Abstract
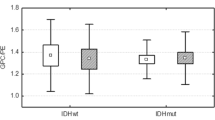
Quantitative multinuclear high-resolution magic angle spinning was performed in order to determine the tissue pH values of and the absolute metabolite concentrations in 33 samples of human brain tumour tissue. Metabolite concentrations were quantified by 1D 1H and 31P HRMAS using the electronic reference to in vivo concentrations (ERETIC) synthetic signal. 1H–1H homonuclear and 1H–31P heteronuclear correlation experiments enabled the direct assessment of the 1H–31P spin systems for signals that suffered from overlapping in the 1D 1H spectra, and linked the information present in the 1D 1H and 31P spectra. Afterwards, the main histological features were determined, and high heterogeneity in the tumour content, necrotic content and nonaffected tissue content was observed. The metabolite profiles obtained by HRMAS showed characteristics typical of tumour tissues: rather low levels of energetic molecules and increased concentrations of protective metabolites. Nevertheless, these characteristics were more strongly correlated with the total amount of living tissue than with the tumour cell contents of the samples alone, which could indicate that the sampling conditions make a significant contribution aside from the effect of tumour development in vivo. The use of methylene diphosphonic acid as a chemical shift and concentration reference for the 31P HRMAS spectra of tissues presented important drawbacks due to its interaction with the tissue. Moreover, the pH data obtained from 31P HRMAS enabled us to establish a correlation between the pH and the distance between the N(CH3)3 signals of phosphocholine and choline in 1H spectra of the tissue in these tumour samples.

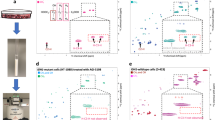
1H-31P HSQC (upper) and TOCSY (lower) spectra with the corresponding 1D 1H and 31P spectra for one GBM sample. The paths for homo and heteronuclear assignment are drawn as dashed lines (in blue for GPC, in red for GPE, in green for PC and in yellow for PE). The signals can be observed in the corresponding 1D 31P spectrum by the right margin of the HSQC spectrum, but not in the crowded 1D 1H spectrum above the HSQC spectrum




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ala:
-
Alanine
- Cho:
-
Choline
- Cr:
-
Creatine
- ERETIC:
-
Electronic reference to in vivo concentrations
- FA:
-
Fatty acids
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma multiforme
- Gln:
-
Glutamine
- Glu:
-
Glutamate
- Gly:
-
Glycine
- GPC:
-
Glycerophosphocholine
- GPE:
-
Glycerophosphorylethanolamine
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- HRMAS:
-
High-resolution magic angle spinning
- MDPA:
-
Methylene diphosphonic acid
- mI:
-
Myo-inositol
- NAA:
-
N-Acetylaspartate
- NAT:
-
Nonaffected tissue
- PC:
-
Phosphocholine
- PCr:
-
Phosphocreatine
- PDE:
-
Phosphodiesters
- PE:
-
Phosphoethanolamine
- PME:
-
Phosphomonoesters
- Tau:
-
Taurine
References
Cheng LL, Chang IW, Louis DN, Gonzalez RG (1998) Cancer Res 58:1825–1832
Opstad KS, Bell BA, Griffiths JR, Howe FA (2008) Magn Reson Med 60:1237–1242
Sjobakk TE, Johansen R, Bathen TF, Sonnewald U, Juul R, Torp SH, Lundgren S, Gribbestad IS (2008) NMR Biomed 21:175–185
Martinez-Bisbal MC, Marti-Bonmati L, Piquer J, Revert A, Ferrer P, Llacer JL, Piotto M, Assemat O, Celda B (2004) NMR Biomed 17:191–205
Erb G, Elbayed K, Piotto M, Raya J, Neuville A, Mohr M, Maitrot D, Kehrli P, Namer IJ (2008) Magn Reson Med 59:959–965
Wilson M, Davies NP, Brundler MA, McConville C, Grundy RG, Peet AC (2009) Mol Cancer 8:6
Martinez-Bisbal MC, Monleon D, Assemat O, Piotto M, Piquer J, Llacer JL, Celda B (2009) NMR Biomed 22:199–206
Martínez-Granados B, Monleón D, Martínez-Bisbal MC, Rodrigo JM, del Olmo J, Lluch P, Ferrández A, Martí-Bonmatí L, Celda B (2006) NMR Biomed 19:90–100
Hubesch B, Sappey-Marinier D, Roth K, Meyerhoff DJ, Matson GB, Weiner MW (1990) Radiology 174:401–409
Albers MJ, Krieger MD, Gonzalez-Gomez I, Gilles FH, McComb JG, Nelson MD Jr, Bluml S (2005) Magn Reson Med 53:22–29
Wijnen JP, Scheenen TW, Klomp DW, Heerschap A (2010) NMR Biomed 23:968–976
Podo F (1999) NMR Biomed 12:413–439
Griffiths JR, Cady E, Edwards RH, McCready VR, Wilkie DR, Wiltshaw E (1983) Lancet 1:1435–1436
Robitaille PL, Robitaille PA, Gordon Brown G, Brown GG (1991) J Magn Reson 92:73–84, 1969
Griffiths JR (1991) Br J Cancer 64:425–427
Payne GS, Troy H, Vaidya SJ, Griffiths JR, Leach MO, Chung YL (2006) NMR Biomed 19:593–598
De Silva SS, Payne GS, Thomas V, Carter PG, Ind TE, deSouza NM (2009) NMR Biomed 22:191–198
Wang Y, Cloarec O, Tang H, Lindon JC, Holmes E, Kochhar S, Nicholson JK (2008) Anal Chem 80:1058–1066
Lehnhardt FG, Rohn G, Ernestus RI, Grune M, Hoehn M (2001) NMR Biomed 14:307–317
Srivastava NK, Pradhan S, Gowda GA, Kumar R (2010) NMR Biomed 23:113–122
Akoka S, Barantin L, Trierweiler M (1999) Anal Chem 71:2554–2557
Albers MJ, Butler TN, Rahwa I, Bao N, Keshari KR, Swanson MG, Kurhanewicz J (2009) Magn Reson Med 61:525–532
Ben Sellem D, Elbayed K, Neuville A, Moussallieh FM, Lang-Averous G, Piotto M, Bellocq JP, Namer IJ (2011) J Oncol 2011:174019
Bourne R, Dzendrowskyj T, Mountford C (2003) NMR Biomed 16:96–101
Martinez-Bisbal MC, Esteve V, Martinez-Granados B, Celda B (2011) J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:763684, Epub 2010 Sep 5
Celda B, Montelione GT (1993) J Magn Reson B 101:189–193
Esteve V, Celda B (2008) Magn Reson Mater Phys MAGMA 21:484–484
Collins TJ (2007) Biotechniques 43:25–30
Govindaraju V, Young K, Maudsley AA (2000) NMR Biomed 13:129–153
Fan TW-M (1996) Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 28:161–219
Ulrich EL, Akutsu H, Doreleijers JF, Harano Y, Ioannidis YE, Lin J, Livny M, Mading S, Maziuk D, Miller Z, Nakatani E, Schulte CF, Tolmie DE, Kent Wenger R, Yao H, Markley JL (2008) Nucleic Acids Res 36:D402–D408
Kriat M, Vion-Dury J, Confort-Gouny S, Favre R, Viout P, Sciaky M, Sari H, Cozzone PJ (1993) J Lipid Res 34:1009–1019
Subramanian A, Shankar Joshi B, Roy AD, Roy R, Gupta V, Dang RS (2008) NMR Biomed 21:272–288
Daykin CA, Corcoran O, Hansen SH, Bjornsdottir I, Cornett C, Connor SC, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK (2001) Anal Chem 73:1084–1090
Griffin JL, Lehtimaki KK, Valonen PK, Grohn OH, Kettunen MI, Yla-Herttuala S, Pitkanen A, Nicholson JK, Kauppinen RA (2003) Cancer Res 63:3195–3201
Petroff OAC, Prichard JW (1995) In: Kraicer J, Dixon SJ (eds) Methods in neurosciences. Academic, San Diego
Barton S, Howe F, Tomlins A, Cudlip S, Nicholson J, Anthony Bell B, Griffiths J (1999) Magn Reson Mater Phys Biol Med 8:121–128
Sitter B, Sonnewald U, Spraul M, Fjosne HE, Gribbestad IS (2002) NMR Biomed 15:327–337
Coen M, Hong YS, Cloarec O, Rhode CM, Reily MD, Robertson DG, Holmes E, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK (2007) Anal Chem 79:8956–8966
Russell D, Rubinstein LJ (1998) Russel and Rubinstein's pathology of tumors of the nervous system. Arnold, London
Tynkkynen T, Tiainen M, Soininen P, Laatikainen R (2009) Anal Chim Acta 648:105–112
Kjaergaard M, Brander S, Poulsen F (2011) J Biomol NMR 49:139–149
Robert O, Sabatier J, Desoubzdanne D, Lalande J, Balayssac S, Gilard V, Martino R, Malet-Martino M (2011) Anal Bioanal Chem 399:987–999
Chadzynski GL, Bender B, Groeger A, Erb M, Klose U (2011) J Magn Reson 212:55–63
Weljie AM, Jirik FR (2011) Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:981–989
Barba I, Cabanas ME, Arus C (1999) Cancer Res 59:1861–1868
Liimatainen T, Hakumaki JM, Kauppinen RA, Ala-Korpela M (2009) NMR Biomed 22:272–279
Opstad KS, Bell BA, Griffiths JR, Howe FA (2008) NMR Biomed 21:677–685
Schmitz JE, Kettunen MI, Hu D, Brindle KM (2005) Magn Reson Med 54:43–50
Glunde K, Artemov D, Penet MF, Jacobs MA, Bhujwalla ZM (2010) Chem Rev 110:3043–3059
Hertz L (2008) Neuropharmacology 55:289–309
Takahashi T, Otsuguro K, Ohta T, Ito S (2010) Br J Pharmacol 161:1806–1816
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the SCSIE-University of Valencia Microscopy Service for the histological preparations. They also acknowledge Martial Piotto (Bruker BioSpin, France) for providing the ERETIC synthetic signal. Furthermore, they acknowledge financial support from the Spanish Government project SAF2007-6547, the Generalitat Valenciana project GVACOMP2009-303, and the E.U.’s VI Framework Programme via the project “Web accessible MR decision support system for brain tumor diagnosis and prognosis, incorporating in vivo and ex vivo genomic and metabolomic data” (FP6-2002-LSH 503094). CIBER-BBN is an initiative funded by the VI National R&D&i Plan 2008–2011, Iniciativa Ingenio 2010, Consolider Program, CIBER Actions, and financed by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III with assistance from the European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 847 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esteve, V., Celda, B. & Martínez-Bisbal, M.C. Use of 1H and 31P HRMAS to evaluate the relationship between quantitative alterations in metabolite concentrations and tissue features in human brain tumour biopsies. Anal Bioanal Chem 403, 2611–2625 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6001-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6001-z