Abstract
Objective:
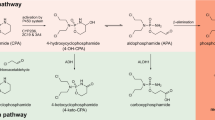
Cyclophosphamide (CP) is an antineoplastic prodrug which requires bioactivation (4-hydroxylation) by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes in human liver. In parallel, P450-mediated side-chain oxidation (N-dealkylation) leads to the formation of the non-alkylating dechloroethylcyclophosphamide (DCl-CP) and chloroacetaldehyde, the latter being a potential neurotoxic agent. The enzyme responsible for side-chain oxidation has not been identified yet. We therefore used an in vitro approach to characterize the enzyme involved in N-dealkylation of CP.
Methods:
CP was incubated with the microsomal fraction of human liver in the presence of specific inhibitors for some P450 enzymes and in the presence of stable expressed P450 enzymes. Dechloroethylcyclophosphamide was analysed using gas chromatography and nitrogen-phosphorus detection.
Results:
Formation of DCl-CP increased linearly with substrate concentration over the entire concentration range (20 μmol ⋅ l−1 to 36 mmol ⋅ l−1). Saturation of the enzyme was not observed. Incubation with stable expressed P450 enzymes and inhibition experiments indicated that CYP 3A4 was the major enzyme involved in side-chain oxidation of CP.
Conclusions:
Our in vitro data indicate that side-chain oxidation of CP occurs in dose-dependent fashion in men with no saturation of this pathway even following dose escalation. Thus enhanced neurotoxicity following CP administration may result in the setting of high-dose chemotherapy. Moreover, we conclude that CP has the potential to interact with other CYP 3A4 substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 January 1996/Accepted in revised form: 27 June 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bohnenstengel, F., Hofmann, U., Eichelbaum, M. et al. Characterization of the cytochrome P450 involved in side-chain oxidation of cyclophosphamide in humans. E J Clin Pharmacol 51, 297–301 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050201
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280050201