Abstract
Purpose. The purpose of this study was to isolate Caco-2 subclones that express high levels of multidrug resistance protein (MDR1) and to characterize their kinetics and affinity parameters for MDR1 substrate/inhibitors.
Methods. The subclones were selected by a dilution cloning technique. The polarized efflux of [3H]-vinblastine across subclone cell monolayers was quantified by measuring the apparent permeability coefficients (Papp) of [3H]-vinblastine in the basolateral (BL)-to-apical (AP) direction and in the AP-to-BL direction (Papp BL-to-AP/Papp AP-to-BL) across the cell monolayers. The expression of MDR1 in the Caco-2 subclones compared with the parental Caco-2 cells was confirmed by Western blotting analysis. The kinetics parameters (K m, V max) of [3H]-vinblastine and the inhibitory constants (K I) of several known MDR1 substrates/inhibitors on the transport of [3H]-digoxin determined in the parental Caco-2 cells and Caco-2 subclones were also compared.
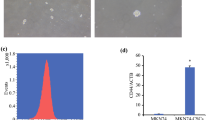
Results. Three subclones (#1, #20, #21) were selected based on their polarized efflux of [3H]-vinblastine. The Papp BL-to-AP/Papp AP-to-BL ratios for #1, #20, and #21 were 110, 140, and 112, respectively, and were about 6-fold higher than the ratio observed for the parental Caco-2 cells. In the presence of GF-120918 (2 μM), a known MDR1-specific inhibitor, the Papp BL-to-AP/Papp AP-to-BL ratios were significantly decreased, suggesting that these cells were overexpressing MDR1. The K m values observed for vinblastine in the Caco-2 subclones were nearly identical to the value observed in the parental Caco-2 cells. In contrast, the V max values observed in the subclones were approximate 26-69% higher. The K I values observed for various known MDR1 substrates/inhibitors on [3H]-digoxin transport were nearly identical to those in the parental Caco-2 cells and Caco-2 subclones. The high functional efflux activities of these subclones were stable up to 6 months.
Conclusions. Subclones #1, #20, #21 express high levels of MDR1. These Caco-2 subclones may be useful models for profiling drugs for their MDR1 substrate activity and for establishing structure-transport relationships for this efflux transporter.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. H. Stephens, C. A. O'Neill, A. Warhurst, G. L. Carlson, M. Rowland and G. Warhurst. Kinetic profiling of P-glycoprotein-mediated drug efflux in rat and human intestinal epithelia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 296:584-591 (2001).
P. Artursson, K. Palm, and K. Luthman. Caco-2 monolayers in experimental and theoretical predictions of drug transport. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 46:27-43 (2001).
C. Bailey, P. Bryla, and A. Malick. The use of the intestinal epithelial cell culture model, Caco-2, in pharmaceutical development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 22:85-103 (1996).
P. Artursson and R. T. Borchardt. Intestinal drug absorption and metabolism in cell cultures: Caco-2 and beyond. Pharm. Res. 14:1655-1658 (1997).
A. H. Dantzig, J. A. Hoskins, L. B. Tabas, S. Bright, R. L. Shepard, I. L. Jenkins, D. C. Duckworth, J. R. Sportsman, D. Mackensen, P. R. Rosteck, and P. L. Skatrud. Association of intestinal peptide transport with a protein related to the cadherin superfamily. Science 264:430-433 (1994).
J. Taipalensuu, H. Tornblom, G. Lindberg, C. Einarsson, F. Sjoqvist, H. Melhus, P. Garberg, B. Sjostrom, B. Lundgren, and P. Artursson. Correlation of gene expression of ten drug efflux proteins of the atp-binding cassette transporter family in normal human jejunum and in human intestinal epithelial caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 299:164-170 (2001).
A. H. Schinkel, U. Mayer, E. Wagenaar, C. A. Mol, L. van Deemter, J. J. Smit, M. A. van der Valk, A. C. Voordouw, H. Spits, O. van Tellingen, J. M. Zijlmans, W. E. Fibbe, and P. Borst. Normal viability and altered pharmacokinetics in mice lacking mdr1-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:4028-4033 (1997).
V. J. Wacher, L. Salphati, and L. Z. Benet. Active secretion and enterocytic drug metabolism barriers to drug absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 46:89-102 (2001).
L. Z. Benet, T. Izumi, Y. Zhang, J. A. Silverman, and V. J. Wacher. Intestinal MDR transport proteins and P-450 enzymes as barriers to oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 62:25-31 (1999).
R. L. Juliano and V. Ling. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455:152-162 (1976).
A. H. Schinkel, C. A. Mol, E. Wagenaar, L. van Deemter, J. J. Smit, and P. Borst. Multidrug resistance and the role of P-glycoprotein knockout mice. Eur. J. Cancer 31A:1295-1298 (1995).
J. Hunter, M. A. Jepson, T. Tsuruo, N. L. Simmons, and B. H. Hirst. Functional expression of P-glycoprotein in apical membranes of human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Kinetics of vinblastine secretion and interaction with modulators. J. Biol. Chem. 268:14991-14997 (1993).
C. L. Cummins, L. M. Mangravite, and L. Z. Benet. Characterizing the expression of CYP3A4 and efflux transporters (P-gp, MRP1, and MRP2) in CYP3A4-transfected Caco-2 cells after induction with sodium butyrate and the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Pharm. Res. 18:1102-1109 (2001).
J. M. Fisher, S. A. Wrighton, P. B. Watkins, P. Schmiedlin-Ren, J. C. Calamia, D. D. Shen, K. L. Kunze, and K. E. Thummel. First-pass midazolam metabolism catalyzed by 1alpha,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3-modified Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 289:1134-1142 (1999).
P. Schmiedlin-Ren, K. E. Thummel, J. M. Fisher, M. F. Paine, K. S. Lown, and P. B. Watkins. Expression of enzymatically active CYP3A4 by Caco-2 cells grown on extracellular matrix-coated permeable supports in the presence of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Mol. Pharmacol. 51:741-754 (1997).
C. L. Crespi, B. W. Penman, and M. Hu. Development of Caco-2 cells expressing high levels of cDNA-derived cytochrome P4503A4. Pharm. Res. 13:1635-1641. (1996).
K. I. Hosoya, K. J. Kim, and V. H. Lee. Age-dependent expression of P-glycoprotein gp170 in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Pharm Res. 13:885-890 (1996).
U. K. Walle, A. Galijatovic, and T. Walle. Transport of the flavonoid chrysin and its conjugated metabolites by the human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Biochem. Pharmacol. 58:431-438 (1999).
P. S. Burton, R. A. Conradi, A. R. Hilgers, and N. F. Ho. Evidence for a polarized efflux system for peptides in the apical membrane of Caco-2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 190:760-766 (1993).
P. Anderle, E. Niederer, W. Rubas, C. Hilgendorf, H. Spahn-Langguth, H. Wunderli-Allenspach, H. P. Merkle, and P. Langguth. P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) mediated efflux in Caco-2 cell monolayers: the influence of culturing conditions and drug exposure on P-gp expression levels. J. Pharm. Sci. 87:757-762 (1998).
V. E. Kostrubsky, V. Ramachandran, R. Venkataramanan, K. Dorko, J. E. Esplen, S. Zhang, J. F. Sinclair, S. A. Wrighton, and S. C. Strom. The use of human hepatocyte cultures to study the induction of cytochrome P-450. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27:887-894 (1999).
J. Gao, E. D. Hugger, M. S. Beck-Westermeyer, and R. T. Borchardt, Estimating intestinal mucosal permeation of compounds using Caco-2 cell monolayers. In A. Doyle, J. B. Griffiths and D. J. Newell (Eds.), Current Protocols in Pharmacology, Vol. 7.2, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 2000 pp. 1-23.
M. M. Gottesman, C. Cardarelli, S. Goldenberg, T. Licht, and I. Pastan. Selection and maintenance of multidrug-resistant cells. Methods Enzymol. 292:248-258 (1998).
J. Gao, O. Murase, R. L. Schowen, J. Aube, and R. T. Borchardt. A functional assay for quantitation of the apparent affinities of ligands of P-glycoprotein in Caco-2 cells. Pharm. Res. 18:171-176 (2001).
R. Evers, M. Kool, L. van Deemter, H. Janssen, J. Calafat, L. C. Oomen, C. C. Paulusma, R. P. Oude Elferink, F. Baas, A. H. Schinkel, and P. Borst. Drug export activity of the human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter in polarized kidney MDCK cells expressing cMOAT (MRP2) cDNA. J. Clin. Invest. 101:1310-1319 (1998).
F. Hyafil, C. Vergely, P. Du Vignaud, and T. Grand-Perret. In vitro and in vivo reversal of multidrug resistance by GF120918, an acridonecarboxamide derivative. Cancer Res. 53:4595-4602 (1993).
S. P. Letrent, G. M. Pollack, K. R. Brouwer, and K. L. Brouwer. Effects of a potent and specific P-glycoprotein inhibitor on the blood-brain barrier distribution and antinociceptive effect of morphine in the rat. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27:827-834 (1999).
R. Evers, N. H. Cnubben, J. Wijnholds, L. van Deemter, P. J. van Bladeren, and P. Borst. Transport of glutathione prostaglandin A conjugates by the multidrug resistance protein 1. FEBS Lett. 419:112-116 (1997).
P. Borst, R. Evers, M. Kool, and J. Wijnholds. The multidrug resistance protein family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1461:347-357 (1999).
S. P. Hammerle, B. Rothen-Rutishauser, S. D. Kramer, M. Gunthert, and H. Wunderli-Allenspach. P-Glycoprotein in cell cultures: a combined approach to study expression, localisation, and functionality in the confocal microscope. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 12:69-77 (2000).
A. Soldner, L. Z. Benet, E. Mutschler, and U. Christians. Active transport of the angiotensin-II antagonist losartan and its main metabolite EXP 3174 across MDCK-MDR1 and caco-2 cell monolayers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 129:1235-1243 (2000).
F. J. Sharom, X. Yu, J. W. Chu, and C. A. Doige. Characterization of the ATPase activity of P-glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem. J. 308:381-390 (1995).
R. Callaghan, G. Berridge, D. R. Ferry, and C. F. Higgins. The functional purification of P-glycoprotein is dependent on maintenance of a lipid-protein interface. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1328:109-124 (1997).
P. van der Bijl, M. Lopes-Cardozo, and G. van Meer. Sorting of newly synthesized galactosphingolipids to the two surface domains of epithelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 132:813-821 (1996).
Y. Romsicki and F. J. Sharom. The membrane lipid environment modulates drug interactions with the P-glycoprotein multidrug transporter. Biochemistry 38:6887-6896 (1999).
J. Ferte. Analysis of the tangled relationships between P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance and the lipid phase of the cell membrane. Eur. J. Biochem. 267:277-294 (2000).
F. Tang, K. Horie, and R. T. Borchardt. Are MDCK cells transfected with the human MDR1 gene a good model of the human intestinal mucosa? Pharm. Res. 19:766-772 (2002).
E. Bakos, R. Evers, G. Szakacs, G. E. Tusnady, E. Welker, K. Szabo, M. de Haas, L. van Deemter, P. Borst, A. Varadi, and B. Sarkadi. Functional multidrug resistance protein (MRP1) lacking the N-terminal transmembrane domain. J. Biol. Chem. 273:32167-32175 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horie, K., Tang, F. & Borchardt, R.T. Isolation and Characterization of Caco-2 Subclones Expressing High Levels of Multidrug Resistance Protein Efflux Transporter. Pharm Res 20, 161–168 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022359300826
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022359300826