Abstract
Purpose. The purpose of the study was to investigate the distribution of codeine across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in rats by micro-dialysis (MD).
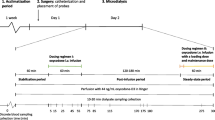
Methods. Rats were administered intravenous infusion of codeine in doses of (1) 10 mg/kg, (2) 20 mg/kg for 10 min, and (3) an exponential infusion for 2 h aiming at a plasma concentration of 2500 ng/ml, in a crossover design (n = 6). Microdialysis was used to determine codeine unbound concentrations in blood and brain extracellular fluid (ECF). Total brain tissue and plasma concentrations were also determined. Nalorphine was used as a calibrator for measurement of in vivo recovery.
Results. Relative recovery and retrodialysis loss of codeine and nalorphine were similar both in vitro and in vivo. Codeine was rapidly transported into the brain ECF with identical influx and efflux clearance across the BBB. The AUC ratios of brain to blood were 0.99 ± 0.25 and 0.95 ± 0.16 for Dose 1 and 2, respectively. The Css ratio of brain to blood was 1.06 ± 0.12 for the exponential infusion. The half-lives were 25 ± 4 min, 22 ± 2 min in blood and 27 ± 5 min, 25 ± 5 min in brain for Dose 1 and Dose 2, respectively. Total brain tissue concentrations were 3.6 ± 1.2-fold higher than the unbound concentrations in brain. Codeine was demethylated to morphine with an unbound AUCbIood,morphine/AUCblood,codeine ratio of 7.7 ± 5.1% in blood. No morphine was detected in brain MD, but total concentrations were possible to measure.
Conclusions. Codeine rapidly reached a distributional equilibrium with equal unbound concentrations in blood and brain. The brain transport of codeine did not show any dose-dependency.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
W. H. Oldendorf. Lipid solubility and drug penetration of the blood brain barrier. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 147:813–816 (1974).
Z. R. Chen, A. A. Somogyi, G. Reynolds, and F. Bochner. Disposition and metabolism of codeine after single and chronic doses in one poor and seven extensive metabolisers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 31:381–390 (1991).
M. Hammarlund-Udenaes, L. K. Paalzow, and E. C. M. de Lange. Drug equilibration across the blood-brain barrier — pharmacokinetic considerations based on the microdialysis methods. Pharm. Res. 14:128–134 (1997).
W. H. Oldendorf, S. Hyman, L. Braun, and S. Z. Oldendorf. Blood-brain barrier: penetration of morphine, codeine, heroin, and methadone after carotid injection. Science 178:984–986 (1972).
M. W. B. Bradbury, C. S. Patlak, and W. H. Oldendorf. Analysis of brain uptake and loss of radiotracers after intracarotid injection. Am. J. Physiol. 229:1110–1115 (1975).
W. F. Elmquist and R. J. Sawchuk. Application of microdialysis in pharmacokinetic studies. Pharm. Res. 14:267–288 (1997).
S. Wong, Y. Wang, and R. J. Sawchuk. Analytical of zidovudine distribution to specific regions in rabbit brain using microdialysis. Pharm. Res. 9:332–338 (1992).
H. Yang, Q. Wang, and W. F. Elmquist. Fluconazole distribution to the brain: a crossover study in freely-moving rats using in vivo microdialysis. Pharm. Res. 13:1570–1575 (1996).
W. H. Oldendorf. The blood-brain barrier. Exp. Eye Res. Suppl.:177–190(1977).
T. Johannesson and L. A. Woods. Analgesic action and brain and plasma levels of morphine and codeine in morphine tolerant, codeine tolerant and non-tolerant rats. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 21:381–396 (1964).
Z. R. Chen, R. J. Irvine, F. Bochner, and A. A. Somogyi. Morphine formation from codeine in rat brain: a possible mechanism of codeine analgesia. Life Sci. 46:1067–1074 (1990).
J. T. Scrafani and C. C. Hug. Active uptake of dihydromorphine and other narcotic analgesics by cerebral cortical slices. Biochem. Pharmacol. 17:1557–1566 (1968).
S. L. Shafer, L. C. Siegel, J. E. Cooke, and J. C. Scott. Testing computer-controlled infusion pumps by simulation. Anesthesiology. 68:261–266 (1988).
S. L. Sharer, J. R. Varvel, N. Aziz, and J. C. Scott. Pharmacokinetics of fentanyl administered by computer-controlled infusion pump. Anesthesiology. 73:1091–1102 (1990).
J. Shah and W. D. Mason. Pharmacokinetics of codeine after parenteral and oral dosing in the rat. Drug Metab. Dispos. 18:670–673 (1990).
H. Benveniste, A. J. Hansen, and N. S. Ottosen. Determination of brain interstitial concentrations by microdialysis. J. Neurochem. 52:1741–1750 (1989).
H. Benveniste. Brain microdialysis. J. Neurochem. 52:1667–1679 (1989).
Y. Wang and D. F. Welty. The simultaneous estimation of the influx and efflux blood-brain barrier permeabilities of gabapentin using a microdialysis pharmacokinetic approach. Pharm. Res. 13:398–403 (1996).
W. L. Chiou. The phenomenon and rationale of marked dependence of drug concentration on blood sampling site. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 17:175–199 (1989).
W. L. Chiou. The significance of marked “universal” dependence of drug concentration on blood sampling site in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, in D. Z. D'Argenio. Advanced methods of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic systems analysis, Plenum Press, New York, 1991, pp. 37–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, R., Hammarlund-Udenaes, M. Blood-Brain Barrier Equilibration of Codeine in Rats Studied with Microdialysis. Pharm Res 15, 570–575 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011929910782
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011929910782