Abstract
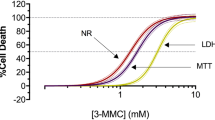
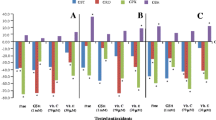
The cytotoxic effects of the herbicides paraquat (1,1′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridylium dichloride), dinoseb (2-sec-butyl-4,6-dinitrophenol) and 2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) on freshly isolated rat hepatocytes were investigated. Paraquat and 2,4-D (1–10 mM) caused a dose and time dependent cell death accompanied by depletion of intracellular glutathione (GSH) and mirroring increase of oxidized glutathione (GSSG). Dinoseb, the most effective cytotoxic compound under study (used in concentrations 1000 fold lower than paraquat and 2,4-D), exhibited moderate effects upon the level of GSH and GSSG. These limited effects are at variance with significant effects upon the adenine and pyridine nucleotide contents. ATP and NADH levels are rapidly depleted by herbicide metabolism. This depletion is observed in the millimolar range for paraquat and 2,4-D and in the micromolar range for dinoseb. 2,4-D completely depletes cellular ATP, with subsequent cell death, as detected by LDH leakage. Paraquat rapidly depletes NADH, according to the redox cycling of the herbicide metabolism. The most effective compound is dinoseb since it exerts similar effects as described for paraquat and 2,4-D at concentrations 1000 fold lower. Simultaneously with NADH and ATP depletion, the levels of ADP, AMP and NAd+ increase in hepatocytes incubated in the presence of the herbicides. In contrast to NADH, the time course and extent of ATP depletion and fall in energy charge correlate reasonably with the time of onset and rate of cell death. It is concluded that the herbicides, paraquat and 2,4-D are hepatotoxic and initiate the process of cell death by decreasing cellular GSH. As a consequence of this primary disturbance, alteration of adenine and pyridine nucleotides contents is a critical event in the induction of irreversible cell injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aw TY, Jones DP (1985) ATP concentration gradient in cytosol of liver cells during hypoxia. Am J Physiol 249: C385-C392
Baillie TA, Slatter JG (1991) Glutathione: a vehicle for the transport of chemically reactive metabolites in vivo. Accounts of Chemical Research 24: 264–270
Bellomo G, Orrenius S (1985) Altered thiol and calcium homeostasis in oxidative hepatocellular injury. Hepatology 5: 876–882
Boobis AR, Fawthrop DJ, Davies DS (1989) Mechanisms of cell death. TIPS 10: 275–280
Brigelius R, Lenzen R, Sies H (1982) Increase in hepatic mixed disulphide and glutathione disulphide levels elicited by paraquat. Biochem Pharmacol 31: 1637–1641
Cadenas E, Brigelius R, Sies H (1983) Paraquat-induced chemiluminescence of microsomal fractions. Biochem Pharmacol 32: 147–150
Casini AF, Maellaro E, Pompella A, Ferrali M, Comporti M (1987) Lipid peroxidation proteins thiols and calcium homeostasis in bromobenzene-induced liver damage. Biochem Pharmacol 36: 3689–3695
Dargel R (1992) Lipid peroxidation—a common pathogenetic mechanism? Exp Toxicol Pathol 44: 169–181
DeGray JA, Rao DNR, Mason RP (1991) Reduction of paraquat and related bipyridylium compounds to free radical metabolites by rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 289: 145–152
DeLeve LD, Kaplowitz N (1991) Glutathione metabolism and its role in hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol Ther 52: 287–305
DiMonte D, Ross D, Bellomo G, Eklow L, Orrenius S (1984) Alterations in intracellular thiol homeostasis during the metabolism of menadione by isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 235: 334–342
DiMonte D, Jewell SA, Ekstrom G, Sandy MS, Smith MT (1986) 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine (MPP+) cause rapid ATP depletion in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 137: 310–315
Donatus IA, Sardjoko, Vermeulen NPE (1990) Cytotoxic and cytoprotective activities of curcumin. Effects on paracetamol-induced cytotoxicity, lipid peroxidation and glutathione depletion in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 39: 1869–1875
Fawthrop DJ, Boobis AR, Davies DS (1991) Mechanisms of cell death. Arch Toxicol 65: 437–444
Ghatineh S, Morgan W, Preece NE, Timbrell JA (1992) A biochemical and NMR spectroscopic study of hydrazine in the isolated hepatocyte. Arch Toxicol 66: 660–668
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JC (1986) Oxygen free radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine: some problems and concepts. Arch Biochem Biophys 246: 501–514
Hara S, Endo T, Kurriwa F, Kano S (1991) Mechanism of paraquat-stimulated lipid peroxidation in mouse brain and pulmonary microsomes. J Pharm Pharmacol 43: 731–733
Harman AW, Kyle ME, Serroni A, Farber JL (1991) The killing of cultured hepatocytes by n-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) as a model of the cytotoxicity of acetaminophen. Biochem Pharmacol 41: 1111–1117
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1976) A fluorometric method for the determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Chem 74: 214–220
Hogberg J, Kristoferson A (1977) A correlation between glutathione levels and cellular damage in isolated hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem 74: 77–82
Holme JA, Hongslo JK, Bjorge C, Nelson SD (1991) Comparative cytotoxic effects of acetaminophen (N-acetyl-p-aminophenol), a non-hepatotoxic regioisomer acetyl-m-aminophenol and their postulated reactive hydroquinone and quinone metabolites in monolayer cultures of mouse hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 42: 1137–1142
Jones DP (1986) Intracellular diffusion gradients of O2 and ATP. Am J Physiol 250: C663-C675
Kappus H (1986) Overview of enzyme systems involved in bio-reduction of drugs and in redox cycling. Biochem Pharmacol 35: 1–6
Krall J, Bagley AC, Mullenbach GT, Hallewell RA, Lynch RE (1988) Superoxide mediates the toxicity of paraquat for cultured mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 263: 1910–1914
Kraus-Friedman N, Biber J, Muren H, Carafoli E (1982) Calcium uptake in isolated hepatic plasma membrane vesicles. Eur J Biochem 129: 7–12
Kroese ED, Bannenberg G, Dogterom P, Noach ABJ, Nagelkerke JF, Meerman JHN (1990) Lipid peroxidation and protein thiol depletion are not involved in the cytotoxicity of N-hydroxy-2-acetylaminofluorene in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 40: 1885–1892
Lemasters JJ, DiGiuseppi J, Nieminen A-L, Herman B (1987) Blebbing, free Ca2+ and mitochondrial membrane potential preceding cell death in hepatocytes. Nature 325: 78–81
Maellaro E, Casini AF, Del Bello B, Comporti M (1990) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant systems in the liver injury produced by glutathione depleting agents. Biochem Pharmacol 39: 1513–1521
Moldéus P, Hogberg J, Orrenius S (1978) Isolation and use of liver cells. In: Fleischer S, Packer L (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 52, Academic Press, New York, pp 60–71
Nakagawa Y, Moldéus P, Moore GA (1992) Cytotoxicity of ortho-phenylphenol in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 43: 159–165
Nicotera P, Thor H, Orrenius S (1989) Cytosolic-free Ca2+ and cell killing in hepatoma lclc7 cells exposed to chemical anoxia. FASEB J 3: 59–64
Nieminen AL, Gores GJ, Wray BE, Tanaka Y, Herman B, Lemasters JJ (1988) Calcium dependence of bleb formation and cell death in hepatocytes. Cell Calcium 9: 237–246
Orrenius S (1985) Biochemical mechanisms of cytotoxicity. TIPS 6 [FEST supplement]: 15–20
Peter B, Wartena M, Kampinga HH, Konings WT (1992) Role of lipid peroxidation and DNA damage in paraquat toxicity and the interaction of paraquat with ionizing radiation. Biochem Pharmacol 43: 705–715
Redegeld FAM, Moison RMW, Koster ASJ, Noordhoek J (1989) Alterations in energy status by menadione metabolism in hepatocytes from fasted and fed rats. Arch Biochem Biophys 273: 215–222
Reed DJ, Fariss MW (1984) Glutathione depletion and susceptibility. Pharmacol Rev 36: 25S-33S
Reitman FA, Shertzer HG, Berger ML (1988) Toxicity of methylating agents in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 37: 3183–3188
Sandy MS, Moldeus P, Ross D, Smith MT (1986) Role of redox cycling and lipid peroxidation in bipyridyl herbicide cytotoxicity. Studies with a compromised isolated hepatocyte model system. Biochem Pharmacol 35: 3095–3101
Silva JM, McGirr L, O'Brien P (1991) Prevention of nitrofurantoininduced cytotoxicity in isolated hepatocytes by fructose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 289: 313–318
Smith PF, Hoke GD, Alberts DW, Bugelski PJ, Lupo S, Mirabelli CKM, Rush G (1989) Mechanism of toxicity of an experimental bidentate phosphine gold complexed antineoplastic agent in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 249: 944–950
Stevens JT, Sumner DD (1991) Herbicides. In: Hayes WJ, Laws ER (eds) Handbook of pesticide toxicology, vol 3, Academic Press, New York, pp 1317–1391.
Stocchi V, Cucchiarini L, Magnani M, Chiarantini L, Palma P, Crescentini G (1985) Simultaneous extraction and reverse-phase highperformance liquid chromatographic determination of adenine and pyridine nucleotides in human red blood cells. Anal Biochem 146: 118–124
Suntres ZE, Hepworth SR, Shek PN (1992) Protective effect of liposome-associated α-tocopherol against paraquat-induced acute lung toxicity. Biochem Phamacol 44: 1811–1818
Thompson D, Moldéus P (1988) Cytotoxicity of butylated hydroxyanisole and butylated hydroxytoluene in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 37: 2201–2207
Van de Straat R, de Vries, J, Debets AJJ, Vermeulen NPE (1987) The mechanism of prevention of paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity by 3,5-dialkyl substitution. The roles of glutathione depletion and oxidative stress. Biochem Pharmacol 36: 2065–2070
Videla LA, Barros SB, Junqueira VBC (1990) Lindane-induced liver oxidative stress. Free Rad Biol Med 9: 169–179
Ware GW (1978) Chemicals used in the control of plants. In: The pesticide book. WH Freeman, San Franscisco, pp 75–94
Zer H, Freedman JH, Peisach J, Chevion M (1991) Inverse correlation between resistance towards copper and towards the redox-cycling compound paraquat: a study in copper-tolerant hepatocytes in tissue culture. Free Rad Biol Med 11: 9–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palmeira, C.M., Moreno, A.J. & Madeira, V.M.C. Metabolic alterations in hepatocytes promoted by the herbicides paraquat, dinoseb and 2,4-D. Arch Toxicol 68, 24–31 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050025
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050025