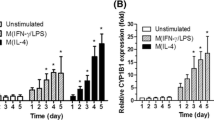
Abstract
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) belongs to the bHLH/PAS transcription factor family and is activated by various polycyclic or halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons, e.g., 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), 3-methylcholanthrene (3MC). In the present study, we showed that in U937 cells and human macrophages AhR, with its partner cofactor Arnt, is expressed and CYP1A1 mRNA expression is induced in the presence of AhR ligand 3MC. Moreover, we showed that AhR, associating with Arnt, binds to target DNA sequences and activates transcription. Since part of AhR is activated into DNA binding species in the absence of exogenous ligand and competitive AhR antagonist α-naphthoflavone inhibits this activation process with reducing CYP1A1 mRNA expression levels, the presence of endogenous ligand is indicated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stephen TC: Control of cell lineage-specific development and transcription by bHLH-PAS proteins. Genes Dev 12: 607–620, 1998
Gudas JM, Karenlampi SO, Hankinson O: Intracellular location of the Ah receptor. J Cell Physiol 128: 441–448, 1986
Whilhelmsson A, Cuthill S, Denis M, Wikström AC, Gustafsson JÅ, Poellinger L: The specific DNA binding activity of the dioxin receptor is modulated by the 90 kD heat shock protein. EMBO J 9: 69–76, 1990
Ma Q, Whitlock JP Jr: A novel cytoplasmic protein that interacts with the Ah receptor, contains tetratricopeptide repeat motifs, and augments the transcriptional response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem 272: 8878–8884, 1997
Carver LA, Bradfield CA: Ligand-dependent interaction of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor with a novel immunophilin homolog in vivo. J Biol Chem 272: 11452–11456, 1997
Reyes H, Reiz-Porszasz S, Hankinsson O: Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor. Science 256: 1193–1195, 1992
Whitelaw M, Pongratz I, Wilhelmsson A, Gustafsson JÅ, Poellinger L: Ligand-dependent recruitment of the Arnt coregulator determines DNA recognition by the dioxin receptor. Mol Cell Biol 13: 2504–2514, 1993
Fujisawa-Sehara A, Sogawa K, Yamane M, Fujii-Kuriyama Y: Characterization of xenobiotic responsive elements upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome p-450c gene: Similarity to glucocorticoid regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 4179–4191, 1987
Jones PBC, Galeazzi DR, Fisher JM, Whitlock JP Jr: Control of cytochrome P1-450 gene expression by dioxin. Science 227: 1499–1502, 1985
Jones PBC, Durrin LK, Galeazzi DR, Whitlock JP Jr: Control of cytochrome P1-450 gene expression: Analysis of a dioxin-responsive enhancer system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2802–2806, 1986
Hines RN, Mathis JM, Jacob CS: Identification of multiple regulatory elements on the human cytochrome p4501A1 gene. Carcinogenesis 9: 1599–1605, 1988
Kobayashi A, Numayama-Tsuruta K, Sogawa K, Fujii-Kuriyama Y: CBP/p300 functions as a possible transcriptional coactivator of Ah receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt). J Biochem 122: 703–710, 1997
Mimura J, Ema M, Sogawa K, Fujii-Kuriyama Y: Identification of a novel mechanism of regulation of Ah (dioxin) receptor function. Genes Dev 13: 20–25, 1999
Kociba RJ, Keyes DG, Beger JE, Carreon RM, Wade CE, Dittenber DA, Kalnins RP, Frauson LE, Park CL, Barnard SD, Hummel RA, Humiston CG: Results of a two-year chronic toxicity and oncogenicity study of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 46: 279–303, 1978
Astroff B, Safe S: 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin as an antiestrogen: Effect on rat uterine peroxidase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 39: 485–488, 1990
Romkes M, Safe S: Comparative activities of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and progesterone as antiestrogens in the female rat uterus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 92: 368–380, 1990
Spink DC, Lincoln DW, Dickerman HW, Gierthy JF: 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin causes an extensive alternation of 17β-estradiol metabolism in MCF-7 breast tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 6917–6921, 1990
Biegel L, Safe S: Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on cell growth and the secretion of the estrogen-induced 34-, 52-and 160-kDa proteins in human breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 37: 725–732, 1990
Harris M, Zacharewski T, Safe S: Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzop-dioxin and related compounds on the occupied nuclear estrogen receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 50: 3579–3584, 1990
Wang X, Porter W, Krishnan V, Narasimhan TR, Safe S: Mechanism of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-mediated decrease of the nuclear estrogen receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 96: 159–166, 1993
Kharat I, Saatcioglu F: Antiestrogenic effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin are mediated by direct transcriptional interference with the liganded estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem 271: 10533–10537, 1996
Gillesby BE, Stanostefano M, Porter W, Safe S, Wu ZF, Zacharewski TR: Identification of a motif within the 5′ regulatory region of pS2 which is responsible for AP-1 binding and TCDD-mediated suppression. Biochemistry 36: 6080–6089, 1997
Mayani A, Barel S, Soback S, Almagor M: Dioxin concentrations in women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod 12: 373–375, 1997
Igarashi T, Osuga Y, Tsutsumi O, Momoeda M, Ando K, Matsumi H, Takai Y, Okagaki R, Hiroi H, Fujiwara T, Yano T, Taketani Y: Expression of Ah receptor and dioxin-related genes in human uterine endometrium in women with or without endometriosis. Endocrine J 46: 765–772, 1999
Yang JH: Expression of dioxin-responsive genes in human endometrial cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257: 259–263, 1999
Jana NR, Sarkar S, Ishizuka M, Yonemoto J, Tohyama C, Sone H: Cross-talk between 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and testosterone signal transduction pathways in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 256: 462–468, 1999
Chen YH, Riby J, Srivastava P, Bartholomew J, Denison M, Bjeldanes L: Regulation of CYP1A1 by indolo[3, 2-b]carbazole in murine hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 270: 22548–22555, 1995
Rannug U, Rannug A, Sjöberg U, Li H, Westerholm R, Bergman J: Structure elucidation of two tryptophan-derived, high affinity Ah receptor ligands. Chem Biol 2: 841–845, 1995
Gradelet S, Astorg P, Pineau T, Canivenc MC, Siess MH, Leclerc J, Lesca P: Ah receptor-dependent CYP1A1 induction by two carotenoids, canthaxanthin and β-apo-8′-carotenal, with no affinity for the TCDD binding site. Biochem Pharmacol 54: 307–315, 1997
Schrenk D, Riebniger D, Till M, Vetter S, Fiedler HP: Tryptanthrins: A novel class of agonists of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Biochem Pharmacol 54: 165–171, 1997
Jeong HG, Lee SS, Kim HK, Yang KH: Murine cyp1a-1 induction in mouse hepatoma Hepa-1c1c7 cells by myristicin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 233: 619–622, 1997
Washburn BS, Rein KS, Baden DG, Walsh PJ, Hinton DE, Tullis K, Denison MS: Brevetoxin-6 (PbTx-6), a nonaromatic marine neurotoxin, is a ligand of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys 343: 149–156, 1997
Ciolino HP, Daschner PJ, Yeh GC: Dietary flavonols quercetin and kaempferol are ligands of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor that affect CYP1A1 transcription differentially. Biochem J 340: 715–722, 1999
Casper RF, Quesne M, Rogers IM, Shirota T, Jolivet A, Milgrom E, Savouret JF: Resveratrol has antagonist activity on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor: Implications for prevention of dioxin toxicity. Mol Pharmacol 56: 784–790, 1999
Ciolino HP, Yeh GC: The flavonoid galangin is an inhibitor of CYP1A1 activity and an agonist/antagonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Br J Cancer 79: 1340–1346, 1999
Crawford RB, Holsapple MP, Kaminski NE: Leukocyte activation induces aryl hydrocarbon receptor up-regulation, DNA binding, and increased cyp1A1 expression in the absence of exogenous ligand. Mol Pharmacol 52: 921–927, 1997
Chang CY, Puga A: Constitutive activation of the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor. Mol Cell Biol 18: 525–535, 1998
Sinal CJ, Bend JR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent induction of cyp1a1 by bilirubin in mouse hepatoma Hepa 1c1c7 cells. Mol Pharmacol 52: 590–599, 1997
Phelan D, Winter GM, Rogers WJ, Lam JC, Denison MS: Activation of the Ah receptor signal transduction pathway by bilirubin and biliverdin. Arch Biochem Biophys 357: 155–163, 1998
Fernandez-Salguero P, Pineau T, Hilbert DM, McPhail T, Lee SST, Kimura S, Nebert DW, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ: Immune system impairment and hepatic fibrosis in mice lacking the dioxin-binding Ah receptor. Science 268: 722–726, 1995
Stone R: Dioxin receptor knock out. Science 268: 638–639, 1995
McDonnell WM, Chensue SW, Askari FK, Moseley RH: Hepatic fibrosis in Ahr-/- mice. Science 271: 223–224, 1996
Fernandez-Salguero PM, Ward JM, Sundberg JP, Gonzalez FJ: Lesions of aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice. Vet Pathol 34: 605–614, 1997
Hayashi S-I, Okabe-Kado J, Honma Y, Kawajiri K: Expression of Ah receptor (TCDD receptor) during monocytic differentiation. Carcinogenesis 16: 1403–1409, 1995
Unanue ER, Allen PM: The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science 236: 551–556, 1987
Tanaka H, Makino Y, Hirano F, Okamoto K, Komura K, Sato Y, Makino I: Ligand-independent activation of the glucocorticoid receptor by ursodeoxycholic acid. J Immunol 156: 1601–1608, 1996
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N: Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159, 1987
Hayashi S-I, Watanabe J, Nakachi K, Eguchi H, Gotoh O, Kawajiri K: Interindividual difference in expression of human Ah receptor and related P450 genes. Carcinogenesis 15: 801–806, 1994
Hirano F, Chung M, Tanaka H, Maruyama N, Makino I, Moore DD, Scheidereit C: Alternative splicing variants of IκBβ signal responsiveness in human cells. Mol Cell Biol 18: 2596–2607, 1998
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685, 1970
Hapgood J, Cuthill S, Denis M, Poellinger L, Gustafsson JÅ: Specific protein-DNA interactions at a xenobiotic-responsive element: Copurification of dioxin receptor and DNA-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 60–64, 1989
Gradin K, Whilhelmsson A, Poellinger L, Berghard A: Nonresponsiveness of normal human fibroblasts to dioxin correlates with the presence of a constitutive xenobiotic response element-binding factor. J Biol Chem 268: 4061–4068, 1993
Makino Y, Okamoto K, Yoshikawa N, Aoshima M, Hirota K, Yodoi J, Umezono K, Makino I, Tanaka H: Thioredoxin: A redox-regulating cellular cofactor for glucocorticoid hormone action. J Clin Invest 98: 2469–2477, 1996
Davarinos AN, Pollenz RS: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor imported into the nucleus following ligand binding is rapidly degraded via the cytoplasmic proteasome following nuclear export. J Biol Chem 274: 28708–28715, 1999
Ma Q, Baldwin KT: 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced degradation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Role of the transcription activation and DNA binding of AhR. J Biol Chem 275: 8432–8438, 2000
Santostefano M, Merchant M, Arellano L, Morrison V, Denison MS, Safe S: α-Naphthoflavone-induced CYP1A1 gene expression and cytosolic aryl hydrocarbon receptor transformation. Mol Pharmacol 43: 200–206, 1993
Wilhelmsson A, Whitelaw ML, Gustafsson JÅ, Poellinger L: Agonistic and antagonistic effects of α-naphthoflavone on dioxin receptor function. J Biol Chem 269: 19028–19033, 1994
Henry EC, Kende AS, Rucci G, Totleben MJ, Willey JJ, Dertinger SD, Pollenz RS, Jones JP, Gasiewicz TA: Flavone antagonists bind competitively with 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor but inhibit nuclear uptake and transformation. Mol Pharmacol 55: 716–725, 1999
Wang F, Wang W, Safe S: Regulation of constitutive gene expression through interactions of Sp1 protein with the nuclear aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex. Biochemistry 38: 11490–11500, 1999
Tian Y, Ke S, Denison MS, Robson AB, Gallo MA: Ah receptor and NF-kappaB interactions, a potential mechanism for dioxin toxicity. J Biol Chem 274: 510–515, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komura, K., Hayashi, Si., Makino, I. et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/dioxin receptor in human monocytes and macrophages. Mol Cell Biochem 226, 107–117 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012762519424
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012762519424