Abstract
Rationale
Mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone) is a still poorly known drug of abuse, alternative to ecstasy or cocaine.
Objective
The major aims were to investigate the pharmacokinetics and locomotor activity of mephedrone in rats and provide a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model.
Methods
Mephedrone was administered to male Sprague–Dawley rats intravenously (10 mg/kg) and orally (30 and 60 mg/kg). Plasma concentrations and metabolites were characterized using LC/MS and LC-MS/MS fragmentation patterns. Locomotor activity was monitored for 180–240 min.
Results
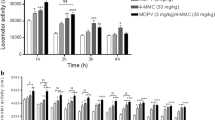
Mephedrone plasma concentrations after i.v. administration fit a two-compartment model (α = 10.23 h−1, β = 1.86 h−1). After oral administration, peak mephedrone concentrations were achieved between 0.5 and 1 h and declined to undetectable levels at 9 h. The absolute bioavailability of mephedrone was about 10 % and the percentage of mephedrone protein binding was 21.59 ± 3.67 %. We have identified five phase I metabolites in rat blood after oral administration. The relationship between brain levels and free plasma concentration was 1.85 ± 0.08. Mephedrone induced a dose-dependent increase in locomotor activity, which lasted up to 2 h. The pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic model successfully describes the relationship between mephedrone plasma concentrations and its psychostimulant effect.
Conclusions
We suggest a very important first-pass effect for mephedrone after oral administration and an easy access to the central nervous system. The model described might be useful in the estimation and prediction of the onset, magnitude, and time course of mephedrone pharmacodynamics as well as to design new animal models of mephedrone addiction and toxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett PH, Bell BM, Cobelli C, Golde H, Schumitzky A, Vicini P, Foster DM (1998) SAAM II: Simulation, Analysis and Modeling Software for tracer and pharmacokinetics studies. Metabolism 147:484–492
Baumann MH, Ayestas MA Jr, Partilla JS, Sink JR, Shulgin AT, Daley PF, Brandt SD, Rothman RB, Ruoho AE, Cozzi NV (2012) The designer methcathinone analogs, mephedrone and methylone, are substrates for monoamine transporters in brain tissue. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:1192–1203
Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Lehner KR (2013) Psychoactive “bath salts”: not so soothing. Eur J Pharmacol 698:1–5
Brunt TM, Koeter MW, Niesink RJ, van den Brink W (2012) Linking the pharmacological content of ecstasy tablets to the subjective experiences of drug users. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 220:751–762
Chu T, Kumagai Y, DiStefano EW, Cho AK (1996) Disposition of mehylenedioxymethamphetamine and three metabolites in the brains of different rat strains and their possible roles in acute serotonin depletion. Biochem Pharmacol 51:789–796
Cozzi NV, Sievert MK, Shulgin AT, Jacobill P, Rhuolo AE (1999) Inhibition of plasma membrane monoamine transporters by betaketoamphetamines. Eur J Pharmacol 381:63–69
Csajka C, Verotta D (2006) Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modeling: history and perspectives. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 33:227–279
Dickson AJ, Vorce SP, Levine B, Past MR (2010) Multiple-drug toxicity caused by the coadministration of 4-methylmethcathinone (mephedrone) and heroin. J Anal Toxicol 34:162–168
Fonsart J, Menet MC, Debray M, Hirt D, Noble F, Scherrmann JM, Declèves X (2009) Sprague–Dawley rats display sex-linked differences in the pharmacokinetics of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and its metabolite 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 241:339–347
Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (2005) Guidance for industry. Estimating the maximum safe starting dose in initial clinical trials for therapeutics in adult healthy volunteers. http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/index.htm. Accessed October 14, 2012
Hadlock GC, Webb KM, McFadden LM, Chu PW, Ellis JD, Allen SC, Andrenyak DM, Vieira-Brock PL, German CL, Conrad KM, Hoonakker AJ, Gibb JW, Wilkins DG, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE (2011) 4-Methylmethcathinone (mephedrone): neuropharmacological effects of a designer stimulant of abuse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 339:530–536
Hitchcock SA, Pennington LD (2006) Structure–brain exposure relationships. J Med Chem 49:7559–7583
Hysek CM, Brugger R, Simmler LD, Bruggisser M, Donzelli M, Grouzmann E, Hoener MC, Liechti ME (2012) Effects of the α2-adrenergic agonist clonidine on the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in healthy volunteers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 340:286–289
Khreit OI, Grant MH, Zhang T, Henderson C, Watson DG, Sutcliffe OB (2013) Elucidation of the phase I and phase II metabolic pathways of (±)-4′-methylmethcathinone (4-MMC) and (±)-4′-(trifluoromethyl)methcathinone (4-TFMMC) in rat liver hepatocytes using LC-MS and LC-MS(2). J Pharm Biomed Anal 72:177–185
López-Arnau R, Martínez-Clemente J, Pubill D, Escubedo E, Camarasa J (2012) Comparative neuropharmacology of three psychostimulant cathinone derivatives: butylone, mephedrone and methylone. Br J Pharmacol 167:407–420
Martínez-Clemente J, Escubedo E, Pubill D, Camarasa J (2012) Interaction of mephedrone with dopamine and serotonin targets in rats. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 22:231–236
Maskell PD, De Paoli G, Seneviratne C, Pounde DJ (2011) Mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone)-related deaths. J Anal Toxicol 35:188–191
Meyer MR, Wilhelm J, Peters FT, Maurer HH (2010) Beta-keto amphetamines: studies on the metabolism of the designer drug mephedrone and toxicological detection of mephedrone, butylone, and methylone in urine using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:1225–1233
Nagai F, Nonaka R, Satoh K, Kamimura SHK (2007) The effects of non-medically used psychoactive drugs on monoamine neurotransmission in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 559:132–137
Porchet HC, Benowitz NL, Sheiner LB, Copelan JR (1987) Apparent tolerance to the acute effect of nicotine results in part from distribution kinetics. J Clin Invest 80:466–741
Schechter MD (1990) Rats become acutely tolerant to cathine after amphetamine or cathinone administration. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 101:126–131
Schifano F, Albanese A, Fergus S, Stair JL, Deluca P, Corazza O, Davey Z, Corkery J, Siemann H, Scherbaum N, Farre M, Torrens M, Demetrovics Z, Ghodse AH (2011) Mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone; ‘meow meow’): chemical, pharmacological and clinical issues. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 214:593–602
Sheiner LB, Stanki DR, Vozeh S, Miller RD, Ham J (1979) Simultaneous modeling of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: application to d-tubocurarine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 25:358–370
Simmler LD, Buser TA, Donzelli M, Schramm Y, Dieu LH, Huwyler J, Chaboz S, Hoener MC, Liechti ME (2013) Pharmacological characterization of designer cathinones in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 168:458–470
Sørensen LK (2011) Determination of cathinones and related ephedrines in forensic whole-blood samples by liquid-chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 879:727–736
Varner KJ, Daigle K, Weed PF, Lewis PB, Mahne SE, Sankaranarayanan A, Winsauer PJ (2013) Comparison of the behavioral and cardiovascular effects of mephedrone with other drugs of abuse in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 225:675–685
Wilkinson P, Van Dyke C, Jatlow P, Barash P, Byck (1980) Intranasal and oral cocaine kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 27:386–394
Winstock A, Mitcheson L, Ramsey J, Davies S, Puchnarewicz M, Marsden J (2011) Mephedrone: use, subjective effects and health risks. Addiction 106:1991–1996
Wood DM, Davies S, Greene SL, Button J, Holt DW, Ramsey J, Dargan PI (2010a) Case series of individuals with analytically confirmed acute mephedrone toxicity. Clin Toxicol 48:924–927
Wood DM, Davies S, Puchnarewicz M, Button J, Archer R, Ovaska H, Ramsey J, Lee T, Holt DW, Dargan PI (2010b) Recreational use of mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone, 4-MMC) with associated sympathomimetic toxicity. J Med Toxicol 6:327–330
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge A.C. Roberts for revising the language of the manuscript. This study was supported by grants from the Generalitat de Catalunya (SGR977), the Plan Nacional sobre Drogas (2010/005), and the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (SAF2010-15948). Martínez-Clemente is a recipient of a fellowship from the Plan Nacional sobre Drogas and López-Arnau is a recipient of a fellowship from Generalitat de Catalunya.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Clemente, J., López-Arnau, R., Carbó, M. et al. Mephedrone pharmacokinetics after intravenous and oral administration in rats: relation to pharmacodynamics. Psychopharmacology 229, 295–306 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3108-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3108-7