Abstract
Purpose. We previously demonstrated the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, pravastatin, is actively taken up into isolated rat hepatocytes through multispecific organic anion transporters. The present study examined whether a newly cloned organic anion transporting polypeptide (oatp2) transports pravastatin.
Methods. We investigated functional expression of oatp2 in Xenopus laevis oocytes, to examine [14C] pravastatin uptake.
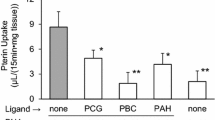
Results. [14C] Pravastatin (30 μM) uptake into oatp2 cRNA-injected oocytes was 40 times higher than that of water-injected control oocytes. The oatp2-mediated pravastatin uptake was Na+-independent and saturable. The Michaelis-Menten constant was 37.5 ± 9.9 μM, a level comparable to that obtained in isolated rat hepatocytes in our previous study. As is the case with rat hepatocytes, the uptake of pravastatin (30 μM) was inhibited by 300 μM concentrations of taurocholate, cholate, bromosulfophthalein, estradiol-17β-glucuronide, and simvastatin acid, but not by para-aminohippurate. On the other hand, [14C] simvastatin acid (30 μM) uptake of oatp2 cRNA-injected oocytes was not significantly different from that of water-injected oocytes.
Conclusions. The cloned oatp2 was identified as the transporter responsible for the active hepatocellular pravastatin uptake.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. M. Grundy. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors for treatment of hyper-cholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 319:324–332 (1988).
D. R. Illingworth. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Lipidology 2:244–34 (1991).
W. A. Scott, E. M. Mahoney, and S. T. Mosley. Mechanism of action and differential pharmacology of pravastatin, a hydrophilic and selective HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. In J. C. LaRosa (eds.), New Advances in the Control of Lipid Metabolism: Focus on Pravastatin, Royal Society of Medicine, 1989, pp. 1–8.
Y. Tsujita, M. Kuroda, Y. Shimada, K. Tanzawa, M. Arai, I. Kaneko, M. Tanaka, H. Masuda, C. Tamura, Y. Watanabe, and S. Fujii. CS-514, a competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: tissue-selective inhibition of sterol synthesis and hypolipidemic effect on various animal species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1045:115–120 (1990).
T. Koga, Y. Shimada, M. Kuroda, Y. Tsujita, K. Hasegawa, and M. Yamazaki. Tissue selective inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in vivo by pravastatin sodium, a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 877: 50–60 (1986).
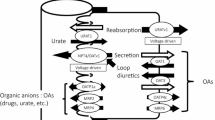
P. J. Meier. Transport polarity of hepatocytes. Semin. Liver Dis. 8:649–661 (1988).
T. Komai, E. Shigehara, T. Tokui, T. Koga, M. Ishigami, C. Kuroiwa, and S. Horiuchi. Carrier-mediated uptake of pravastatin by rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Biochem. Pharmacol. 43:667–670 (1992).
M. Yamazaki, H. Suzuki, M. Hanano, T. Tokui, T. Komai, and Y. Sugiyama. Na+-independent multispecific anion transporter mediates active transport of pravastatin into rat liver. Am. J. Physiol. 264:G36–G44 (1993).
M. Yamazaki, T. Tokui, M. Ishigami, and Y. Sugiyama. Tissue-selective uptake of pravastatin in rats: contribution of a specific carrier-mediated uptake system. Biopharm. Drug Disposit. 17:990.1–15 (1996).
M. Ishigami, T. Tokui, T. Komai, K. Tsukahara, M. Yamazaki, and Y. Sugiyama. Evaluation of the uptake of pravastatin by perfused rat liver and primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Pharm. Res. 12:1741–1745 (1995).
M. Yamazaki, H. Suzuki, and Y. Sugiyama. Recent advances in carrier-mediated hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of xenobiotics. Pharm. Res. 13:497–513 (1996).
E. Jacquemin, B. Hagenbuch, B. Stieger, A. W. Wolkoff, and P. J. Meier. Expression cloning of a rat liver Na+-independent organic anion transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:133–137 (1994).
A. J. Bergwerk, X. Shi, A. C. Ford, N. Kanai, E. Jacquemin, R. D. Burk, S. Bai, P. M. Novikoff, B. Stieger, P. J. Meier, V. L. Schuster, and A. W. Wolkoff. Immunologic distribution of an organic anion transport protein in rat liver and kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 271:G231–G238 (1996).
X. Bossuyt, M. Muller, B. Hagenbuch, and P. J. Meier. Polyspecific drug and steroid clearance by an organic anion transporter of mammalian liver. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 276:891–896 (1996).
U. Eckhardt, J. A. Horz, E. Petzinger, W. Stuber, M. Reers, G. Dickneite, H. Daniel, M. Wagener, B. Hagenbuch, B. Stieger, and P. J. Meier. The peptide-based thrombin inhibitor CRC 220 is a new substrate of basolateral rat liver organic anion transporting polypeptide. Hepatology 24:380–384 (1996).
H. Kouzuki, H. Suzuki, K. Ito, R. Ohashi, and Y. Sugiyama. Contribution of organic anion transporting polypeptide to the uptake of its possible substrates into rat hepatocytes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. in press.
T. Abe, M. Kakyo, H. Sakagami, T. Tokui, T. Nishio, M. Tanemoto, H. Nomura, S. C. Hebert, S. Matsuno, H. Kondo, and H. Yawo. Molecular characterization and tissue distribution of a new organic anion transporter subtype (oatp3) that transports thyroid hormones and taurocholate, and comparison with oatp2. J. Biol. Chem. 273:22395–22401 (1998).
B. Noe, B. Hagenbuch, B. Stieger, and P. J. Meier. Isolation of a multispecific organic anion and cardiac glycoside transporter from rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94:10346–10350 (1997).
M. Kakyo, H. Sakagami, T. Nishio, D. Nakai, R. Nakagomi, T. Tokui, T. Naitoh, S. Matsuno, T. Abe, and H. Yawo. Immunohistochemical distribution and functional characterization of an organic anion transporting polypeptide 2 (oatp2). FEBS Letter (in press).
A. Goldin. Maintenance of Xenopus laevis and oocyte injection. Methods in Enzymology 207:266–279 (1992).
E. R. Liman, J. Tytgat, and P. Hess. Subunit stoichiometry of a mammalian K+ channel determined by construction of multimeric cDNAs. Neuron 9:861–871 (1992).
T. Sekine, N. Watanabe, M. Hosoyamada, Y. Kanai, and H. Endou. Expression cloning and characterization of a novel multispecific organic anion transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 272:18526–18529 (1997).
T. Komai, K. Kawai, T. Tokui, Y. Tokui, C. Kuroiwa, E. Shigehara, and M. Tanaka. Disposition and metabolism of pravastatin sodium in rats, dogs and monkeys. Eur. J. Met. Pharmacokin. 17:103–113 (1992).
I. Tamai, H. Takanaga, H. Maeda, T. Ogihara, M. Yoneda, and A. Tsuji. Proton-cotransport of pravastatin across intestinal brush-border membrane. Pharm. Res. 12:1727–1732 (1995).
M. Yamazaki, S. Akiyama, K. Ni'inuma, R. Nishigaki, and Y. Sugiyama. Biliary excretion of pravastatin in rats: contribution of the excretion pathway mediated by canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter (cMOAT). Drug Metab. Disposit. 25:1123–1129 (1997).
K. Zieglar and W. Stunkel. Tissue-selective action of pravastatin due to hepatocellular uptake via a sodium-independent bile acid transporter. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1139:203–209 (1992).
A. Saheki, T. Terasaki, I. Tamai, and A. Tsuji. In vivo and in vitro blood-brain barrier transport of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors. Pharm. Res. 11:305–311 (1994).
L. Li, T. K. Lee, P. J. Meier, and N. Ballatori. Identification of glutathione as a driving force and leukotriene C4 as a substrate for oatp1, the hepatic sinusoidal organic solute transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 273:16184–16191 (1998).
A. K. van Vliet, G. C. F. van Thiel, R. H. Huisman, H. Moshage, S. H. Yap, and L. H. Cohen. Different effects of 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on sterol synthesis in various human cell types. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1254:105–111 (1995).
G. A. Kullak-Ublick, B. Hagenbuch, B. Stieger, A. W. Wolkoff, and P. J. Meier. Functional characterization of the basolateral rat liver organic anion transporting polypeptide. Hepatol. 20:411–416 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokui, T., Nakai, D., Nakagomi, R. et al. Pravastatin, an HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor, Is Transported by Rat Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide, oatp2. Pharm Res 16, 904–908 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018838405987
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018838405987