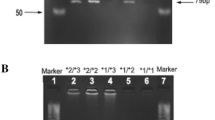
Abstract
Genetic polymorphism of drug metabolizing enzymes, particularly cytochrome P450 (CYP), is an important cause of adverse drug reactions. Multiple gene mutations in CYP have been shown to be phenotype. The occurrence of genetic polymorphism has been seen in genes for CYP1A1, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A5. This review discusses the molecular mechanism of two genetic polymorphisms, debrisoquine/sparteine (CYP2D6) coumarin (CYP2A6) polymorphisms. In addition, elucidation of gene mutations of CYP2D6 and CYP2A6 in Japanese will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. R. Nelson, L. Koymans, T. Kamataki, J. J. Stageman, R. Feyereisen, D. J. Waxman, M. R. Waterman, O. Gotoh, M. J. Coon, R. W. Estabrook, I. G. Gunsalus, and D. W. Nebert. P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers and nomenclature. Pharamacogenetics 6:1–42 (1996).
K. Broøsen, S. M. F. de Morais, U. A. Meyer, and J. A. Goldstein. A multifamily study on the relationship between CYP2C19 genotype and S-mephenytoin oxidation phenotype. Pharmacogenetics 5:312–317 (1995).
S. M. F. de Morais, G. R. Wilkinson, J. Blaisdell, K. Nakamura, U. A. Meyer, and J. A. Goldstein. The major genetic defect responsible for the polymorphism of S-mephenytoin in humans. J. Biol. Chem. 269:15419–15422 (1994).
S. M. F. de Morais, G. R. Wilkinson, K. Nakamura, U. A. Meyer, and J. A. Goldstein. Identification of a new genetic defect responsible for the polymorphism of S-mephenytoin metabolism in Japanese. Mol. Pharmacol, 46:594–598 (1994).
J. A. Goldstein, T. Ishizaki, K. Chiba, S. M. F. de Morais, D. Bell, P. M. Krahn, and D. A. P. Evans. Frequencies of the defective CYP2C19 alleles responsible for the mephenytoin poor metabolizer phenotype in various Oriental, Caucasian, Saudi Arabian and American black populations. Pharamacogenetics 7:59–64 (1997).
A. K. Daly, M. Armstrong, S. C. Monkman, M. E. Idle, and J. R. Idle. Genetic and metabolic criteria for the assignment of debrisoquine 4-hydroxylation (cytochrome P450 2D6) phenotypes. Pharmacogenetics 1:33–41 (1991).
E. Evans and M. V. Relling. Concordance of P450 2D6 debrisoquine hydroxylase phenotype and genotype: inability of dextromethorphan metabolic ratio to discriminate reliably heterozygous and homozygous extensive metabolizers. Pharmacogenetics 1:143–148 (1991).
K. Nakamura, T. Yokoi, K. Inoue, N. Shimada, N. Ohashi, T. Kume, and T. Kamataki. CYP2D6 is the principal cytochrome P450 responsible for metabolism of the histamine H1 antagonist promethazine in human liver microsomes. Pharamacogenetics 6:449–457 (1996).
F. J. Gonzalez. The CYP2D subfamily. In C. Ioannides, (ed.), Cytochromes P450, metabolic and toxicological aspects, CRC Press, New York, 1996, pp. 183–211.
M. Eichelbaum, N. Spannbrucker, B. Stincke, and H. J. Dengler. Defective N-oxidation of sparteine in man: a new pharmacogenetic defect. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 16:183–187 (1979).
D. A. P. Evans, A. Mahgoub, T. P. Sloan, J. R. Idle, and R. L. Smith. A family and population study of the genetic polymorphism of debrisoquine oxidation in a white British population. J. Med. Genet. 17:102–105 (1980).
K. Nakamura, F. Goto, A. Ray, C. B. McAllister, E. Jacqz, G. R. Wilkinson, and R. A. Branch. Interethnic differences in genetic polymorphism of debrisoquine and mephenytoin hydroxylation between Japanese and Caucasian populations. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 38:402–408 (1985).
T. Ishizaki, M. Eichelbaum, Y. Horai, K. Hashimoto, K. Chiba, and H. J. Dengler. Evidence for polymorphic oxidation of sparteine in Japanese subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 23:482–485 (1987).
Y. Horai, M. Nakano, T. Ishizaki, K. Ishikawa, H. H. Zhou, B. J. Zhou, C. L. Liao, and L. M. Zhang. Metoprolol and mephenytoin oxidation polymorphisms in Far Eastern Oriental subjects: Japanese versus mainland Chinese. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 46:198–207 (1987).
D. R. Sohn, S. G. Shin, C. W. Park, M. Kusaka, K. Chiba, and T. Ishizaki. Metoprolol oxidation polymorphism in a Korean population: comparison with native Japanese and Chinese populations. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 32:504–507 (1991).
A. K. Daly. Molecular basis of polymorphic drug metabolism. J. Mol. Med. 73:539–553 (1995).
M. L. Dahl, I. Johansson, M. Porsmyr-Palmertz, M. Ingelmen-Sundberg, and F. Sjüqvist. Analysis of the CYP2D6 gene in relation to debrisoquin and desipramine hydroxylation in a Swedish population. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 51:12–17 (1992).
W. Cairns, C. A. D. Smith, A. W. McLaren, and C. R. Wolf. Characterization of the human cytochrome P4502D6 promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 271:25269–25276 (1996).
F. J. Gonzalez, F. Vilbois, J. P. Hardwick, O. McBride, D. W. Nebert, H. V. Gelboin, and U. A. Mayer. Human debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase (P450IID1): cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence and assignment of the CYP2D locus to chromosome 22. Genomics 2:174–182 (1988).
S. Kimura, M. Umeno, R. C. Skoda, U. A. Meyer, and F. J. Gonzalez. The human debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase (CYP2D) locus: sequence and identification of the polymorphic CYP2D6 gene, a related gene, and a pseudogene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 45:889–904 (1989).
A. K. Daly, J. Brockmöller, F. Broly, M. Eichelbaum, W. E. Evans, F. J. Gonzalez, J.-D. Huang, J. R. Idle, M. Ingelman-Sundberg, T. Ishizaki, E. Jacqz-Aigrain, U. A. Meyer, D. W. Nebert, V. M. Steen, C. R. Wolf, and U. M. Zanger. Nomenclature of human CYP2D6 alleles. Pharmacogenetics 6:193–201 (1996).
R. Saxena, G. L. Shaw, M. V. Relling, J. N. Frame, D. T. Moir, W. E. Evans, N. Caporaso, and B. Weiffenbach. Identification of a new variant CYP2D6 allele with a single base deletion in exon 3 and its association with the poor metabolizer phenotype. Hum. Mol. Genet. 3:923–926 (1994).
R. Tyndale, T. Aoyama, F. Broly, T. Matsunaga, T. Inaba, W. Kalow, H. V. Gelboin, U. A. Mayer, and F. J. Gonzalez. Identification of a new CYP2D6 allele lacking the codon encoding Lys-281: possible association with the poor metabolizer phenotype. Pharmacogenetics 1:26–32 (1991)
H. Yokota, S. Tamura, H. Furuya, S. Kimura, M. Watanabe, I. Kanazawa, I. Kondo, and F. J. Gonzalez. Evidence for a new variant CYP2D6 allele CYP2D6J in a Japanese population associated with lower in vitro rates of sparteine metabolism. Pharmacogenetics 3:256–263 (1993).
I. Johansson, E. Lundqvist, L. Bertilsson, M. L. Dahl, F. Sjöqvist, and M. Ingelman-Sundberg. Inherited amplification of an active gene in the cytochrome P450 2D-locus as a cause of ultrarapid metabolism of debrisoquine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90:11825–11829 (1993).
I. Johansson, M. Oscarson, Q. Y. Yue, L. Bertilsson, F. Sjöqvist, and M. Ingelman-Sundberg. Genetic analysis of the Chinese cytochrome P450 2D locus. Characterization of variant CYP2D6-genes present in subjects with diminished capacity for debrisoquine hydroxylation. Mol. Pharmacol. 46:452–459 (1994).
M. Armstrong, K. Fairbrother, J. R. Idle, and A. K. Daly. The cytochrome P450 CYP2D6 allelic variant CYP2D6J and related polymorphisms in a European population. Pharmacogenetics 4:73–81 (1994).
M.-L. Lai, S.-L. Wang, M.-D. Lai, E. T. Lin, M. Tse, and J.-D. Huang. Propranolol desposition in Chinese subjects of different CYP2D6 genotypes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 58:264–268 (1995).
Z.-Y. Hou, C.-P. Chen, W.-C. Yang, M.-D. Lai, E. T. Buchert, H.-M. Chung, L. W. Pickle, and R. L. Woosley. Determination of dextromethorphan metabolic phenotype by salivary analysis with a reference to genotype in Chinese patients receiving renal hemodialysis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 59:411–417 (1996).
C.-Y. Tseng, S.-L. Wang, M.-D. Lai, M.-L. Lai, and J.-D. Huang. Formation of morphine from codeine in Chinese subjects of different CYP2D6 genotypes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 60:177–182 (1996).
T. Yokoi, Y. Kosaka, M. Chida, K. Chiba, H. Nakamura, T. Ishizaki, M. Kinoshita, K. Sato, F. J. Gonzalez, and T. Kamataki. A new CYP2D6 allele with poor metabolizer phenotype. Pharmacogenetics 6:395–401 (1996).
P. Dayer, T. Leemann, A. Marmay, and J. Rosenthaler. Interindividual variation of β-adenoreceptor blocking drugs, plasma concentrations and effect: influence of genetic status on behavior of atenolol, bopindolol and metoprolol. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 28:149–153 (1985).
M. Eichelbaum, S. Mineshita, E. E. Ohnhaus, and C. Zekorn. The influence of enzyme induction on polymorphic sparteine oxidation. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 22:49–53 (1986).
H. Raunio, T. Syngelma, M. Pasanen, R. Juvane, P. Honkakoski, M. A. Kairaluoma, E. Sotaniemi, M. A. Lang, and O. Pelkonen. Immunochemical and catalytical studies on hepatic coumarin 7-hydroylase in man, rat, and mouse. Biochem. Pharmacol. 37:3889–3895 (1988)
J. S. Miles, A. W. McLaren, L. M. Forester, M. J. Glancey, M. A. Lang, and C. R. Wolf. Identification of the human liver cytochromes P-450 responsible for coumarin 7-hydroxylase activity. Biochem. J. 267:365–371 (1990).
T. Aoyama, S. Yamano, P. S. Guzelian, H. V. Gelboin, and F. J. Gonzalez. Five of 12 forms of vaccinia virus-expressed human cytochrome P450 metabolically activate aflatoxin B1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87:4790–4793 (1990).
C. Crespi, B. W. Penman, J. A. E. Leakey, M. P. Arlotto, A. Stark, A. Parkinson, T. Turner, D. T. Steimel, K. Rudo, R. L. Davies, and R. Langenbach. Human cytochrome P450IIA3: cDNA sequence, role of the enzyme in the metabolic activation of promutagens, comparison to nitrosamine activation by human cytochrome P450IIE1. Carcinogenesis 11:1293–1300 (1990)
C. L. Crespi, B. W. Penman, H. V. Gelboin, and F. J. Gonzalez. A tobacco smoke-derived nitrosamine, 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone, is activated by multiple human cytochrome P450s including the polymorphic cytochrome P4502D6. Carcinogenesis 12:1197–1201 (1991).
H. Yamazaki, Y. Inui, C. H. Yun, F. P. Guengerich, and T. Shimada. Cytochrome P450 2E1 and 2A6 enzymes as major catalysts for metabolic activation of N-nirtosodialkylamines and tobacco-related nitrosamines in human liver microsomes. Carcinogenesis 13:1789–1794 (1992).
S. Cholerton, M. E. Idle, A. Vas, F. J. Gonzalez, and J. R. Idle. Comparison of a novel thin-layer chromatographic-fluorescence detection method with a spectrofluorometric method for the determination of 7-hydroxycoumarin in human urine. J. Chromatogr. 575:325–330 (1992).
A. Rautio, H. Kraul, A. Kojo, E. Salmela, and O. Pelkonen. Interindividual variation of coumarin 7-hydroxylase in healthy volunteers. Pharmacogenetics 2:227–233 (1992)
M. Maurice, L. Pichard, M. Daujat, I. Fabre, H. Joyeux, J. Domergue, and P. Maurel. Effects of imidazole derivatives on cytochromes P450 form human hepatocytes in primary culture. FASEB J. 6:752–759 (1990).
T. K. H. Chang and D. J. Waxman. The CYP2A subfamily. In C. Ioannides (ed.), Cytochromes P450, metabolic and toxicological aspects, CRC Press, New York, 1996, pp. 99–134.
P. Fernadez-Salguero and F. J. Gonzalez. The CYP2A gene subfamily: species differences, regulation, catalytic activities and role in chemical carcinogenesis. Pharamacogenetics 5:S123–S128 (1995).
S. Yamano, J. Tatsuno, and F. J. Gonzalez. The CYP2A3 gene product catalyzes coumarin 7-hydroxylation in human liver microsomes. Biochemistry 29:1322–1329 (1990).
P. Fernandez-Salguero, S. M. G. Hoffman, S. Cholerton, H. Mohrenweiser, H. Raunio, A. Rautio, O. Pelkonen, J.-D. Huang, W. E. Evans, J. R. Idle, and F. J. Gonzalez. A genetic polymorphism in coumarin 7-hydroxylation: sequence of the human CYP2A genes and identification of variant CYP2A6 alleles. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 57:651–660 (1995).
K. Nunoya, T. Yokoi, K. Itoh, S. Itoh, K. Kimura, and T. Kamataki. S-Oxidation of (+)-cis-3,5-dimethyl-2-(3-pyridyl) thiazolidin-4-one hydrochloride by hepatic rat flavin-containing monooxygenase 1 expressed in yeast. Xenobiotica 25:1283–1291 (1995).
K. Nunoya, T. Yokoi, K. Kimura, T. Kodama, M. Funayama, K. Inoue, K. Nagashima, Y. Funae, N. Schimada, C. Green, and T. Kamataki. (+)-Cis-3,5-dimethyl-2-(3-pyridyl) thiazolidin-4-one hydrochloride (SM-12502) as a novel substrate for cytochrome P450 2A6 in human liver microsomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 277:768–774 (1996).
G. A. Kyerematen and E. S. Vesell. Metabolism of nicotine. Drug Metab. Rev. 23:3–41 (1991).
P. Jacob, III, N. L. Benowitz, and A. T. Shulgins. Recent studies of nicotine metabolism in humans. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 30:249–253 (1988).
S. Cholerton, A. Arpanahi, N. McCracken, C. Boustead, H. Taber, E. Johnstone, J. Leathart, A. K. Daly, and J. R. Idle. Poor metabolisers of nicotine and CYP2D6 polymorphism. Lancet 343:62–63 (1994).
N. L. Benowitz, P. Jacob, III, and D. P. L. Sachs. Deficient C-oxidation of nicotine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 57:590–594 (1995).
M. Nakajima, T. Yamamoto, K. Nunoya, T. Yokoi, K. Nagashima, K. Inoue, Y. Funae, N. Shimada, T. Kamataki, and Y. Kuroiwa. Role of human cytochrome P4502A6 in C-oxidation of nicotine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 24:1212–1217 (1996)
M. Nakajima, T. Yamamoto, K. Nunoya, T. Yokoi, K. Nagashima, K. Inoue, Y. Funae, N. Shimada, T. Kamataki, and Y. Kuroiwa. Characterization of CYP2A6 involved in 3'-hydroxylation of cotinine in human liver microsomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 277:1010–1015 (1996).
K. Nunoya, T. Yokoi, K. Kimura, K. Inoue, T. Kodama, M. Funayama, K. Nagashima, Y. Funae, C. Green, M. Kinoshita, and T. Kamataki. A new deleted allele in human cytochrome P450 2A6 gene (CYP2A6) causing poor capacity to metabolize (+)-cis-3,5-dimethyl-2-(3-pyridyl)thiazolidin-4-one hydrochroride (SM-12502) in human liver microsomes. Pharmacogenetics, in press.
D. Hoffman and S. S. Hecht. Nicotine-derived N-nitrosoamines and tobacco-related cancer: current status and future directions. Cancer Res. 45:935–944 (1985).
A. Gaedigk, M. Blum, R. Gaedigk, M. Eichelbaum, and U. A. Mayer. Deletion of the entire cytochrome P450 CYP2D6 gene as a cause of impaired drug metabolism in poor metabolizers of the debrisoquine/sparteine polymorphism. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 48:943–950 (1991)
V. M. Steen, A. Molven, N. K. Aarskog, and A.-K. Gulbrandsen. Homologous unequal cross-over involving a 2.8 kb direct repeat as a mechanism for the generation of allelic variants of the human cytochrome P450 CYP2D6 gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4:2251–2257 (1995).
D. Egans, R. O'Kennedy, E. Moran, D. Cox, E. Prosser, and R. D. Thornes. The pharmacology, metabolism, analysis, and 2 applications of coumarin and coumarin-related compounds. Drug. Metab. Rev. 22:503–529 (1990).
N. Imanishi, M. Murakami-Uchida, H. Koike, Y. Natsume, and S. Morooka. Biological effects of the new platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist (+)-cis-3,5-dimethyl-2-(3-pyridyl) thiazolidin-4-one hydrochloride. Arzneim.-Forsh./Drug Res. 44:317–322 (1994)
C.-H. Yun, T. Shimada, and F. P. Guengerich. Purification and characterization of human liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 2A6. Mol. Pharmacol. 40:679–685 (1991).
J. Maenpaa, H. Sigusch, H. Raunio, T. Syngelma, P. Vuorela, H. Vuorela, and O. Pelkonen. Differential inhibition of coumarin 7-hydroxylase activity in mouse and human liver microsomes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 45:1035–1042 (1993).
A. M. Camus, O. Geneste, P. Honkakoski, J. C. Bereziat, C. J. Henderson, C. R. Wolf, H. Bartsch, and M. A. Lang. High variability of nitrosamine metabolism among individuals: role of cytochromes P450 2A6 and 2E1 in the dealkylation of N-nitrosodimethylamine and N-nitrosodiethylamine in mice and humans. Mol. Carcinog. 7:268–275 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yokoi, T., Kamataki, T. Genetic Polymorphism of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes: New Mutations in CYP2D6 and CYP2A6 Genes in Japanese. Pharm Res 15, 517–524 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011913407147
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011913407147