Abstract.
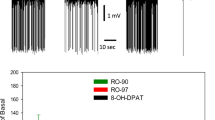
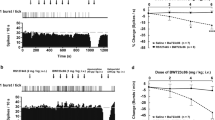
Rationale: Bupropion is widely used in the treatment of depression and as an anti-craving medication for the cessation of tobacco smoking. Because it is a very weak inhibitor of norepinephrine (NE) and dopamine (DA) reuptake, its mechanisms of action remain to be elucidated. Methods: Bupropion was administered subcutaneously via osmotic minipumps over 2 days to determine its effects on the spontaneous firing activity of NE, serotonin (5-HT), and DA neurons in the brain of anaesthetised male Sprague-Dawley rats. This treatment was used in order to obtain levels of the parent compound and its putatively active metabolites that would more adequately reflect the clinical condition than utilizing acute injections. Results: When given by minipump for 2 days, bupropion produced a dose-dependent attenuation of the mean spontaneous firing NE neurons (7.5 mg/kg per day: 15%; 15 mg/kg per day: 61%; 30 mg/kg per day: 80%) which was reversed by the α2-adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan. At the highest regimen, the mean firing rate of 5-HT neurons was 100% higher than in control rats, but unaffected in NE-lesioned rats. In contrast, DA neurons in the ventral tegmental area displayed a normal firing rate during the latter bupropion treatment. Conclusions: Sustained bupropion administration decreased the firing rate of NE neurons due to an increased activation of their inhibitory somatodendritic α2-adrenoceptors. This effect of the bupropion treatment would be attributable mainly to an enhancement of NE release and not to reuptake inhibition. This contention is based essentially on the observation that NE reuptake blockers leave unaltered the firing rate of 5-HT neurons, whereas bupropion enhanced it via a NE-dependent mechanism. The present study did not put into evidence any DA activity of bupropion at the level of the cell body of mesolimbic/cortical DA neurons at a regimen exerting profound alterations of the firing activity of NE and 5-HT neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, J., Blier, P. Modification of norepinephrine and serotonin, but not dopamine, neuron firing by sustained bupropion treatment. Psychopharmacology 155, 52–57 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000665
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000665