Abstract
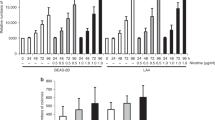
The nicotine-derived N-nitrosamine, 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK), is one of the most abundant and potent carcinogens found in tobacco smoke. NNK induces lung tumors in rodents and is most likely involved in lung carcinogenesis in humans. Studies on the metabolism and carcinogenicity of NNK have been extensive. However, its effects on the immune system have not been investigated thoroughly. Considering that tobacco smoking partially suppresses the immune response in humans, and that immune surveillance plays a critical role in cancer development, we examined the effects of NNK on the production of selected cytokines. In a previous study, we observed an inhibition of NK cell activity and IgM secretory cell number in NNK-treated A/J mice [Rioux and Castonguay (1997) J Natl Cancer Inst 89: 874]. In this study, we demonstrate that U937 human macrophages activate NNK to alkylating intermediates by α-carbon hydroxylation and detoxify NNK by N-oxidation. We observed that NNK, following activation, induces the release of soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF), but inhibits interleukin(IL)-10 synthesis. We also report that 4-(acetoxymethylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone, and nitroso(acetoxymethyl)methylamine, which generate the same alkylating intermediates as NNK, have similar effects on TNF and IL-10. This suggests that pyridyloxobutylating and methylating intermediates generated from NNK are potent modulators of the immune response. The levels of IL-6, granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor and macrophage chemotactic protein 1 were also decreased in supernatants of NNK-treated U937 macrophages. In contrast, IL-2 synthesis in Jurkat cells was inhibited by NNK treatment. This is the first study demonstrating that NNK, via its alkylating intermediates, alters the cytokine synthesis profile in human cells. Modulation of cytokine synthesis by NNK might partially explain the immunosuppresion observed in smokers. Inhibition of immune functions, resulting from NNK activation to alkylating agents, may facilitate lung tumor development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 February 2000 / Accepted: 15 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rioux, N., Castonguay, A. 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone modulation of cytokine release in U937 human macrophages. Cancer Immunol Immunother 49, 663–670 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002620000157
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002620000157