Abstract
Objective
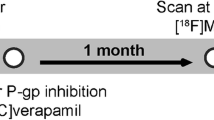
To investigate the effects of the clinical dose of clarithromycin, a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), on P-gp function using positron emission tomography (PET) with [11C]verapamil.
Methods
Two PET scanning with [11C]verapamil were performed before and after administration of 400 mg/day of clarithromycin on each of four healthy male subjects. The rate constant of transfer from plasma to brain (K 1) was estimated by integration plot method.
Results
K1 values of [11C]verapamil before administration of clarithromycin were 0.042–0.070 mL/cm3/min (0.054 ± 0.012) and those after administration were 0.037–0.066 mL/cm3/min (0.055 ± 0.013). No significant change in K1 values of [11C]verapamil was observed between before and after administration of clarithromycin (P = 0.85).
Conclusion
K1 values of [11C]verapamil were not changed by clinical dose administration of clarithromycin, suggesting that a clinical dose of clarithromycin does not affect P-gp function at the blood–brain barrier.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chinn LW, Kroetz DL. ABCB1 pharmacogenetics: progress, pitfalls, and promise. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;81:265–9.
Ambudkar SV, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Sauna ZE, Gottesman MM. P-glycoprotein: from genomics to mechanism. Oncogene. 2003;22:7468–85.
Linnet K, Ejsing TB. A review on the impact of P-glycoprotein on the penetration of drugs into the brain. Focus on psychotropic drugs. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;18:157–69.
Liu X, Chen C, Smith BJ. Progress in brain penetration evaluation in drug discovery and development. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;325:349–56.
Sadeque AJ, Wandel C, He H, Shah S, Wood AJ. Increased drug delivery to the brain by P-glycoprotein inhibition. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000;68:231–7.
Troger U, Lins H, Scherrmann JM, Wallesch CW, Bode-Boger SM. Tetraparesis associated with colchicine is probably due to inhibition by verapamil of the P-glycoprotein efflux pump in the blood-brain barrier. BMJ. 2005;331:613.
Fenner KS, Troutman MD, Kempshall S, Cook JA, Ware JA, Smith DA, et al. Drug-drug interactions mediated through P-glycoprotein: clinical relevance and in vitro-in vivo correlation using digoxin as a probe drug. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009;85:173–81.
Ikoma Y, Takano A, Ito H, Kusuhara H, Sugiyama Y, Arakawa R, et al. Quantitative analysis of 11C-verapamil transfer at the human blood-brain barrier for evaluation of P-glycoprotein function. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1531–7.
Brunner M, Langer O, Sunder-Plassmann R, Dobrozemsky G, Muller U, Wadsak W, et al. Influence of functional haplotypes in the drug transporter gene ABCB1 on central nervous system drug distribution in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;78:182–90.
Takano A, Kusuhara H, Suhara T, Ieiri I, Morimoto T, Lee YJ, et al. Evaluation of in vivo P-glycoprotein function at the blood-brain barrier among MDR1 gene polymorphisms by using 11C-verapamil. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1427–33.
Kortekaas R, Leenders KL, van Oostrom JC, Vaalburg W, Bart J, Willemsen AT, et al. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in parkinsonian midbrain in vivo. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:176–9.
Bartels AL, Willemsen AT, Kortekaas R, de Jong BM, de Vries R, de Klerk O, et al. Decreased blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in the progression of Parkinson’s disease, PSP and MSA. J Neural Transm. 2008;115:1001–9.
Bartels AL, van Berckel BN, Lubberink M, Luurtsema G, Lammertsma AA, Leenders KL. Blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function is not impaired in early Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2008;14:505–8.
Langer O, Bauer M, Hammers A, Karch R, Pataraia E, Koepp MJ, et al. Pharmacoresistance in epilepsy: a pilot PET study with the P-glycoprotein substrate R-[11C]verapamil. Epilepsia. 2007;48:1774–84.
Sasongko L, Link JM, Muzi M, Mankoff DA, Yang X, Collier AC, et al. Imaging P-glycoprotein transport activity at the human blood-brain barrier with positron emission tomography. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;77:503–14.
Lee YJ, Maeda J, Kusuhara H, Okauchi T, Inaji M, Nagai Y, et al. In vivo evaluation of P-glycoprotein function at the blood-brain barrier in nonhuman primates using [11C]verapamil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:647–53.
Wang L, Kitaichi K, Hui CS, Takagi K, Sakai M, Yokogawa K, et al. Reversal of anticancer drug resistance by macrolide antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000;27:587–93.
Zhang L, Liu XD, Xie L, Wang GJ. P-glycoprotein restricted transport of nimodipine across blood–brain barrier. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003;24:903–6.
Wegman TD, Maas B, Elsinga PH, Vaalburg W. An improved method for the preparation of [11C]verapamil. Appl Radiat Isot. 2002;57:505–7.
Alvarez-Elcoro S, Enzler MJ. The macrolides: erythromycin, clarithromycin, and azithromycin. Mayo Clin Proc. 1999;74:613–34.
Jain R, Danziger LH. The macrolide antibiotics: a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic overview. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:3045–53.
Jorga A, Holt DW, Johnston A. Therapeutic drug monitoring of cyclosporine. Transplant Proc. 2004;36:396S–403S.
Midtvedt K. Therapeutic drug monitoring of cyclosporine. Transplant Proc. 2004;36:430S–3S.
Kurata Y, Ieiri I, Kimura M, Morita T, Irie S, Urae A, et al. Role of human MDR1 gene polymorphism in bioavailability and interaction of digoxin, a substrate of P-glycoprotein. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002;72:209–19.
Pinto AG, Wang YH, Chalasani N, Skaar T, Kolwankar D, Gorski JC, et al. Inhibition of human intestinal wall metabolism by macrolide antibiotics: effect of clarithromycin on cytochrome P450 3A4/5 activity and expression. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;77:178–88.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Katsuyuki Tanimoto, Mr. Takahiro Shiraishi and Mr. Toshio Miyamoto for their assistance in performing the PET experiments, and Ms. Yoshiko Fukushima for her help as clinical research coordinator at the National Institute of Radiological Sciences. We also thank Dr. Mizuno Kenji for the measurement of plasma concentration of clarithromycin at the Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism, Drug Safety and Pharmacokinetics Laboratories, Taisho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported by a consignment expense for the Molecular Imaging Program on “Research Base for PET Diagnosis” from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japanese Government. None of the authors has any conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arakawa, R., Ito, H., Okumura, M. et al. No inhibitory effect on P-glycoprotein function at blood–brain barrier by clinical dose of clarithromycin: a human PET study with [11C]verapamil. Ann Nucl Med 24, 83–87 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-009-0336-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-009-0336-3