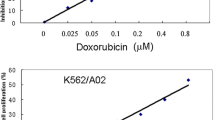
Abstract
Chemotherapeutic drug resistance is a frequent cause of treatment failure in colon cancer patients. Several mechanisms have been implicated in drug resistance. However, they are not sufficient to exhaustively account for this resistance emergence. In this study, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) and the PDQuest software analysis were applied to compare the differential expression of irinotecan-resistance-associated protein in human colon adenocarcinoma LoVo cells and irinotecan-resistant LoVo cells (LoVo/irinotecan). The differential protein dots were excised and analysed by ESI-Q-TOF mass spectrometry (MS). Fifteen proteins were identified, including eight proteins with decreased expression and seven proteins with increased expression. The identified known proteins included those that function in diverse biological processes such as cellular transcription, cell apoptosis, electron transport/redox regulation, cell proliferation/differentiation and retinol metabolism pathways. Identification of such proteins could allow improved understanding of the mechanisms leading to the acquisition of chemoresistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACN:
-
acetonitrile
- AKR:
-
aldo-keto reductase
- AR1A1:
-
aldose reductase
- CBB:
-
Coomassie brilliant blue
- CFL1:
-
Cofilin-1
- CRYAB:
-
alpha-crystallin B chain
- 2-DE:
-
two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- 5-FU:
-
5-fluorouracil
- HSP27:
-
heat shock protein 27
- IEF:
-
isoelectric focusing
- IPG:
-
immobilised pH gradient
- LoVo cells:
-
human colon adenocarcinoma
- LoVo/irinotecan:
-
irinotecan-resistant human colon adenocarcinoma
- MDR:
-
multidrug resistance
- MS:
-
mass spectrometry
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffered saline
- Pgp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- PVDF:
-
polyvinylidene difluoride
- Q-TOF:
-
quadrupole time-of-flight
- TBST:
-
Tris-buffered saline Tween-20
- TFA:
-
trifluoroacetic acid
References
Arrigo A P, Simon S, Gibert B, Kretz-Remy C, Nivon M, Czekalla A, Guillet D, Moulin M, Diaz-Latoud C and Vicart P 2007 Hsp27 (HspB1) and alphaB-crystallin (HspB5) as therapeutic targets; FEBS Lett. 581 3665–3674
Chen R, Pan S, Brentnall T A and Aebersold R 2005 Proteomic profiling of pancreatic cancer for biomarker discovery; Mol. Cell Proteomics 4 523–533
Flagiello D, Apiou F, Gibaud A, Poupon M F, Dutrillaux B and Malfoy B 1997 Assignment of the genes for cellular retinoic acid binding protein 1 (CRABP1) and 2 (CRABP2) to human chromosome band 15q24 and 1q21.3, respectively, by in situ hybridization; Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 76 17–18
Forrest G L and Gonzalez B 2000 Carbonyl reductase; Chem. Biol. Interact. 129 2140
Goldberg R M 2006 Therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer; Oncologist 11 981–987
Hütter G and Sinha P 2001 Proteomics for studying cancer cells and the development of chemoresistance; Proteomics 1 1233–1248
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and Thun M J 2009 Cancer statistics, 2009; CA-Cancer J. Clin. 59 225–249
Jin Y and Penning T M 2007 Aldo-keto reductases and bioactivation/detoxication; Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 47 263–292
Judson L K, William P H and Adrience C S 2004 Molecular analysis of alpha B-crystallin in human malignant glioma cell populations; AACR Meeting #2263
Kelly H and Goldberg R M 2005 Systemic therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: current options, current evidence; J. Clin. Oncol. 23 4553–4560
Kuffel M J, Reid J M and Ames M M 1992 Anthracyclines and their C-13 alcohol metabolites: growth inhibition and DNA damage following incubation with human tumor cells in culture; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 30 51–57
Lage H 2003 ABC-transporters: implications on drug resistance from microorganisms to human cancers; Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 22 188–199
Li X, Cusack B J, Boucek Jr R J, Mushlin P S, Bledsoe T B, Brenner D E and Olson R D 1991 Effects of daunorubicin and its primary metabolite, daunorubicinol, on cardiac contractility and calcium loading of sarcoplasmic reticulum; FASEB J. 5 A1395
Licata S, Saponiero A, Mordente A and Minotti G 2000 Doxorubicin metabolism and toxicity in human myocardium: role of cytoplasmic deglycosidation and carbonyl reduction; Chem. Res. Toxicol. 13 414–420
Ling V 1997 Multidrug resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. Suppl. 40 S 38
Mariann P, Michael S, Christoph H, Lutz K and Edmund M 2007 Increased resistance of tumor cells to daunorubicin after transfection of CDNAs coding for anthracycline inactivating enzymes; Cancer Lett. 255 49–56
Matsunaga T, Shintani S and Hara A 2006 Multiplicity of mammalian reductases for xenobiotic carbonyl compounds; Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 21 118
Mordente A, Minotti G, Martorana G E, Silvestrini A, Giardina B and Meucci E 2003 Anthracycline secondary alcohol metabolite formation in human or rabbit heart: biochemical aspects and pharmacologic implications; Biochem. Pharmacol. 66 989–998
Ohara H, Miyabe Y, Deyashiki Y, Matsuura K and Hara A 1995 Reduction of drug ketones by dihydrodiol dehydrogenases, carbonyl reductase and aldehyde reductase of human liver; Biochem. Pharmacol. 50 221–227
Olson R D, Mushlin P S, Brenner D E, Fleischer S, Cusack B J, Chang B K and Boucek Jr R J 1988 Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity may be caused by its metabolite, doxorubicinol; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85 3585–3589
Perez R P 1998 Cellular and molecular determinants of cisplatin resistance; Eur. J. Cancer 34 1535–1542
Pommier Y, Pourquier P, Fan Y and Strumberg D 1998 Mechanism of action of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I and drugs targeted to the enzyme; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1400 83–105
Schott B and Robert J 1989 Comparative activity of anthracycline 13-hydroxymetabolites against rat glioblastoma cells in culture; Biochem. Pharmacol. 38 4069–4074
Sinha P, Hütter G, Kottgen E, Dietel M, Schadendorf D and Lage H 1999 Increased expression of epidermal fatty acid binding protein, cofilin, and 14-3-3-σ(stratifin) detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, mass spectrometry and microsequencing of drug-resistant human adenocarcinoma of the pancreas; Electrophoresis 20 2952–2960
Slatter J G, Su P, Sams J P, Schaaf L J and Wienkers L C 1997 Bioactivation of the anticancer agent CPT-11 to SN-38 by human hepatic microsomal carboxylesterases and the in vitro assessment of potential drug interactions; Drug Metab. Dispos. 25 1157–1164
Tanaka K, Imoto I, Inoue J, Kozaki K, Tsuda H, Shimada Y, Aiko S, Yoshizumi Y, Iwai T, Kawano T and Inazawa J 2007 Frequent methylation-associated silencing of a candidate tumorsuppressor, CRABP1, in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma; Oncogene 26 6456–6468
Tong A, Zhang H, Li Z, Gou L, Wang Z, Wei H, Tang M, Liang S, Chen L, Huang C and Wei Y 2007 Proteomic analysis of liver cancer cells treated with suberonylanilide hydroxamic acid; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 61 791–802
Vimalachandran D and Costello E 2004 Proteomic technologies and their application to pancreatic cancer; Expert Rev. Proteomics 1 493–501
Watanabe G, Kato S, Nakata H, Ishida T, Ohuchi N and Ishioka C 2009 alphaB-crystallin: a novel p53-target gene required for p53-dependent apoptosis; Cancer Sci. 100 2368–2375
Yu D H 1998 The role of oncogenes in drug resistance; Cytotechnology 27 283–292
Zeng H, Liu G, Rea P A and Kruh G D 2000 Transport of amphipathic anions by human multidrug resistance protein 3; Cancer Res. 60 4779–4784
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, XC., Gong, FM., Wei, M. et al. Proteomic analysis of cell lines to identify the irinotecan resistance proteins. J Biosci 35, 557–564 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-010-0064-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-010-0064-9