Abstract.
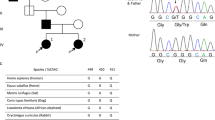
Patients with primary renal glucosuria have normal blood glucose levels, normal oral glucose tolerance test results, and isolated persistant glucosuria. Congenital renal glucosuria is postulated to be attributable to defects in the SGLT2 gene. The Na+/glucose cotransporter gene SGLT2 (=SLC5A2) was analyzed in a Turkish patient with congenital isolated renal glucosuria. Genomic DNA was used as a template for amplification by the polymerase chain reaction of each of the 14 exons of the SGLT2 gene. The amplification products were sequenced. DNA sequence analysis revealed a homozygous nonsense mutation in exon 11 of the SGLT2 gene leading to the formation of a truncated cotransporter. Both parents and a younger brother, all three without renal glucosuria, are heterozygous for the nonsense mutation. Our data provide the first direct evidence of an etiologic role for the sodium/glucose cotransporter type 2 in the pathogenesis of renal glucosuria.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van den Heuvel, .L., Assink, .K., Willemsen, .M. et al. Autosomal recessive renal glucosuria attributable to a mutation in the sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT2). Hum Genet 111, 544–547 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-002-0820-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-002-0820-5