Abstract
Purpose. To further characterize cytochrome P450 (CYP) and P-glyco-protein (Pgp) expression in monolayers of the Caco-2 cell clone TC7, a cell culture model of the human intestinal epithelium. To study the interplay between CYP3A and Pgp as barriers to intestinal drug absorption in TC7 cells using terfenadine and its metabolites as substrates.
Methods. mRNA expression of eight CYPs and Pgp was investigated in TC7 and parental Caco-2 (Caco-2p) cell monolayers using RT-PCR. The CYP3A kinetics was determined in microsomes from both cell lines. The transport, metabolism and efflux of terfenadine and its metabolites were investigated in TC7 monolayers.
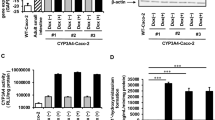
Results. Both TC7 and Caco-2p cells expressed mRNA for Pgp and several important CYPs. However, mRNA for CYP3A4 was detectable only from TC7 cells. The relative affinity of CYP3A for terfenadine metabolism in the two cell lines was comparable, but the maximum reaction rate in the TC7 cells was 8-fold higher. The rate of transport of terfenadine and its metabolites hydroxy-terfenadine (HO-T) and azacyclonol across TC7 monolayers was 7.1-, 3.5- and 2.1-fold higher, respectively, in the basolateral to apical direction than it was in the apical to basolateral (AP-BL) direction. Inhibition studies indicated that the efflux was mediated by Pgp. Ketoconazole increased the AP-BL transport terfenadine dramatically by inhibiting both terfenadine metabolism and Pgp efflux.
Conclusions. Cell culture models such as TC7 provide qualitative information on drug interactions involving intestinal CYP3A and Pgp.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
L. S. Kaminsky, and M. J. Fasco. Small intestinal cytochrome P450. Toxicology 21:407-422 (1992).
A. P. Li, D. L. Kaminski, and A. Rasmussen. Substrates of human hepatic cytochrome P450 3A4. Toxicology 104:1-8 (1995).
W. Chi-Yuan, L. Z. Benet, M. F. Hebert, S. K. Gupta, M. Rowland, D. Y. Gomez, and V. J. Wacher. Differentiation of absorption and first-pass gut and hepatic metabolism in humans: Studies with cyclosporin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 58:492-497 (1995).
K. E. Thummel, D. O'Shea, M. F. Paine, D. D. Shen, K. L. Kunze, J. D. Perkins, and G. R. Wilkinson. Oral first-pass elimination of midazolam involves both gastrointestinal and hepatic CYP3A-mediated metabolism. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 59:491-502 (1996).
V. J. Wacher, C.-Y. Wu, and L. Z. Benet. Overlapping substrate specificities and tissue distribution of cytochrome P450 3A and P-glycoprotein: Implication for drug delivery and activity in cancer chemotherapy. Carcinogenesis 13:129-134 (1995).
A. H. Schinkel, U. Mayer, E. Wagenaar, C. A. Mol, L. van Deemeter, J. J. Smit, M. A. van der Valk, A. C. Voordouw, H. Spits, O. van Tellingen, J. M. Zijlmans, W. E. Fibbe, and P. Borst. Normal viability and altered pharmaceutics in mice lacking mdrl-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins. Med. Sci. 94:4028-4033 (1997).
A. Sparreboom, J. van Asperen, U. Mayer, A. H. Schinkel, J. W. Smit, D. K. Meijer, P. Borst, W. J. Nooijen, J. H. Beijnen, and O. van Tellingen. Limited oral bioavailability and active epithelial excretion of paclitaxel (Taxol) caused by P-glycoprotein in the intestine. Pharmacology 94:2031-2035 (1997).
R. B. Kim, M. F. Fromm, C. Wandel, B. Leake, A. J. Wood, D. M. Roden, and G. R. Wilkinson. The drug transporter P-glycoprotein limits oral absorption and brain entry of HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 101:289-294 (1998).
K. S. Lown, R. R. Mayo, A. B. Leichtman, H-L. Hsiao, K. Turgeon, P. Schmiedlin-Ren, M. B. Brown, W. Guo, S. J. Rossi, L. Z. Benet, and P. B. Watkins. Role of intestinal P-glycoprotein (mdrl) in interpatient variation in the oral bioavailability of cyclosporine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 62:248-260 (1997).
R. Sandstrom, A. Karlsson, L. Knutson, and H. Lennernäs. Jejunal absorption and metabolism of R/S-verapamil in humans. Pharm Res. 15:856-862 (1998).
X. Boulenc, M. Bourrie, I. Fabre, C. Roque, H. Joyeux, Y. Berger, and G. J. Fabre. Regulation of cytochrome P450IA1 expression in a human intestinal cell line, Caco-2. J. Pharmacol Exp. Ther. 263:1471-1478 (1992).
P. Schmiedlin-Ren, K. E. Thummel, J. M. Fisher, M. F. Paine, K. S. Lown, and P. B. Watkins. Expression of enzymatically active CYP3A4 by Caco-2 cells grown on extracellular matrix-coated permeable supports in the presence of 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Mol. Pharmacol. 51:741-754 (1997).
V. Carriere, T. Lesuffleur, A. Barbat, M. Rousset, E. Dussaulx, P. Costet, I. de Waziers, P. Beaune, and A. Zweibaum. Expression of cytochrome P450 3A in HT29-MTX cells and Caco-2 Clone TC7. FEBS Lett. 355:247-250 (1994).
L. Gervot, V. Carriere, P. Costet, P-H. Cugnenc, A. Berger, P. H. Beaune, and I. de Waziers, CYP3A5 is major cytochrome P450 3A expressed in human colon and colonic cell lines. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2:381-388 (1996).
S. D. Raeissi, Z. Guo G. L. Dobson P. Artursson, and I. J. Hidalgo. Comparison of CYP3A activities in a subclone of Caco-2 cells (TC7) and human intestine. Pharm. Res. 14:1019-1025 (1997).
D. A. Garteiz, R. H. Hook, B. J. Walker, and R. A. Okerholm. Pharmacokinetics and biotransformation studies of terfenadine in man. Arzneimittelforschung 32:1185-1190 (1982).
K. T. Kirvisto, P. J. Neuronen, and U. Klotz. Inhibition of terfenadine metabolism: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic consequences. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 27:1-5 (1994).
I. de Waziers, P. H. Cugnenc, C. S. Yang, J.-P. Leroux and P. H. Beaune. Cytochrome P450 isoenzymes, epoxide hydrolase and glutathione transferases in rat and human hepatic and extrahepatic tissues. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 253:387-394 (1990).
M. G. Mercurio, S. J. Shiff, R. A. Galbraith, and S. Sassa. Expression of cytochrome P450 mRNAs in the colon and the rectum in normal human subjects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 210:350-355 (1995).
J. Kolars, K. S. Lown, P. Schmiedlin-Ren, M. Ghosh, C. Fang, S. A. Wrighton, R. M. Merion, and P. B. Watkins. CYP3A gene expression in human gut epithelium. Pharmacogenetics 4:247-259 (1994).
M. H. Gault, L. L. Longerich J. C. K. Lou, P. T. H. Ko, A. Fine, S. C. Vasdev, and M. A. Dawe. Digoxin biotransformation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 35:74-82. (1984).
B. Lacarelle, R. Rahmani, G. de Sousa, A. Durand, M. Placidi, and J. P. Cano. Metabolism of digoxin, digoxigenin digitoxosides and digoxigenin in human hepatocytes and liver microsomes. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 5:567-582 (1991).
H. Engman, H. Lennerns, and P. Artursson. Expression of cytochrome P450 3A4 and MDR1 in normal and transformed human intestinal epithelial cell lines. Pharm. Res. (supplement) 15:S6 (1998).
A. Zweibaum, H. P. Hauri, E. Sterchi, I. Chantret, K. Haffen, J. Bamat, and B. Sordat. Immunohistological evidence obtained with monoclonal antibodies, of small intestinal brush border hydrolases in human colon cancers and foetal colons. Int. J. Cancer 35:591-598 (1984).
W. N. Hait, J. F. Gesmonde, J. R. Murren, J. Yang, H. Chen, and M. Reiss. A new drug for restoring sensitivity to multidrug resistant cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 45:401-406 (1995).
A. Seelig. A general pattern for substrate recognition by P-glycoprotein. Eur. J. Biochem. 251:252-261 (1998).
J. Karlsson, S-M. Kuo, J. Ziemniak, and P. Artursson. Transport of celiprolol across human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells: mediation of secretion by multiple transporters including P-glycoprotein. Br. J. Pharmacol. 110:1009-1016 (1993).
R. Sandstrom. Intestinal permeability and presystemic metabolism of R/S-verapamil and fluvastatin. Thesis 185, Uppsala University Library (1998).
K. S. Lown, R. R. Mayo, A. B. Leichtman, H. L. Hsiao, D. K. Turgeon, R. P. Schmiedlin-Ren, M. B. Brown, W. Guo, S. J. Rossi, L. Z. Benet, and P. B. Watkins. Role of intestinal P-glycoprotein (mdrl) in interpatient variation in the oral bioavailability of cyclosporine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 62:248-260 (1997).
T. J. Raub, C. L. Barsuhn, L. R. Williams, D. E. Decker, G. A. Swada, and N. F. Ho. Use of a biophysical-kinetic model to understand the roles of protein binding and membrane partitioning on passive diffusion of highly lipophilic molecules across cellular barriers. J. Drug Target. 1:269-286 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raeissi, S.D., Hidalgo, I.J., Segura-Aguilar, J. et al. Interplay Between CYP3A-Mediated Metabolism and Polarized Efflux of Terfenadine and Its Metabolites in Intestinal Epithelial Caco-2 (TC7) Cell Monolayers. Pharm Res 16, 625–632 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018851919674
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018851919674