Abstract
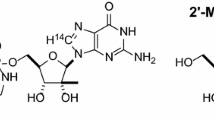
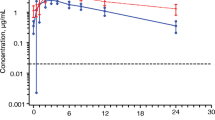
The bioavailability of PMEA from three oral formulations of the prodrug bis(POM)-PMEA has been evaluated in fasted male cynomolgus monkeys. The formulations examined included a hydroxy-propyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPBCD) complex, a PEG based cosolvent solution, and an aqueous suspension. Oral formulations containing 3H-bis(POM)-PMEA were compared to intravenous 3H-PMEA at 10.9 mg-eq/kg in a crossover study in four monkeys, with a 7 day washout period. No intact bis(POM)-PMEA or monoester were detected in plasma. Bioavailabilities of PMEA from the prodrug were 24.7 ± 6.5%, 27.3 ± 12.3% and 22.2 ± 15.6% for the HPBCD complex, PEG solution and aqueous suspension, respectively. The oral bioavailability of PMEA from bis(POM)-PMEA was not limited by dissolution rate of the prodrug. Data for the PEG cosolvent solution and suspension indicate that the prodrug could potentially be formulated as a soft gelatin capsule or a tablet.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Balzarini, L. Naesens, P. Herdewijn, I. Rosenberg, A. Holy, R. Pauwels, M. Baba, D. G. Johns and E. De Clercq. Marked in vivo antiretrovirus activity of 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine, a selective anti-human immunodeficiency virus agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86:332–336 (1989).
M. R. Blum, S. H. T. Liao, S. S. Good and P. de Miranda. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of zidovudine in humans. Am. J. Med. 85(Suppl. 2A):189–194 (1988).
J. Balzarini, L. Naesens, J. Slachmuylders, H. Niphius, I. Rosenberg, A. Holy, H. Schellekens and E. De Clercq. Potent anti-simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) activity and pharmacokinetics of 9-(2-phosphonyl-methoxyethyl)adenine (PMEA) in rhesus monkeys. In H. Schellekens, and M. C. Horzinek (eds.), Animal Models in AIDS, Elsevier Science Publications, Amsterdam, 1990, pp. 131–138.
J. Balzarini, L. Naesens, J. Slachmuylders, H. Niphius, I. Rosenberg, A. Holy, H. Schellenkens and E. De Clercq. 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine (PMEA) effectively inhibits retrovirus replication in vitro and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection in rhesus monkeys, AIDS 5:21–28 (1991).
J. E. Starrett, M. M. Mansuri, J. C. Martin, D. R. Tortolani and J. J. Bronson. April 1992. European Patent 481,214,A1.
K. C. Cundy, and W. A. Lee. Oral, subcutaneous and intramuscular bioavailability of the antiviral nucleotide analog 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxy-ethyl)adenine (PMEA) in cynomolgus monkeys. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 38:365–368.
G. Palu, S. Stefanelli, M. Rassu, C. Parolin, J. Balzarini and E. De Clercq. Cellular Uptake of Phosphonylmethoxyalkylpurine Derivatives, Antiviral Res. 16:115–119 (1991).
J. E. Starrett, D. R. Tortolani, M. J. M. Hitchcock, J. C. Martin and M. M. Mansuri. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of a phosphonate prodrug: bis(pivaloyloxymethyl)-9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine, Antiviral Res. 19:267–273 (1992).
J. Balzarini, Z. Hao, P. Herdewijn, D. G. Johns and E. De Clercq. Intracellular metabolism and antiretrovirus action of 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine (PMEA) a potent anti-HIV compound. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:1499–1503 (1991).
J. P. Shaw and K. C. Cundy. Biological screens of PMEA prodrugs. Pharm Res. 10(Suppl.):S294 (1993).
K. Uekama and M. Otagiri. Cyclodextrins in drug carrier systems. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 3:1–40 (1987).
L. Naesens, J. Balzarini and E. De Clercq. Pharmacokinetics in mice of the antiretrovirus agent 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine. Drug Metab. and Disposit. 20:747–752 (1992).
J. W. Russell, D. Marrero, V. J. Whiterock, L. J. Klunk and J. E. Starrett. Determination of 9-[(2-phosphonylmethoxy)ethyl]adenine in rat urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. (Netherlands) 572:321–326 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cundy, K.C., Fishback, J.A., Shaw, JP. et al. Oral Bioavailability of the Antiretroviral Agent 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine (PMEA) from Three Formulations of the Prodrug Bis(pivaloyloxymethyl)-PMEA in Fasted Male Cynomolgus Monkeys. Pharm Res 11, 839–843 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018925723889
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018925723889