Abstract
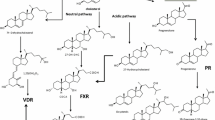
Ileal bile acid-binding protein (I-BABP) is a soluble bile acids (BA) carrier protein which belongs to the fatty acid-binding protein (FABP) family. In the gut, its expression is strictly restricted to the ileum, where it is thought to be involved in the active BA reabsorption. Therefore, I-BABP gene expression levels might be rate limiting for the BA enterohepatic circulation, and hence, might be crucial for cholesterol (CS) homeostasis. Indeed, BA not reclaimed by intestinal absorption constitute the main way to eliminate a CS excess. However, such a function is not yet established. Because generally rate limiting genes are tightly controlled, we have undertaken the study of the I-BABP gene regulation. It was found that both BA and CS, probably via oxysterols, are able to up-regulate the trancription rate of I-BABP gene. The fact that intracellular sterol sensors (FXR, LXR and SREBP1c) are involved in the control of I-BABP gene expression strongly suggest a crucial role for I-BABP in the ileum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russell DW, Setchell KD: Bile acid biosynthesis. Biochemistry 31: 4737–4749, 1992
Kramer W, Girbig F, Gutjahr U, Kowalewski S, Jouvenal K, Muller G, Tripier D, Wess G: Intestinal bile acid absorption. Na(+)-dependent bile acid transport activity in rabbit small intestine correlates with the coexpression of an integral 93-kDa and a peripheral 14-kDa bile acid-binding membrane protein along the duodenumileum axis. J Biol Chem 268: 18035–18046, 1993
Saeki T, Matoba K, Furukawa H, Kirifuji K, Kanamoto R, Iwami K: Characterization, cDNA cloning, and functional expression of mouse ileal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. J Biochem 125: 846–851, 1999
Veerkamp JH, Maatman RG: Cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding proteins: Their structure and genes. Prog Lipid Res 34: 17–52, 1995
Weinberg SL, Burckhardt G, Wilson FA: Taurocholate transport by rat intestinal basolateral membrane vesicles. Evidence for the presence of an anion exchange transport system. J Clin Invest 78: 44–50, 1986
Abe T, Kakyo M, Sakagami H, Tokui T, Nishio T, Tanemoto M, Nomura H, Hebert SC, Matsuno S, Kondo H, Yawo H: Molecular characterization and tissue distribution of a new organic anion transporter subtype (oatp3) that transports thyroid hormones and taurocholate and comparison with oatp2. J Biol Chem 273: 22395–22401, 1998
Inokuchi A, Hinoshita E, Iwamoto Y, Kohno K, Kuwano M, Uchiumi T: Enhanced expression of the human multidrug resistance protein 3 by bile salt in human enterocytes: A transcriptional control of a plausible bile acid transporter. J Biol Chem 2001 (in press)
Gantz I, Nothwehr SF, Lucey M, Sacchettini JC, DelValle J, Banaszak LJ, Naud M, Gordon JI, Yamada T: Gastrotropin: Not an enterooxyntin but a member of a family of cytoplasmic hydrophobic ligand binding proteins. J Biol Chem 264: 20248–20254, 1989
Sacchettini JC, Hauft SM, Van Camp SL, Cistola DP, Gordon JI: Developmental and structural studies of an intracellular lipid binding protein expressed in the ileal epithelium. J Biol Chem 265: 19199–19207, 1990
Amano O, Kanda T, Ono T, Iseki S: Immunocytochemical localization of rat intestinal 15 kDa protein, a member of cytoplasmic fatty acid-binding proteins. Anat Rec 234: 215–222, 1992
Stengelin S, Apel S, Becker W, Maier M, Rosenberger J, Bewersdorf U, Girbig F, Weyland C, Wess G, Kramer W: The rabbit ileal lipid-binding protein. Gene cloning and functional expression of the recombinant protein. Eur J Biochem 239: 887–896, 1996
Fujita M, Fujii H, Kanda T, Sato E, Hatakeyama K, Ono T: Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of a human intestinal 15-kDa protein. Eur J Biochem 233: 406–413, 1995
Walz DA, Wider MD, Snow JW, Dass C, Desiderio DM: The complete amino acid sequence of porcine gastrotropin, an ileal protein which stimulates gastric acid and pepsinogen secretion. J Biol Chem 263: 14189–14195, 1988
Alpini G, Glaser SS, Rodgers R, Phinizy JL, Robertson WE, Lasater J, Caligiuri A, Tretjak Z, LeSage GD: Functional expression of the apical Na+-dependent bile acid transporter in large but not small rat cholangiocytes. Gastroenterology 113: 1734–1740, 1997
Watanabe K, Hoshi N, Tsuura Y, Kanda T, Fujita M, Fujii H, Ono T, Suzuki T: Immunohistochemical distribution of intestinal 15 kDa protein in human tissues. Arch Histol Cytol 58: 303–306, 1995
Iseki S, Amano O, Kanda T, Fujii H, Ono T: Expression and localization of intestinal 15 kDa protein in the rat. Mol Cell Biochem 123: 113–120, 1993
Crossman MW, Hauft SM, Gordon JI: The mouse ileal lipid-binding protein gene: A model for studying axial patterning during gut morphogenesis. J Cell Biol 126: 1547–1564, 1994
Gong YZ, Kato T, Schwartz DA, Norris JS, Wilson FA: Ontogenic and glucocorticoid-accelerated expression of rat 14 kDa bile acidbinding protein. Anat Rec 245: 532–538, 1996
Hwang ST, Henning SJ: Hormonal regulation of expression of ileal bile acid binding protein in suckling rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 278: R1555–R1563, 2000
Lucke C, Zhang F, Ruterjans H, Hamilton JA, Sacchettini JC: Flexibility is a likely determinant of binding specificity in the case of ileal lipid binding protein. Structure 4: 785–800, 1996
Lucke C, Zhang F, Hamilton JA, Sacchettini JC, Ruterjans H: Solution structure of ileal lipid binding protein in complex with glycocholate. Eur J Biochem 267: 2929–2938, 2000
Kramer W, Sauber K, Baringhaus KH, Kurz M, Stengelin S, Lange G, Corsiero D, Girbig F, Konig W, Weyland C: Identification of the bile acid-binding site of the ileal lipid-binding protein by photoaffinity labeling, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionizationmass spectrometry, and nmr structure. J Biol Chem 276: 7291–7301, 2001
Miller KR, Cistola DP: Titration calorimetry as a binding assay for lipid-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biochem 123: 29–37, 1993
Kramer W, Corsiero D, Friedrich M, Girbig F, Stengelin S, Weyland C: Intestinal absorption of bile acids: Paradoxical behaviour of the 14 kDa ileal lipid-binding protein in differential photoaffinity labelling. Biochem J 333: 335–341, 1998
Kanda T, Niot I, Foucaud L, Fujii H, Bernard A, Ono T, Besnard P: Effect of bile on the intestinal bile-acid binding protein (IBABP) expression. In vitro and in vivo studies. FEBS Lett 384: 131–134, 1996
Kanda T, Foucand L, Nakamura Y, Niot I, Besnard P, Fujita M, Sakai Y, Hatakeyama K, Ono T, Fujii H: Regulation of expression of human intestinal bile acid-binding protein in Caco-2 cells. Biochem J 330: 261–265, 1998
Escher P, Wahli W: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: Insight into multiple cellular functions. Mutat Res 448: 121–138, 2000
Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK, Chandra G, Consler TG, Kliewer SA, Stimmel JB, Willson TM, Zavacki AM, Moore DD, Lehmann JM: Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science 284: 1365–1368, 1999
Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, Tu H, Learned RM, Luk A, Hull MV, Lustig KD, Mangelsdorf DJ, Shan B: Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science 284: 1362–1365, 1999
Wang H, Chen J, Hollister K, Sowers LC, Forman BM: Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol Cell 3: 543–553, 1999
Forman BM, Goode E, Chen J, Oro AE, Bradley DJ, Perlmann T, Noonan DJ, Burka LT, McMorris T, Lamph WW et al.: Identification of a nuclear receptor that is activated by farnesol metabolites. Cell 81: 687–693, 1995
Grober J, Zaghini I, Fujii H, Jones SA, Kliewer SA, Willson TM, Ono T, Besnard P: Identification of a bile acid-responsive element in the human ileal bile acid-binding protein gene. Involvement of the farnesoid x receptor/9-cis-retinoic acid receptor heterodimer. J Biol Chem 274: 29749–29754, 1999
Sinal CJ, Tohkin M, Miyata M, Ward JM, Lambert G, Gonzalez FJ: Targeted disruption of the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell 102: 731–744, 2000
Shimano H: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): Transcriptional regulators of lipid synthetic genes. Prog Lipid Res 40: 439–452, 2001
Zaghini I, Landrier JF, Grober J, Krief S, Jones SA, Monnot MC, Lefrere I, Watson MA, Collins JL, Fujii H, Besnard P: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c is responsible for cholesterol regulation of ileal bile-acid binding protein gene in vivo. 2001 (submitted)
Repa JJ, Liang G, Ou J, Bashmakov Y, Lobaccaro JM, Shimomura I, Shan B, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Mangelsdorf DJ: Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXRalpha and LXRbeta. Genes Dev 14: 2819–2830, 2000
DeBose-Boyd RA, Ou J, Goldstein JL, Brown MS: Expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c) mRNA in rat hepatoma cells requires endogenous LXR ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 1477–1482, 2001
Yoshikawa T, Shimano H, Amemiya-Kudo M, Yahagi N, Hasty AH, Matsuzaka T, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J, Harada K, Gotoda T, Kimura S, Ishibashi S, Yamada N: Identification of liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor as an activator of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol 21: 2991–3000, 2001
Lu TT, Makishima M, Repa JJ, Schoonjans K, Kerr TA, Auwerx J, Mangelsdorf DJ: Molecular basis for feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol Cell 6: 507–515, 2000
Goodwin B, Jones SA, Price RR, Watson MA, McKee DD, Moore LB, Galardi C, Wilson JG, Lewis MC, Roth ME, Maloney PR, Willson TM, Kliewer SA: A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell 6: 517–526, 2000
Schwartz K, Lawn RM, Wade DP: ABC1 gene expression and ApoA-I-mediated cholesterol efflux are regulated by LXR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 274: 794–802, 2000
Repa JJ, Turley SD, Lobaccaro JA, Medina J, Li L, Lustig K, Shan B, Heyman RA, Dietschy JM, Mangelsdorf DJ: Regulation of absorption and ABC1-mediated efflux of cholesterol by RXR heterodimers. Science 289: 1524–1529, 2000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landrier, JF., Grober, J., Zaghini, I. et al. Regulation of the ileal bile acid-binding protein gene: An approach to determine its physiological function(s). Mol Cell Biochem 239, 149–155 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020557502795
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020557502795