Abstract
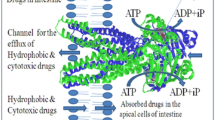
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is an ATP-dependent drug pump that can transport a broad range of hydrophobic compounds out of the cell. The protein is clinically important because of its contribution to the phenomenon of multidrug resistance during AIDS/HIV and cancer chemotherapy. P-gp is a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family of proteins. It is a single polypeptide that contains two repeats joined by a linker region. Each repeat has a transmembrane domain consisting of six transmembrane segments followed by a hydrophilic domain containing the nucleotide-binding domain. In this mini-review, we discuss recent progress in determining the structure and mechanism of human P-glycoprotein.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- M6M,:
-
1,6-hexanediyl bismethanethiosulfonate;
- M8M,:
-
3,6-dioxaoctane-1,8-diyl bismethanethiosulfonate;
- NBD1,:
-
amino-terminal nucleotide binding domain;
- NBD2,:
-
carboxy-terminal nucleotide binding domain;
- P-gp,:
-
P-glycoprotein;
- TMD,:
-
transmembrane domain;
- TM,:
-
transmembrane
References
Al-Shawi M.K., Polar M.K., Omote H., Figler R.A. 2003. Transition state analysis of the coupling of drug transport to ATP hydrolysis by P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 278:52629–52640
al-Shawi M.K., Senior A.E. 1993. Characterization of the adenosine triphosphatase activity of Chinese hamster P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 268:4197–4206
Alien J.D., Brinkhuis R.F., Wijnholds J., Schinkel A.H. 1999. The mouse Bcrp1/Mxr/Abcp gene: amplification and overexpression in cell lines selected for resistance to topotecan, mitoxantrone, or doxorubicin. Cancer Res. 59:4237–4241
Allikmets R., Schriml L.M., Hutchinson A., Romano-Spica V., Dean M. 1998. A human placenta-specific ATP-binding cassette gene (ABCP) on chromosome 4q22 that is involved in multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 58:5337–5339
Ambudkar S.V., Kimchi-Sarfaty C., Sauna Z.E., Gottesman M.M. 2003. P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene 22:7468–7485
Ambudkar S.V., Lelong I.H., Zhang J., Cardarelli C.O., Gottesman M.M., Pastan. 1992. Partial purification and reconstitution of the human multidrug- resistance pump: characterization of the drug-stimulatable ATP hydrolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:8472–8476
Biedler J.L., Riehm H. 1970. Cellular resistance to actinomycin D in Chinese hamster cells in vitro: cross-resistance, radioautographic, and cytogenetic studies. Cancer Res. 30:1174–1184
Borges-Walmsley M.I., McKeegan K.S., Walmsley A.R. 2003. Structure and function of efflux pumps that confer resistance to drugs. Biochem. J. 376:313–338
Bruggemann E.P., Currier S.J., Gottesman M.M., Pastan I. 1992. Characterization of the azidopine and vinblastine binding site of P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 267:21020–21026
Chang G. 2003. Structure of MsbA from Vibrio cholera: A Multidrug Resistance ABC transporter Homolog in a Closed Conformation. J. Mol. Biol. 330:419–430
Chang G., Roth C.B. 2001. Structure of MsbA from E. coli: a homolog of the multidrug resistance ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters. Science 293:1793–1800
Chen C.J., Chin J.E., Ueda K., Clark D.P., Pastan I., Gottesman M.M., Roninson I.B. 1986. Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdrl (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Cell 47:381–389
Chen J.H., Chang X.B., Aleksandrov A.A., Riordan J.R. 2002. CFTR is a monomer: biochemical and functional evidence. J. Membrane Biol. 188:55–71
Choi K.H., Chen C.J., Kriegler M., Roninson I.B. 1988. An altered pattern of cross-resistance in multidrug-resistant human cells results from spontaneous mutations in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene. Cell 53:519–529
Dano K. 1972. Cross resistance between vinca alkaloids and anthracyclines in Ehrlich ascites tumor in vivo. Cancer Chemother. Rep. 56:701–708
Dean M., Rzhetsky A., Allikmets R. 2001. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. Genome Res. 11:1156–1166
Dearden J.C., A1-Noobi A., Scott A.C., Thomson S.A. 2003. QSAR studies on P-glycoprotein-regulated multidrug resistance and on its reversal by phenothiazines. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 14:447–454
Demeule M., Laplante A., Murphy G.F., Wenger R.M., Beliveau R. 1998. Identification of the cyclosporin-binding site in P-glycoprotein. Biochemistry 37:18110–18118
Demmer A., Thole H., Kubesch P., Brandt T., Raida M., Fislage R., Tummler B. 1997. Localization of the iodomycin binding site in hamster P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 272:20913–20919
Dey S., Ramachandra M., Pastan I., Gottesman M.M., Ambudkar S.V. 1997. Evidence for two nonidentical drug-interaction sites in the human P-glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:10594–10599
Doige C.A., Yu X., Sharom F.J. 1992. ATPase activity of partially purified P-glycoprotein from multidrug- resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1109:149–160
Dong J., Yang G., McHaourab H.S. 2005. Structural basis of energy transduction in the transport cycle of MsbA. Science 308:1023–1028
Doyle L.A., Yang W., Abruzzo L.V., Krogmann T., Gao Y., Rishi A.K., Ross D.D. 1998. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:15665–15670
Druley T.E., Stein W.D., Roninson I.B. 2001. Analysis of mdr1 p-glycoprotein conformational changes in permeabilized cells using differential immunoreactivity. Biochemistry 40:4312–4322
Eckford P.D., Sharom F.J. 2005. The reconstituted P-glycoprotein multidrug transporter is a flippase for glucosylceramide and other simple glycosphingolipids. Biochem. J. 389: 517–526
Ekins S., Kim R.B., Leake B.F., Dantzig A.H., Schuetz E.G., Lan L.B., Yasuda K., Shepard R.L., Winter M.A., Schuetz J.D., Wikel J.H., Wrighton S.A. 2002. Application of three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships of P-glycoprotein inhibitors and substrates. Mol. Pharmacol. 61:974–981
Garrigues A., Loiseau N., Delaforge M., Ferte J., Garrigos M., Andre F., Orlowski S. 2002. Characterization of two pharmacophores on the multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein. Mol. Pharmacol. 62:1288–1298
Gerlach J.H., Endicott J.A., Juranka P.F., Henderson G., Sarangi F., Deuchars K.L., Ling V. 1986. Homology between P-glycoprotein and a bacterial haemolysin transport protein suggests a model for multidrug resistance. Nature 324:485–489
Gottesman M.M., Pastan I. 1988. The multidrug transporter, a double-edged sword. J. Biol. Chem. 263:12163–12166
Gottesman M.M., Pastan I. 1993. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 62:385–427
Graf G.A., Yu L., Li W.P., Gerard R., Tuma P.L., Cohen J.C., Hobbs H.H. 2003. ABCG5 and ABCG8 are obligate heterodimers for protein trafficking and biliary cholesterol excretion. J. Biol. Chem. 278:48275–48282
Greenberger L.M. 1993. Major photoaffinity drug labeling sites for iodoaryl azidoprazosin in P- glycoprotein are within, or immediately C-terminal to, transmembrane domains 6 and 12. J. Biol. Chem. 268:11417–11425
Gros P., Ben Neriah Y.B., Croop J.M., Housman D.E. 1986. Isolation and expression of a complementary DNA that confers multidrug resistance. Nature 323:728–731
Heldwein E.E., Brennan R.G. 2001. Crystal structure of the transcription activator BmrR bound to DNA and a drug. Nature 409:378–82
Higgins C.F. 1992. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 8:67–113
Higgins C.F., Gottesman M.M. 1992. Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends. Biochem. Sci. 17:18–21
Homolya L., Hollo Z., Germann U.A., Pastan I., Gottesman M.M., Sarkadi B. 1993. Fluorescent cellular indicators are extruded by the multidrug resistance protein. J. Biol. Chem. 268:21493–21496
Hopfner K.P., Karcher A., Shin D.S., Craig L., Arthur L.M., Carney J.P., Tainer J.A. 2000. Structural biology of Rad50 ATPase: ATP-driven conformational control in DNA double-strand break repair and the ABC-ATPase superfamily. Cell 101:789–800
Hrycyna C.A. 2001. Molecular genetic analysis and biochemical characterization of mammalian P-glycoproteins involved in multidrug resistance. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 12:247–256
Hrycyna C.A., Ramachandra M., Ambudkar S.V., Ko Y.H., Pedersen P.L., Pastan I., Gottesman M.M. 1998. Mechanism of action of human P-glycoprotein ATPase activity. Photochemical cleavage during a catalytic transition state using orthovanadate reveals cross-talk between the two ATP sites. J. Biol. Chem. 273:16631–16634
Hrycyna C.A., Ramachandra M., Germann U.A., Cheng P.W., Pastan I., Gottesman M.M. 1999. Both ATP sites of human P-glycoprotein are essential but not symmetric. Biochemistry 38:13887–13899
Janas E., Hofacker M., Chen M., Gompf S., van der Does C., Tampe R. 2003. The ATP hydrolysis cycle of the nucleotide-binding domain of the mitochondrial ATP-binding cassette transporter Mdllp. J. Biol. Chem. 278:26862–26869
Juliano R.L., Ling V. 1976. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455:152–162
Karpowich N., Martsinkevich O., Millen L., Yuan Y.R., Dai P.L., MacVey K., Thomas P.J., Hunt J.F. 2001. Crystal structures of the MJ1267 ATP binding cassette reveal an induced- fit effect at the ATPase active site of an ABC transporter. Structure (Camb) 9:571–586
Kast C., Canfield V., Levenson R., Gros P. 1996. Transmembrane organization of mouse P-glycoprotein determined by epitope insertion and immunofluorescence. J. Biol. Chem. 271:9240–9248
Lee C.G., Gottesman M.M., Cardarelli C.O., Ramachandra M., Jeang K.T., Ambudkar S.V., Pastan I., Dey S. 1998. HIV-1 protease inhibitors are substrates for the MDR1 multidrug transporter. Biochemistry 37:3594–3601
Lee J.Y., Urbatsch I.L., Senior A.E., Wilkens S. 2002. Projection structure of P-glycoprotein by electron microscopy. Evidence for a closed conformation of the nucleotide binding domains. J. Biol. Chem. 271:40125–40131
Leith C.P., Kopecky K.J., Chen I.M., Eijdems L., Slovak M.L., McConnell T.S., Head D.R., Weick J., Grever M.R., Appelbaum F.R., Willman C.L. 1999. Frequency and clinical significance of the expression of the multidrug resistance proteins MDR1/P-glycoprotein, MRP1, and LRP in acute myeloid leukemia: a Southwest Oncology Group Study. Blood 94:1086–1099
Ling V., Thompson L.H. 1974. Reduced permeability in CHO cells as a mechanism of resistance to colchicine. J. Cell Physiol. 83:103–116
Locher K.P., Lee A.T., Rees D.C. 2002. The E. coli BtuCD structure: a framework for ABC transporter architecture and mechanism. Science 296:1091–1098
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2002. The “LSGGQ” motif in each nucleotide-binding domain of human P-glycoprotein is adjacent to the opposing walker A sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 277:41303–41306
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2003a. Drug binding in human P-glycoprotein causes conformational changes in both nucleotide-binding domains. J. Biol. Chem. 278:1575–1578
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2003b. Methanethiosulfonate derivatives of rhodamine and verapamil activate human P-glycoprotein at different sites. J. Biol. Chem. 278:50136–50141
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2003c. Permanent activation of the human p-glycoprotein by covalent modification of a residue in the drug-binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 278:20449–20452
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2003d. Simultaneous binding of two different drugs in the binding pocket of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 278:39706–39710
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2003e. Substrate-induced conformational changes in the transmembrane segments of human P-glycoprotein. Direct evidence for the substrate-induced fit Mechanism for drug binding. J. Biol. Chem. 278:13603–13606
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2004a. Disulfide cross-linking analysis shows that transmembrane segments 5 and 8 of human P-glycoprotein are close together on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 279:7692–7697
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2004b. The drug-binding pocket of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein is accessible to the aqueous medium. Biochemistry 43:12081–12089
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2004c. Residues V133 and C137 in transmembrane segment 2 are close to residues A935 and G939 in transmembrane segment 11 of human P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 279:18232–18238
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2004d. Thapsigargin or curcumin does not promote maturation of processing mutants of the ABC transporters, CFTR, and P-glycoprotein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 325:580–585
Loo T.W., Bartlett M.C., Clarke D.M. 2005. ATP hydrolysis promotes interactions between the extracellular ends of transmembrane segments 1 and 11 of human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Biochemistry 44:10250–10258
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1993a. Functional consequences of phenylalanine mutations in the predicted transmembrane domain of P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 268:19965–19972
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1993b. Functional consequences of proline mutations in the predicted transmembrane domain of P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 268:3143–3149
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1994a. Functional consequences of glycine mutations in the predicted cytoplasmic loops of P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 269:7243–7248
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1994b. Mutations to amino acids located in predicted transmembrane segment 6 (TM6) modulate the activity and substrate specificity of human P-glycoprotein. Biochemistry 33:14049–14057
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1994c. Prolonged association of temperature-sensitive mutants of human P- glycoprotein with calnexin during biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 269:28683–28689
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1994d. Reconstitution of drug-stimulated ATPase activity following co- expression of each half of human P-glycoprotein as separate polypeptides. J. Biol. Chem. 269:7750–7755
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1995a. Covalent modification of human P-glycoprotein mutants containing a single cysteine in either nucleotide-binding fold abolishes drug- stimulated ATPase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 270:22957–22961
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1995b. Membrane topology of a cysteine-less mutant of human P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 270:843–848
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1996a. Inhibition of oxidative cross-linking between engineered cysteine residues at positions 332 in predicted transmembrane segments (TM) 6 and 975 in predicted TM12 of human P-glycoprotein by drug substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 271:27482–27487
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1996b. The minimum functional unit of human P-glycoprotein appears to be a monomer. J. Biol. Chem. 271:27488–27492
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1997a. Correction of defective protein kinesis of human P-glycoprotein mutants by substrates and modulators. J. Biol. Chem. 272:709–712
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1997b. Drug-stimulated ATPase activity of human P-glycoprotein requires movement between transmembrane segments 6 and 12. J. Biol. Chem. 272:20986–20989
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1997c. Identification of residues in the drug-binding site of human P- glycoprotein using a thiol-reactive substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 272:31945–31948
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1998. Superfolding of the partially unfolded core-glycosylated intermediate of human P-glycoprotein into the mature enzyme is promoted by substrate- induced transmembrane domain interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 273:14671–14674
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1999a. Identification of residues in the drug-binding domain of human P-glycoprotein: Analysis of transmembrane segment 11 by cysteine-scanning mutagenesis and inhibition by dibromobimane. J. Biol. Chem. 274:35388–35392
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 1999b. The transmembrane domains of the human multidrug resistance P- glycoprotein are sufficient to mediate drug binding and trafficking to the cell surface. J. Biol. Chem. 274:24759–24765
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2000a. Drug-stimulated ATPase activity of human P-glycoprotein is blocked by disulfide cross-linking between the nucleotide-binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 275:19435–19438
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2000b. Identification of residues within the drug-binding domain of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein by cysteine-scanning mutagenesis and reaction with dibromobimane. J. Biol. Chem. 275:39272–39278
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2000c. The packing of the transmembrane segments of human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein is revealed by disulfide cross-linking analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 275:5253–5256
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2001a. Cross-linking of human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein by the substrate, Tris-(2-maleimidoethyl)amine, is altered by ATP hydrolysis: Evidence for rotation of a transmembrane helix. J. Biol. Chem. 276:31800–31805
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2001b. Defining the drug-binding site in the human multidrug resistance P- glycoprotein using MTS-verapamil. J. Biol. Chem. 276:14972–14919
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2001c. Determining the dimensions of the drug-binding domain of human P-glycoprotein using thiol cross-linkers as molecular rulers. J. Biol. Chem. 276:36877–36880
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2002a. Location of the rhodamine-binding site in the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 277:44332–44338
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2002b. Vanadate trapping of nucleotide at the ATP-binding sites of human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein exposes different residues to the drug-binding site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:3511–3516
Loo T.W., Clarke D.M. 2005. Do drug substrates enter the common drug-binding pocket of P-glycoprotein through “gates”? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 329:419–422
Lugo M.R., Sharom F.J. 2005. Interaction of LDS-751 with P-glycoprotein and mapping of the location of the R drug binding site. Biochemistry 44:643–655
Martin C., Walker J., Rothnie A., Callaghan R. 2003. The expression of P-glycoprotein does influence the distribution of novel fluorescent compounds in solid tumour models. Br. J. Cancer 89:1581–1589
Mechetner E.B., Schott B., Morse B.S., Stein W.D., Druley T., Davis K.A., Tsuruo T., Roninson I.B. 1997. P-glycoprotein function involves conformational transitions detectable by differential immunoreactivity. Proc.Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:12908–12913
Miyake K., Mickley L., Litman T., Zhan Z., Robey R., Cristensen B., Brangi M., Greenberger L., Dean M., Fojo T., Bates S.E. 1999. Molecular cloning of cDNAs which are highly overexpressed in mitoxantrone-resistant cells: demonstration of homology to ABC transport genes. Cancer Res. 59:8–13
Moody I.E., Millen L., Binns D., Hunt J.F., Thomas P.J. 2002. Cooperative, ATP-dependent association of the nucleotide binding cassettes during the catalytic cycle of ATP-binding cassette transporters. J. Biol. Chem. 277:21111–21114
Murakami S., Nakashima R., Yamashita E., Yamaguchi A. 2002. Crystal structure of bacterial multidrug efflux transporter AcrB. Nature 419:587–593
Omote H., Al-Shawi M.K. 2002. A novel electron paramagnetic resonance approach to determine the mechanism of drug transport by P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 277:45688–45694
Omote H., Figler R.A., Polar M.K., Al-Shawi M.K. 2004. Improved energy coupling of human P-glycoprotein by the glycine 185 to valine mutation. Biochemistry 43:3917–3928
Pascaud C., Garrigos M., Orlowski S. 1998. Multidrug resistance transporter P- glycoprotein has distinct but interacting binding sites for cytotoxic drugs and reversing agents. Biochem. J. 333:351–8
Penzotti J.E., Lamb M.L., Evensen E., Grootenhuis P.D. 2002. A computational ensemble pharmacophore model for identifying substrates of P-glycoprotein. J. Med. Chem. 45:1737–1740
Pleban K., Kopp S., Csaszar E., Peer M., Hrebicek T., Rizzi A., Ecker G.F., Chiba P. 2005. P-glycoprotein substrate binding domains are located at the transmembrane domain/transmembrane domain interfaces: a combined photoaffinity labeling-protein homology modeling approach. Mol. Pharmacol. 67:365–374
Poruchynsky M.S., Ling V. 1994. Detection of oligomeric and monomeric forms of P-glycoprotein in multidrug resistant cells. Biochemistry 33:4163–4174
Qu Q., Chu J.W., Sharom F.J. 2003. Transition state P-glycoprotein binds drugs and modulators with unchanged affinity, suggesting a concerted transport mechanism. Biochemistry 42:1345–1353
Qu Q., Sharom F.J. 2001. FRET analysis indicates that the two ATPase active sites of the P- glycoprotein multidrug transporter are closely associated. Biochemistry 40:1413–1422
Qu Q., Sharom F.J. 2002. Proximity of bound Hoechst 33342 to the ATPase catalytic sites places the drug binding site of P-glycoprotein within the cytoplasmic membrane leaflet. Biochemistry 41:4744–4752
Ramachandra M., Ambudkar S.V., Chen D., Hrycyna C.A., Dey S., Gottesman M.M., Pastan I. 1998. Human P-glycoprotein exhibits reduced affinity for substrates during a catalytic transition state. Biochemistry 37:5010–5019
Ramjeesingh M., Li C., Kogan I., Wang Y., Huan L.J., Bear C.E. 2001. A monomer is the minimum functional unit required for channel and ATPase activity of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Biochemistry 40:10700–10706
Raviv Y., Pollard H.B., Bruggemann E.P., Pastan I., Gottesman M.M. 1990. Photosensitized labeling of a functional multidrug transporter in living drug-resistant tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 265:3975–3980
Reyes C.L., Chang G. 2005. Structure of the ABC transporter MsbA in complex with ADP-vanadate and lipopolysaccharide. Science 308:1028–1031
Riordan J.R., Ling V. 1985. Genetic and biochemical characterization of multidrug resistance. Pharmacol. Ther. 28:51–75
Romsicki Y., Sharom F.J. 2001. Phospholipid flippase activity of the reconstituted P-glycoprotein multidrug transporter. Biochemistry 40:6937–6947
Rosenberg M.F., Callaghan R., Ford R.C., Higgins C.F. 1997. Structure of the multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein to 2.5 nm resolution determined by electron microscopy and image analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 272:10685–10694
Rosenberg M.F., Callaghan R., Modok S., Higgins C.F., Ford R.C. 2005. Three-dimensional structure of P-glycoprotein: the transmembrane regions adopt an asymmetric configuration in the nucleotide-bound state. J. Biol. Chem. 280:2857–2862
Rosenberg M.F., Kamis A.B., Callaghan R., Higgins C.F., Ford R.C. 2003. Three-dimensional structures of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein demonstrate major conformational changes in the transmembrane domains upon nucleotide binding. J. Biol. Chem. 278:8294–8299
Rosenberg M.F., Velarde G., Ford R.C., Martin C., Berridge G., Kerr I.D., Callaghan R., Schmidlin A., Wooding C., Linton K.J., Higgins C.F. 2001. Repacking of the transmembrane domains of P-glycoprotein during the transport ATPase cycle. EMBO J. 20:5615–5625
Rothnie A., Storm J., Campbell J., Linton K.J., Kerr I.D., Callaghan R. 2004. The topography of transmembrane segment six is altered during the catalytic cycle of P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 279:34913–34921
Sarkadi B., Price E.M., Boucher R.C., Germann U.A., Scarborough G.A. 1992. Expression of the human multidrug resistance cDNA in insect cells generates a high activity drug-stimulated membrane ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 267:4854–4858
Sauna Z.E., Ambudkar S.V. 2000. Evidence for a requirement for ATP hydrolysis at two distinct steps during a single turnover of the catalytic cycle of human P-glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:2515–2520
Sauna Z.E., Andrus M.B., Turner T.M., Ambudkar S.V. 2004. Biochemical basis of polyvalency as a strategy for enhancing the efficacy of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) modulators: stipiamide homodimers separated with defined-length spacers reverse drug efflux with greater efficacy. Biochemistry 43:2262–2271
Sauna Z.E., Muller M., Peng X.H., Ambudkar S.V. 2002. Importance of the conserved Walker B glutamate residues, 556 and 1201, for the completion of the catalytic cycle of ATP hydrolysis by human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1). Biochemistry 41:13989–4000
Schinkel A.H., Smit J.J., van Tellingen O., Beijnen J.H., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C.A., van der Valk M.A., Robanus-Maandag E.G., te Riele H.P., Berns A.J.M., Borst P. 1994. Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell 77:491–502
Schumacher M.A., Miller M.C., Grkovic S., Brown M.H., Skurray R.A., Brennan R.G. 2001. Structural mechanisms of QacR induction and multidrug recognition. Science 294:2158–2163
Schwab M., Eichelbaum M., Fromm M.F. 2003. Genetic polymorphisms of the human MDR1 drug transporter. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 43:285–307
See Y.P., Carlsen S.A., Till J.E., Ling V. 1974. Increased drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cells in the presence of cyanide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 373:242–252
Seelig A. 1998. A general pattern for substrate recognition by P-glycoprotein. Eur. J. Biochem. 251:252–261
Senior A.E., al-Shawi M.K., Urbatsch I.L. 1995. The catalytic cycle of P-glycoprotein. FEBS Lett. 377:285–289
Shapiro A.B., Ling V. 1997. Extraction of Hoechst 33342 from the cytoplasmic leaflet of the plasma membrane by P-glycoprotein. Eur. J. Biochem. 250:122–129
Sharom F.J. 1997. The P-glycoprotein efflux pump: how does it transport drugs? J. Membrane Biol. 160:161–175
Sharom F.J., Yu X., Doige C.A. 1993. Functional reconstitution of drug transport and ATPase activity in proteoliposomes containing partially purified P-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 268:24197–24202
Shen D.W., Cardarelli C., Hwang J., Corawell M., Richert N., Ishii S., Pastan I., Gottesman M.M. 1986. Multiple drug-resistant human KB carcinoma cells independently selected for high-level resistance to colchicine, adriamycin, or vinblastine show changes in expression of specific proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 261:7762–7770
Smith P.C., Karpowich N., Millen L., Moody I.E., Rosen J., Thomas P.J., Hunt J.F. 2002. ATP binding to the motor domain from an ABC transporter drives formation of a nucleotide sandwich dimer. Mol. Cell 10:139–149
Sonveaux N., Vigano C., Shapiro A.B., Ling V., Ruysschaert J.M. 1999. Ligand-mediated tertiary structure changes of reconstituted P-glycoprotein. A tryptophan fluorescence quenching analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 274:17649–17654
Stenham D.R., Campbell J.D., Sansom M.S., Higgins C.F., Kerr I.D., Linton K.J. 2003. An atomic detail model for the human ATP binding cassette transporter P-glycoprotein derived from disulfide cross-linking and homology modeling. FASEB J. 17:2281–2289
Tang-Wai D.F., Kajiji S., DiCapua F., de Graaf D., Roninson I.E., Gros P. 1995. Human (MDR1) and mouse (mdr1, mdr3) P-glycoproteins can be distinguished by their respective drug resistance profiles and sensitivity to modulators. Biochemistry 34:32–39
Thiebaut F., Tsuruo T., Hamada H., Gottesman M.M., Pastan I., Willingham M.C. 1987. Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P- glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:7735–7738
Tombline G., Bartholomew L., Gimi K., Tyndall G.A., Senior A.E. 2004a. Synergy between conserved ABC signature Ser residues in P-glycoprotein catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 279:5363–5373
Tombline G., Bartholomew L.A., Tyndall G.A., Gimi K., Urbatsch I.L., Senior A.E. 2004b. Properties of P-glycoprotein with mutations in the “catalytic carboxylate” glutamate residues. J. Biol. Chem. 279:46518–46526
Tombline G., Bartholomew L.A., Urbatsch I.L., Senior A.E. 2004c. Combined mutation of catalytic glutamate residues in the two nucleotide binding domains of P-glycoprotein generates a conformation that binds ATP and ADP tightly. J. Biol. Chem 279:31212–31220
Tran T.T., Mittal A., Aldinger T., Polli J.W., Ayrton A., Ellens H., Bentz J. 2005. The elementary mass action rate constants of P-gp transport for a confluent monolayer of MDCKII-hMDR1 cells. Biophys. J. 88:715–738
Urbatsch I.L., al-Shawi M.K., Senior A.E. 1994. Characterization of the ATPase activity of purified Chinese hamster P- glycoprotein. Biochemistry 33:7069–7076
Urbatsch I.L., Gimi K., Wilke-Mounts S., Lerner-Marmarosh N., Rousseau M.E., Gros P., Senior A.E. 2001. Cysteines 431 and 1074 are responsible for inhibitory disulfide cross- linking between the two nucleotide-binding sites in human P- glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 276:26980–26987
Urbatsch I.L., Sankaran B., Bhagat S., Senior A.E. 1995a. Both P-glycoprotein nucleotide-binding sites are catalytically active. J. Biol. Chem. 270:26956–26961
Urbatsch I.L., Sankaran B., Weber J., Senior A.E. 1995b. P-glycoprotein is stably inhibited by vanadate-induced trapping of nucleotide at a single catalytic site. J. Biol. Chem. 270:19383–19390
van der Kolk D.M., de Vries E.G., van Putten W.J., Verdonck L.F., Ossenkoppele G.J., Verhoef G.E., Vellenga E. 2000. P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance protein activities in relation to treatment outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 6:3205–3214
Vigano C., Julien M., Carrier I., Gros P., Ruysschaert J.M. 2002. Structural and functional asymmetry of the nucleotide-binding domains of P-glycoprotein investigated by attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 277:5008–5016
Wang R.B., Kuo C.L., Lien L.L., Lien E.J. 2003. Structure-activity relationship: analyses of p-glycoprotein substrates and inhibitors. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 28:203–228
Watkins R.E., Wisely G.B., Moore L.B., Collins J.L., Lambert M.H., Williams S.P., Willson T.M., Kliewer S.A., Redinbo M.R. 2001. The human nuclear xenobiotic receptor PXR: structural determinants of directed promiscuity. Science 292:2329–33
Wiese M., Pajeva I.K. 2001. Structure-activity relationships of multidrug resistance reversers. Curr. Med. Chem. 8:685–713
Yu E.W., McDermott G., Zgurskaya H.I., Nikaido H., Koshland D.E., Jr. 2003. Structural basis of multiple drug-binding capacity of the AcrB multidrug efflux pump. Science 300:976–980
Yuan Y.R., Blecker S., Martsinkevich O., Millen L., Thomas P.J., Hunt J.F. 2001. The crystal structure of the MJ0796 ATP-binding cassette. Implications for the structural consequences of ATP hydrolysis in the active site of an ABC transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 276:32313–32321
Zhang Z.R., Cui G., Liu X., Song B., Dawson D.C., McCarty N.A. 2005 Determination of the functional unit of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channel. One polypeptide forms one pore. J. Biol. Chem. 280:458–468
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute of Canada through the Canadian Cancer Society and from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. DMC is the recipient of the Canada Research Chair in Membrane Biology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loo, T., Clarke, D. Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanism of P-Glycoprotein-mediated Drug Efflux. J Membrane Biol 206, 173–185 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0792-1
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-005-0792-1