Abstract
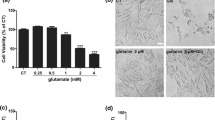
The root of Paeonia lactiflora Pall (family Ranunculaceae) or peony root, a herbal medicine, possesses therapeutic potential for neurodegenerative diseases. The isomers paeoniflorin (PF) and albiflorin (AF) are major constituents contained in peony root. Our previous study has shown notable neuroprotective effects of PF. In the present study, we further compared the effects of AF and PF against glutamate (Glu)-induced cell damage and the underlying mechanisms in differentiated PC12 cells. Both AF and PF significantly ameliorated Glu-induced reduction of cell viability, nuclear and mitochondrial apoptotic alteration, reactive oxygen species accumulation, and B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2)/Bax ratio. The two isomers also enhanced phosphorylation of AKT and its downstream element glycogen synthase kinase-3β, and this effect was abrogated by the AKT inhibitor LY294002. PF, but not AF, however, suppressed intracellular Ca2+ overload and the expression of calcium/calmodulin protein kinase II (CaMKII). The improvement of cell damage by the CaMKII inhibitor KN93 further confirms the role of CaMKII in PF-mediated neuroprotection. These results suggest that both AF and PF possess robust effects in protecting neuronal cells against Glu toxicity. PF further displayed remarkable effects in preventing intracellular Ca2+ overload and suppressing overexpression of CaMKII. Differential mechanisms may be involved in neuroprotective action of the two isomers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaishi T, Nakazawa K, Sato K, Saito H, Ohno Y, Ito Y (2004) Hydrogen peroxide modulates whole cell Ca2+ currents through L-type channels in cultured rat dentate granule cells. Neurosci Lett 356(1):25–28
Bezprozvanny I (2009) Calcium signaling and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol Med 15(3):89–100
Cao BY, Yang YP, Luo WF, Mao CJ, Han R, Sun X, Cheng J, Liu CF (2010) Paeoniflorin, a potent natural compound, protects PC12 cells from MPP+ and acidic damage via autophagic pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 131(1):122–129
Chan SL, Yu VC (2004) Proteins of the bcl-2 family in apoptosis signalling: from mechanistic insights to therapeutic opportunities. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 31(3):119–128
Giorgi C, Baldassari F, Bononi A, Bonora M, De Marchi E, Marchi S, Missiroli S, Patergnani S, Rimessi A, Suski JM, Wieckowski MR, Pinton P (2012) Mitochondrial Ca(2+) and apoptosis. Cell Calcium 52(1):36–43
Hur EM, Zhou FQ (2010) GSK3 signalling in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(8):539–551
Jang JY, Kim HN, Kim YR, Choi YW, Choi YH, Lee JH, Shin HK, Choi BT (2013) Hexane extract from Polygonum multiflorum attenuates glutamate-induced apoptosis in primary cultured cortical neurons. J Ethnopharmacol 145(1):261–268
Jiang D, Chen Y, Hou X, Xu J, Mu X, Chen W (2011) Influence of Paeonia lactiflora roots extract on cAMP-phosphodiesterase activity and related anti-inflammatory action. J Ethnopharmacol 137(1):914–920
Kirkland RA, Franklin JL (2001) Evidence for redox regulation of cytochrome C release during programmed neuronal death: antioxidant effects of protein synthesis and caspase inhibition. J Neurosci 21(6):1949–1963
Li CR, Zhou Z, Zhu D, Sun YN, Dai JM, Wang SQ (2007) Protective effect of paeoniflorin on irradiation-induced cell damage involved in modulation of reactive oxygen species and the mitogen-activated protein kinases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(2):426–438
Liang J, Slingerland JM (2003) Multiple roles of the PI3K/PKB (Akt) pathway in cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle 2(4):339–345
Lu S, Lu C, Han Q, Li J, Du Z, Liao L, Zhao RC (2011) Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect PC12 cells from glutamate excitotoxicity-induced apoptosis by upregulation of XIAP through PI3-K/Akt activation. Toxicology 279(1–3):189–195
Mao QQ, Zhong XM, Feng CR, Pan AJ, Li ZY, Huang Z (2010) Protective effects of paeoniflorin against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells via antioxidant mechanisms and Ca(2+) antagonism. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30(7):1059–1066
Mao QQ, Xian YF, Ip SP, Tsai SH, Che CT (2011) Protective effects of peony glycosides against corticosterone-induced cell death in PC12 cells through antioxidant action. J Ethnopharmacol 133(3):1121–1125
Mayer B, Oberbauer R (2003) Mitochondrial regulation of apoptosis. News Physiol Sci 18:89–94
Nicholls DG (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction and glutamate excitotoxicity studied in primary neuronal cultures. Curr Mol Med 4(2):149–177
Pan ZW, Zhang Y, Mei DH, Zhang R, Wang JH, Zhang XY, Xu CQ, Lu YJ, Yang BF (2010) Scutellarin exerts its anti-hypertrophic effects via suppressing the Ca2+-mediated calcineurin and CaMKII signaling pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 381(2):137–145
Pitt GS (2007) Calmodulin and CaMKII as molecular switches for cardiac ion channels. Cardiovasc Res 73(4):641–647
Praetorius HA, Leipziger J (2009) Released nucleotides amplify the cilium-dependent, flow-induced [Ca2+]i response in MDCK cells. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 197(3):241–251
Raisova M, Hossini AM, Eberle J, Riebeling C, Wieder T, Sturm I, Daniel PT, Orfanos CE, Geilen CC (2001) The Bax/Bcl-2 ratio determines the susceptibility of human melanoma cells to CD95/Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Invest Dermatol 117(2):333–340
Reynolds IJ, Hastings TG (1995) Glutamate induces the production of reactive oxygen species in cultured forebrain neurons following NMDA receptor activation. J Neurosci 15(5 Pt 1):3318–3327
Tahir SK, Trogadis JE, Stevens JK, Zimmerman AM (1992) Cytoskeletal organization following cannabinoid treatment in undifferentiated and differentiated PC12 cells. Biochem Cell Biol 70(10–11):1159–1173
Tan JW, Tham CL, Israf DA, Lee SH, Kim MK (2013) Neuroprotective effects of biochanin A against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells via apoptosis inhibition. Neurochem Res 38:512–518
Thatte U, Bagadey S, Dahanukar S (2000) Modulation of programmed cell death by medicinal plants. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 46(1):199–214
Thress K, Kornbluth S, Smith JJ (1999) Mitochondria at the crossroad of apoptotic cell death. J Bioenerg Biomembr 31(4):321–326
Timmins JM, Ozcan L, Seimon TA, Li G, Malagelada C, Backs J, Backs T, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN, Anderson ME, Tabas I (2009) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II links ER stress with Fas and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. J Clin Invest 119(10):2925–2941
van Woerden GM, Harris KD, Hojjati MR, Gustin RM, Qiu S, de Avila Freire R, Jiang YH, Elgersma Y, Weeber EJ (2007) Rescue of neurological deficits in a mouse model for Angelman syndrome by reduction of alphaCaMKII inhibitory phosphorylation. Nat Neurosci 10(3):280–282
Wang L, Jing W, Hang YN (2008) Glutamate-induced c-Jun expression in neuronal PC12 cells: the effects of ketamine and propofol. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 20(2):124–130
Wang D, Wong HK, Feng YB, Zhang ZJ (2013) Paeoniflorin, a natural neuroprotective agent, modulates multiple anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic pathways in differentiated PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33(4):521–529
Wankun X, Wenzhen Y, Min Z, Weiyan Z, Huan C, Wei D, Lvzhen H, Xu Y, Xiaoxin L (2011) Protective effect of paeoniflorin against oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelium in vitro. Mol Vis 17:3512–3522
Wheeler DG, Barrett CF, Groth RD, Safa P, Tsien RW (2008) CaMKII locally encodes L-type channel activity to signal to nuclear CREB in excitation-transcription coupling. J Cell Biol 183(5):849–863
Wu CF (1985) A review on the pharmacology of Paeonia lactiflora and its chemical components. Zhong Yao Tong Bao 10(6):43–45
Wu SH, Wu DG, Chen YW (2010) Chemical constituents and bioactivities of plants from the genus Paeonia. Chem Biodivers 7(1):90–104
Xu W, Zhou L, Ma X, Chen Y, Qin B, Zhai X, You S (2011) Therapeutic effects of combination of paeoniflorin and albiflorin from Paeonia radix on radiation and chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression in mice and rabbits. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 12(8):2031–2037
Yoshimura Y, Ichinose T, Yamauchi T (2003) Phosphorylation of tau protein to sites found in Alzheimer’s disease brain is catalyzed by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II as demonstrated tandem mass spectrometry. Neurosci Lett 353(3):185–188
Zhang GR, Cheng XR, Zhou WX, Zhang YX (2009) Age-related expression of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II A in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of senescence accelerated mouse prone/8 mice is modulated by anti-Alzheimer’s disease drugs. Neuroscience 159(1):308–315
Zhang M, Li J, Geng R, Ge W, Zhou Y, Zhang C, Cheng Y, Geng D (2013) The Inhibition of ERK Activation Mediates the Protection of Necrostatin-1 on Glutamate Toxicity in HT-22 Cells. Neurotox Res [Epub ahead of print]
Zhao Q, Yokozawa T, Yamabe N, Tsuneyama K, Li X, Matsumoto K (2010) Kangen-karyu improves memory deficit caused by aging through normalization of neuro-plasticity-related signaling system and VEGF system in the brain. J Ethnopharmacol 131(2):377–385
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Health and Health Service Research Fund (HHSRF) (09101141) and HKU intramural seed funds (201011159095 and 201102160005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Tan, QR. & Zhang, ZJ. Neuroprotective Effects of Paeoniflorin, But Not the Isomer Albiflorin, are Associated with the Suppression of Intracellular Calcium and Calcium/Calmodulin Protein Kinase II in PC12 Cells. J Mol Neurosci 51, 581–590 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0031-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0031-7