Abstract
Purpose. To evaluate the potential of phosphate ester prodrugs to significantly improve the absorptive flux of poorly soluble parent drugs.
Methods. Absorptive transport studies of parent drugs and their prodrugs were carried out in Caco-2 cells. Prodrugs of parent drugs with variable aqueous solubilities were tested: Hydrocortisone-phosphate/Hydrocortisone, Fosphenytoin/phenytoin, TAT-59/DP-TAT-59, and Entacapone phosphate/Entacapone. Additional absorption studies were carried out in rats.
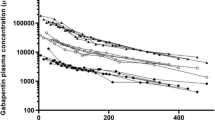
Results. Absorptive fluxes of DP-TAT-59 and phenytoin increased 9.8 or 3.3-fold after dosing TAT-59 and 500 μM fosphenytoin, respectively. Hydrocortisone's flux did not increase with hydrocortisone-phosphate at 100 μM. Permeability of the highly lipophilic and protein bound compound, DP-TAT-59, was significantly increased with serosal albumin. No permeability increase was observed for the other drugs with albumin. Entacapone phosphate failed to improve the flux of entacapone compared to an entacapone solution, but the prodrug solution did yield higher entacapone plasma levels in rats when compared with an entacapone suspension.
Conclusion. Ideal phosphate prodrug candidates are characterized by high permeability and low solubility (BCS Class II drugs). For low dose BCS Class II drug candidates, however, no biopharmaceutical advantage may be gained. Phosphate prodrugs of parent drugs with limited permeability may fail. When screening highly lipophilic parent drugs transport studies should be done with albumin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Fleisher, R. Bong, and B. H. Stewart. Improved oral drug delivery: solubility limitations overcome by the use of prodrugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 19:115–130 (1996).
A. S. Kearney and V. J. Stella. The in vitro enzymic labilities of chemically distinct phosphomonoester prodrugs. Pharm. Res. 9:497–503 (1992).
V. J. Stella. A case for prodrugs: Fosphenytoin. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 19:311–330 (1996).
P. Rohdewald, H. Möllmann, J. Barth, J. Rehder, and H. Derendorf. Pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone and its phosphate ester. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 8:205–212 (1987).
K. R. Hande. Etoposide: four decades of development of a topoisomerase II inhibitor. Eur. J. Cancer 34:1514–1521 (1998).
A. S. Kearney and V. J. Stella. Hydrolysis of pharmaceutically relevant phosphate monoester monoanions: correlation to an established structure-reactivity relationship. J. Pharm. Sci. 82:69–72 (1993).
P. O. Gunnarsson, S. B. Andersson, S. A. Johansson, T. Nilsson, and G. Plym-Forshell. Pharmacokinetics of estramustine phosphate (Estracyt) in prostatic cancer patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 26:113–119 (1984).
P. van Asten, S. A. Duursma, J. H. Glerum, F. F. Ververs, H. J. van Rijn, and A. van Dijk. Absolute bioavailability of fluoride from disodium monofluorophosphate and enteric-coated sodium fluoride tablets. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 50:321–326 (1996).
M. A. Boogaerts, A. Van Hoof, D. Catovsky, M. Kovacs, M. Montillo, P. L. Zinzani, J. L. Binet, W. Feremans, R. Marcus, F. Bosch, G. Verhoef, and M. Klein. Activity of oral fludarabine phosphate in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 19:4252–4258 (2001).
L. A. Sorbera, L. Martin, J. Castaner, and R. M. Castaner. Fosamprenavir. Drugs of the Future 26:224–231 (2001).
R. S. de Jong, N. H. Mulder, D. R. Uges, S. Kaul, B. Winograd, D. Sleijfer, H. J. Groen, P. H. Willemse, W. T. van der Graaf, and E. G. de Vries. Randomized comparison of etoposide pharmacokinetics after oral etoposide phosphate and oral etoposide. Br. J. Cancer 75:1660–1666 (1997).
S. Hawser and R. F. Hoechst Marion Roussel. LY-303366 (Eli Lilly & Co). Curr. Opin. Anti-Infect. Invest. Drugs 1:353–360 (1999).
Y. Ueda, A. B. Mikkilineni, J. O. Knipe, W. C. Rose, A. M. Casazza, and D. M. Vyas. Novel water soluble phosphate prodrugs of taxol possessing in vivo antitumor activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 3:1761–1766 (1993).
G. L. Amidon, H. Lennernaes, V. P. Shah, and J. R. Crison. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 12:413–420 (1995).
T. Heimbach. Oral Phosphate Prodrugs: Absorption Rate Limit Considerations. Ph.D. Thesis: University of Michigan (2003).
B. J. Aungst, N. H. Nguyen, J. P. Bulgarelli, and K. Oates-Lenz. The influence of donor and reservoir additives on Caco-2 permeability and secretory transport of HIV protease inhibitors and other lipophilic compounds. Pharm. Res. 17:1175–1180 (2000).
M. Pinto, S. Robine Leon, and M. D. Appay. Enterocyte-like differentiation and polarization of the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture. Biol. Cell 47:323–330 (1983).
D. Fleisher, N. Sheth, H. Griffin, M. McFadden, and G. Aspacher. Nutrient influences on rat intestinal phenytoin uptake. Pharm. Res. 6:332–337 (1989).
L. Y. Li, G. L. Amidon, J. S. Kim, T. Heimbach, F. Kesisoglou, J. T. Topliss, and D. Fleisher. Intestinal metabolism promotes regional differences in apical uptake of indinavir: Coupled effect of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 3A on indinavir membrane permeability in rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301:586–593 (2002).
J. Savolainen, M. Forsberg, H. Taipale, P. T. Mannisto, K. Jarvinen, J. Gynther, P. Jarho, and T. Jarvinen. Effects of aqueous solubility and dissolution characteristics on oral bioavailability of entacapone. Drug Dev. Res. 49:238–244 (2000).
K. Palm, K. Luthman, J. Ros, J. Grasjo, and P. Artursson. Effect of molecular charge on intestinal epithelial drug transport: pH-dependent transport of cationic drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 291:435–443 (1999).
D. Fleisher, K. C. Johnson, B. H. Stewart, and G. L. Amidon. Oral absorption of 21-corticosteroid esters: a function of aqueous stability and intestinal enzyme activity and distribution. J. Pharm. Sci. 75:934–939 (1986).
K. Ikeda, M. Nagamachi, H. Masuda, S. Nagayama, and Y. Kawaguchi. Metabolic fate of TAT-59. (3rd report). Absorption and metabolism of TAT-59. Yakuri to Chiryo 26:797–807 (1998).
P. Wils, A. Warnery, V. Phung-Ba, S. Legrain, and D. Scherman. High lipophilicity decreases drug transport across intestinal epithelial cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 269:654–658 (1994).
G. L. Amidon, B. H. Stewart, and S. Pogany. Improving the intestinal mucosal cell uptake of water insoluble compounds. J. Control. Release 2:13–26 (1985).
G. L. Amidon, G. D. Leesman, and R. L. Elliott. Improving intestinal absorption of water-insoluble compounds: a membrane metabolism strategy. J. Pharm. Sci. 69:1363–1368 (1980).
D. A. Johnson and G. L. Amidon. Determination of intrinsic membrane transport parameters from perfused intestine experiments: a boundary layer approach to estimating the aqueous and unbiased membrane permeabilities. J. Theor. Biol. 131:93–106 (1988).
R. B. McComb, G. N. J. Bowers, and S. Posen. Alkaline Phosphatase, Plenum Press, New York and London, 1979.
J. Leppänen, J. Huuskonen, J. Savolainen, T. Nevalainen, H. Taipale, J. Vepsalainen, J. Gynther, and T. Jarvinen. Synthesis of a water-soluble prodrug of entacapone. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 10:1967–1969 (2000).
A. Olivsei. Oral Prednisolone-21-phosphate is absorbed at the same rate and to the same extent as oral prednisolone in normal adults. Therapie 40:1–4 (1985).
W. K. Sietsema. The absolute oral bioavailability of selected drugs. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 27:179–211 (1989).
A. H. Burstein, D. Cox, B. Mistry, and N. Eddington. Phenytoin pharmacokinetics following oral administration of phenytoin suspension and fosphenytoin solution to rats. Epilepsy Res. 34:129–133 (1999).
Y. Nomura, O. Abe, K. Enomoto, K. Fujiwara, T. Tominaga, K. Hayashi, J. Uchino, M. Takahashi, A. Hayasaka, K. Asaishi, M. Okazaki, R. Abe, I. Kimishima, T. Kajiwara, S. Haga, T. Shimizu, I. Miyazaki, M. Noguchi, M. Yoshida, S. Miura, T. Taguchi, J. Oota, K. Sakai, H. Kinoshita, and H. Tashiro. Phase I study of TAT-59 (a new antiestrogen) in breast cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 25:553–561 (1998).
Y. Matsunaga, R. Ohta, N. Bando, H. Yamada, H. Yuasa, and Y. Kanaya. Effects of water content on physical and chemical stability of tablets containing an anticancer drug TAT-59. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 41:720–724 (1993).
B. S. Chong and T. L. Mersfelder. Entacapone. Ann. Pharmacother. 34:1056–1065 (2000).
J. Savolainen, J. Leppänen, M. Forsberg, H. Taipale, T. Nevalainen, J. Huuskonen, J. Gynther, P. T. Mannisto, and T. Jarvinen. Synthesis and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of novel oral N-alkyl-and N,N-dialkyl-carbamate esters of entacapone. Life Sci. 67:205–216 (2000).
C. Li, D. Fleisher, L. Li, J. R. Schwier, S. A. Sweetana, V. Vasudevan, L. L. Zornes, L. H. Pao, S. Y. Zhou, and R. E. Stratford. Regional-dependent intestinal absorption and meal composition effects on systemic availability of LY303366, a lipopeptide antifungal agent, in dogs. J. Pharm. Sci. 90:47–57 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heimbach, T., Oh, DM., Li, L.Y. et al. Absorption Rate Limit Considerations for Oral Phosphate Prodrugs. Pharm Res 20, 848–856 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023827017224
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023827017224