abstract
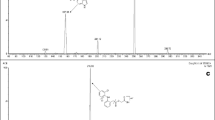
Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (HPLC/MS) with an electrospray ionization (ESI) interface was applied to the identification of metabolites of IY 81149 in the rat plasma. Fragments obtained using collision-induced dissociation (CID) in both positive and negative modes were utilized to elucidate the structure of metabolites. The eluent from the conventional HPLC column was split and directly introduced into an ESI-mass spectrometer for the identification of the structures. The CID technique allowed the sensitive identification of sulfonyl-IY81149 and hydroxy-IY81149 from the rat plasma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Andersson, T., Lagerstrom, P. O., Miners, J. O., Veronese, M. E., Weidolf, L. and Birkett, D. J., High-performance liquid chromatographic assay for human liver microsomal omeprazole metabolism.J. Chromatogr. B, 619, 291–297 (1993).
Beattie, I. G. and Blake, T. J., The structural identification of drug metabolites using thermospray liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry.Biomed. Environment. Mass Spectrom., 18, 872–877 (1989).
Black, J., Reflections on the analytical pharmacology of histamine H2-receptor antagonists.Gastroenterology, 105, 963–968 (1993).
Hewlett-Packard, inAPI-Electrospray LC/MS System, User’s Guide, manual part number 59987-90005, pp. 52, 1994.
Kim, S. U., Kim, D. Y., Chung, G. J., Hong, S. K., Park, S. J., Nam, S. H. and Lee, Y. S.,United States Patent, Pat. 5,703,097, Dec. 30, 1997.
Kobayashi, K., Chiba, K., Sohn, D., Kato, Y. and Ishizaki, T., Simultaneous determination of omeprazole and its metabolites in plasma and urine by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with an alkaline-resistant polymer-coated C18 column,J. Chromatogr. B, 579, 299–305 (1992).
Lindberg, P., Brandstorm, A., Wallmark, B., Mattsson, H., Rikner, L. and Hoffmann, K. J., Omeprazole: the first proton pump inhibitor.Med. Res. Rev., 10, 1–54 (1990).
McArthur, K. E., Collen, M. J., Maton, P. N., Cherner, J. A., Howard, J. M., Ciarleglio, C. A., Cornelius, M. J., Jensen, R. T. and Gardner, J. D., Omeprazole: effective, conbenient therapy for Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.Gastroenterology, 88, 939–944 (1985).
McTavish, D., Buckley, M. M. and Heel, R. C., Omeprazole. An updated review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in acid-related disorders.Drugs, 42, 138–170 (1991).
Weidolf, L. and Covey, T. R., Studies on the metabolism of omeprazole in the rat using liquid chromatography/ionspray mass spectrometry and the isotope cluster technique with [34S] omeprazole.Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 6, 192–196 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myung, SW., Min, HK., Jin, C. et al. Identification of IY81149 and its metabolites in the rat plasma using the on-line HPLC/ESI mass spectrometry. Arch Pharm Res 22, 189–193 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976545
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976545