Purpose
Due to protease inhibitor (PI) efflux transport by P-glycoprotein (P-gp), insufficient PI concentrations result in low ongoing HIV replication in the so-called virus sanctuaries (brain and testes). The aim of the present study was to evaluate indinavir-loaded nanocapsules (Ind-LNC) including Solutol® HS15, an excipient reported to possess in vitro P-gp inhibiting properties, as a means to improve indinavir distribution into brain and testes of mice.
Methods
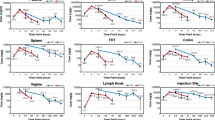
Normal mdr1a (+/+) or P-gp-deficient mdr1a (−/−) CF-1 mice were dosed with Ind-LNC (10 mg indinavir/kg, i.v.). At 30 min postadministration, indinavir was determined in plasma, brain, testes, as well as in kidneys, liver, and heart by LC-MS/MS, and tissue/plasma concentration ratios were calculated. Results were compared with those of control groups that received an indinavir solution (Ind-Sol).
Results
Using Ind-Sol, ratios were 21.3- and 3.3-fold higher in brains and testes of mdr1a (−/−) mice than of mdr1a (+/+) mice, respectively, whereas in the other organs ratios were not significantly different between the two substrains. When Ind-LNC was used, a similar [mdr1a (−/−) vs. mdr1a (+/+) mice] trend was observed. Moreover, ratios were found to be significantly increased (1.9-fold increase in average) in most organs (brain and testes in particular) with Ind-LNC compared to Ind-Sol, regardless of the substrain used.
Conclusions
In agreement with previous works, P-gp governs at least in part indinavir uptake into brain and testes. LNC formulation increased indinavir uptake in brain and testes by mechanisms other than, or additional to, P-gp inhibition.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ind-LNC:
-
indinavir-loaded lipid nanocapsules
- Ind-Sol:
-
indinavir solution
- LNC:
-
lipid nanocapsule
References
J. S. Lewis C. M. Terriff D. R. Coulston M. W. Garrison (1997) ArticleTitleProtease inhibitors: a therapeutic breakthrough for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus Clin. Ther. 19 187–214 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0149-2918(97)80110-5 Occurrence Handle9152561
R. J. Pomerantz (2002) ArticleTitleReservoirs of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: the main obstacles to viral eradication Clin. Infect. Dis. 34 91–97 Occurrence Handle10.1086/338256 Occurrence Handle11731950
T. W. Chun A. S. Fauci (1999) ArticleTitleLatent reservoirs of HIV: obstacles to the eradication of virus Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96 10958–10961 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.96.20.10958 Occurrence Handle10500107
D. L. Kolson E. Lavi F. Gonzalvez-Scarano (1998) ArticleTitleThe effects of human immunodeficiency virus in the central nervous system Adv. Virus Res. 50 1–47 Occurrence Handle9520995
H. Zhang G. Dornadula M. Beaumont L. J. Livornese B. Uitert ParticleVan K. Henning R. J. Pomerantz (1998) ArticleTitleHuman immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the semen of men receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy N. Engl. J. Med. 339 1803–1809 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199812173392502 Occurrence Handle9854115
T. B. Kepler A. S. Perelson (1998) ArticleTitleDrug concentration heterogeneity facilitates the evolution of drug resistance Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 11514–11519 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.95.20.11514 Occurrence Handle9751697
F. Thiebaut T. Tsuruo H. Hamada M. M. Gottesman I. Pastan M. C. Willingham (1987) ArticleTitleCellular localization of the multidrug resistance gene product in normal human tissues Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84 7735–7738 Occurrence Handle2444983
C. Cordon-Cardo J. P. O'Brien D. Casals L. Rittman-Grauer J. L. Biedler M. R. Melamed J. R. Bertino (1989) ArticleTitleMultidrug resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood brain barrier sites Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86 695–698 Occurrence Handle2563168
E. C. Lange Particlede (1989) ArticleTitlePotential role of ABC transporters as a detoxification system at the blood–CSF barrier Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 56 1793–1809 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.addr.2004.07.009
N. Melaine M. O. Lienard I. Dorval C. Goascogne ParticleLe H. Lejeune B. Jegou (2002) ArticleTitleMultidrug resistance genes and P-glycoprotein in the testis of the rat, mouse, guinea pig and human Biol. Reprod. 67 1699–1707 Occurrence Handle10.1095/biolreprod.102.003558 Occurrence Handle12444043
R. B. Kim M. F. Fromm C. Wandel A. J. Wood D. M. Roden G. R. Wilkinson (1998) ArticleTitleThe drug transporter P-glycoprotein limits oral absorption and brain entry of HIV protease inhibitors J. Clin. Invest. 101 289–294 Occurrence Handle9435299
E. F. Choo B. Leake C. Wandel H. Imamura A. J. Wood G. R. Wilkinson R. B. Kim (2000) ArticleTitlePharmacological inhibition of P-glycoprotein transport enhances the distribution of HIV-1 protease inhibitors into brain and testes Drug Metab. Dispos. 28 655–660 Occurrence Handle10820137
J. H. Lin (2004) ArticleTitleHow significant is the role of P-glycoprotein in drug absorption and brain uptake? Drugs Today (Barc.) 40 5–22 Occurrence Handle10.1358/dot.2004.40.1.799434
A. R. Bender H. Briesen Particlevon J. Kreuter I. B. Duncan H. Rubsamen-Waigmann (1996) ArticleTitleEfficiency of nanoparticles as a carrier system for antiviral agents in human immunodeficiency virus-infected human monocytes/macrophages in vitro Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 40 1467–1471 Occurrence Handle8726020
J. F. Gagne A. Desormeaux S. Perron M. J. Tremblay M. G. Bergeron (2002) ArticleTitleTargeted delivery of indinavir to HIV-1 primary reservoirs with immunoliposomes Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1558 198–210 Occurrence Handle11779569
B. Heurtault, P. Saulnier, B. Pech, J. E. Proust, J. Richard, J. P. Benoit. A novel phase inversion-based process for the preparation of lipidic nanocarriers, 2000. Patent FR 0002688.
A. Cahouet B. Denizot F. Hindre C. Passirani B. Heurtault M. Moreau J. Jeune ParticleLe J. P. Benoit (2002) ArticleTitleBiodistribution of dual radiolabeled lipidic nanocapsules in the rat using scintigraphy and gamma counting Int. J. Pharm. 242 367–371 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00218-1 Occurrence Handle12176281
J. S. Coon W. Knudson K. Clodfelter B. Lu R. S. Weinstein (1991) ArticleTitleSolutol HS 15, non toxic polyethylene esters of 12-hydroxystearic acid reverses multidrug resistance Cancer Res. 51 897–902 Occurrence Handle1988130
L. E. Buckingham M. Balasubramanian A. R. Safa H. Shah P. Komarov R. M. Emanuele J. S. Coon (1996) ArticleTitleReversal of multi-drug resistance in vitro by fatty acid–PEG–fatty acid diester Int. J. Cancer 65 74–79 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19960103)65:1<74::AID-IJC13>3.0.CO;2-I Occurrence Handle8543400
R. C. Bravo Gonzalez J. Huwyler F. Boess I. Walter B. Bittner (2004) ArticleTitleIn vitro investigation on the impact of the surface-active excipients Cremophor EL, Tween 80 and Solutol HS 15 on the metabolism of midazolam Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 25 37–49 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bdd.383 Occurrence Handle14716751
L. Y. Li G. L. Amidon J. S. Kim T. Heimbach F. Kesisoglou J. T. Topliss D. Fleisher (2002) ArticleTitleIntestinal metabolism promotes regional differences in apical uptake of indinavir: coupled effect of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 3A on indinavir membrane permeability in rat J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301 586–593 Occurrence Handle10.1124/jpet.301.2.586 Occurrence Handle11961060
F. L. S. Tse (1995) Pharmacokinetics in drug discovery and development: nonclinical studies P. G. Welling F. L. S. Tse (Eds) Pharmacokinetics: Regulatory, Industrial, Academic Perspectives EditionNumber2 Marcel Dekker New York 281–334
E. Y. Wu J. M. Wilkinson D. G. Naret V. L. Daniels L. J. Williams D. A. Khalil B. V. Shetty (1997) ArticleTitleHigh-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of nelfinavir, a novel HIV-1 protease inhibitor, in human plasma J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 695 373–380 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-4347(97)00193-X Occurrence Handle9300874
R. P. Heeswijk Particlevan R. M. Hoetelmans R. Harms P. L. Meenhorst J. W. Mulder J. M. Lange J. H. Beijnen (1998) ArticleTitleSimultaneous quantitative determination of the HIV protease inhibitors amprenavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir and saquinavir in human plasma by ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 719 159–168 Occurrence Handle9869376
J. Chi A. L. Jayewardene J. A. Stone T. Motoya F. T. Aweeka (2002) ArticleTitleSimultaneous determination of five HIV protease inhibitors nelfinavir, indinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and amprenavir in human plasma by LC/MS/MS J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 30 675–684 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0731-7085(02)00357-6 Occurrence Handle12367693
J. M. Croop M. Raymond D. Haber A. Devault R. J. Arceci P. Gros D. E. Housman (1989) ArticleTitleThe three mouse multidrug resistance (mdr) genes are expressed in a tissue-specific manner in normal mouse tissues Mol. Cell Biol. 9 1346–1350 Occurrence Handle2471060
T. R. Pippert D. R. Umbenhauer (2001) ArticleTitleThe subpopulation of CF-1 mice deficient in P-glycoprotein contains a murine retroviral insertion in the mdr1a gene J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 15 83–89 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jbt.3 Occurrence Handle11284049
E. G. Schuetz D. R. Umbenhauer K. Yasuda C. Brimer L. Nguyen M. V. Relling J. D. Schuetz A. H. Schinckel (2000) ArticleTitleAltered expression of hepatic cytochromes P-450 in mice deficient in one or more mdr1 genes Mol. Pharmacol. 57 188–197 Occurrence Handle10617694
G. R. Lankas M. E. Cartwright D. Umbenhauer (1997) ArticleTitleP-glycoprotein deficiency in a subpopulation of CF-1 mice enhances ivermectin-induced neurotoxicity Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 143 357–365 Occurrence Handle10.1006/taap.1996.8086 Occurrence Handle9144452
J. A. Bush G. Li (2002) ArticleTitleRegulation of the mdr1 isoforms in a p53-deficient mouse model Carcinogenesis 23 1603–1607 Occurrence Handle10.1093/carcin/23.10.1603 Occurrence Handle12376467
N. Mizuno T. Niwa Y. Yotsumoto Y. Sugiyama (2003) ArticleTitleImpact of drug transporter studies on drug discovery and development Pharmacol. Rev. 55 425–461 Occurrence Handle10.1124/pr.55.3.1 Occurrence Handle12869659
A. H. Schinkel U. Mayer E. Wagenaar C. A. Mol L. Deemter Particlevan J. J. Smit M. A. Valk Particlevan der A. C. Voordouw H. Spits O. Tellingen Particlevan J. M. Zijlmans W. E. Fibbe P. Borst (1997) ArticleTitleNormal viability and altered pharmacokinetics in mice lacking mdr1-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94 4028–4033 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.94.8.4028 Occurrence Handle9108099
J. A. Holash S. I. Harik G. Perry P. A. Stewart (1993) ArticleTitleBarrier properties of testis microvessels Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90 11069–11073 Occurrence Handle7902579
J. Asperen Particlevan O. Tellingen Particlevan F. Tijssen A. H. Schinkel J. H. Beijnen (1999) ArticleTitleIncreased accumulation of doxorubicin and doxorubicinol in cardiac tissue of mice lacking mdr1a P-glycoprotein Br. J. Cancer 79 108–113 Occurrence Handle10408701
J. Jodoin M. Demeule L. Fenart R. Cecchelli S. Farmer K. J. Linton C. F. Higgins R. Beliveau (2003) ArticleTitleP-glycoprotein in blood–brain barrier endothelial cells: interaction and oligomerization with caveolins J. Neurochem. 87 1010–1023 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02081.x Occurrence Handle14622130
M. T. Huisman J. W. Smit K. M. Crommentuyn N. Zelcer H. R. Wiltshire J. H. Beijnen A. H. Schinkel (2002) ArticleTitleMultidrug resistance protein 2 (MRP2) transports HIV protease inhibitors and transport can enhanced by other drugs AIDS 16 2295–2301 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002030-200211220-00009 Occurrence Handle12441801
A. Rosati S. Maniori G. Decorti L. Candussio T. Giraldi F. Bartoli (2003) ArticleTitlePhysiological regulation of P-glycoprotein MRP1, MRP2 and cytochrome P 450 3A2 during rat ontogeny Dev. Growth Differ. 45 377–387 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1440-169X.2003.00699.x Occurrence Handle12950279
A. S. Chong P. N. Markham H. M. Gebel S. D. Bines J. S. Coon (1993) ArticleTitleDiverse multidrug-resistance-modification agents inhibit cytolytic activity of natural killer cells Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 36 133–139 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01754414 Occurrence Handle8093856
K. Buszello S. Harnisch R. H. Muller B. W. Muller (2000) ArticleTitleThe influence of alkali fatty acids on the properties and the stability of parenteral O/W emulsions modified with Solutol HS15 Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 49 143–149 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0939-6411(99)00081-8 Occurrence Handle10704897
K. Woodburn E. Sykes D. Kessel (1995) ArticleTitleInteractions of Solutol HS 15 and Cremophor EL with plasma lipoproteins Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 27 693–699 Occurrence Handle10.1016/1357-2725(95)00030-S Occurrence Handle7648425
L. E. Buckingham M. Balasubramanian R. M. Emanuele K. E. Clodfelter J. S. Coon (1995) ArticleTitleComparison of Solutol HS 15, Cremophor EL and novel ethoxylated fatty acid surfactants as multidrug resistance modification agents Int. J. Cancer 62 436–442 Occurrence Handle7635569
P. G. Komarov A. A. Shtil L. E. Buckingham M. Balasubramanian O. Piraner R. M. Emanuele I. B. Roninson J. S. Coon (1996) ArticleTitleInhibition of cytarabine-induced MDR1 (P-glycoprotein) gene activation in human tumor cells by fatty acid–polyethylene glycol–fatty acid diesters, novel inhibitors of P-glycoprotein function Int. J. Cancer 68 245–250 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19961009)68:2<245::AID-IJC18>3.0.CO;2-9 Occurrence Handle8900436
B. Bittner R. C. Gonzalez I. Walter M. Kapps J. Huwyler (2003) ArticleTitleImpact of Solutol HS 15 on the pharmacokinetic behaviour of colchicine upon intravenous administration to male Wistar rats Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 24 173–181 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bdd.353 Occurrence Handle12698501
B. Bittner R. C. Gonzalez H. Isel C. Flament (2003) ArticleTitleImpact of Solutol HS 15 on the pharmacokinetic behavior of midazolam upon intravenous administration to male Wistar rats Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 56 143–146 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0939-6411(03)00041-9 Occurrence Handle12837492
P. R. Lockman J. Koziara K. E. Roder J. Paulson T. J. Abbruscato R. J. Mumper D. D. Allen (2003) ArticleTitleIn vivo and in vitro assessment of baseline blood–brain barrier parameters in the presence of novel nanoparticles Pharm. Res. 56 705–713 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1023492015851
A. Vonarbourg P. Saulnier C. Passirani J. P. Benoit (2005) ArticleTitleElectrokinetic properties of noncharged lipid nanocapsules: influence of the dipolar distribution at the interface Electrophoresis 26 2066–2075 Occurrence Handle10.1002/elps.200410145 Occurrence Handle15852355
P. K. Dudeja K. M. Anderson J. S. Harris L. Buckingham J. S. Coon (1995) ArticleTitleReversal of multidrug resistance phenotype by surfactants: relationship to membrane lipid fluidity Arch Biochem. Biophys. 319 309–315 Occurrence Handle10.1006/abbi.1995.1298 Occurrence Handle7771801
Acknowledgment
We are grateful for the excellent technical assistance of Mrs. Isabelle Lamarche.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira de Oliveira, M., Garcion, E., Venisse, N. et al. Tissue Distribution of Indinavir Administered as Solid Lipid Nanocapsule Formulation in mdr1a (+/+) and mdr1a (−/−) CF-1 Mice. Pharm Res 22, 1898–1905 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-7147-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-7147-6