Abstract
Purpose.The purpose of present study is to investigate the involvement of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (Mrp1), Mrp2, and P-glycoprotein (Mdr1a) in the efflux transport of 17β—estradiol-D-17β-glucuronide (E217βG) across the blood—brain barrier (BBB).
Methods. The expression of Mrp1 and Mrp2 at the BBB was investigated by RT-PCR and Western blot analyses. The time profiles of the remaining radioactivity of [3H]E217βG in the brain were compared in wild-type, Mdr1a/Mdr1b and Mrp1 knockout mice and normal and Mrp2-deficient mutant rats [Sprague-Dawley and Eisai hyperbilirubinemic rats (EHBR), respectively] after intracerebral microinjection.
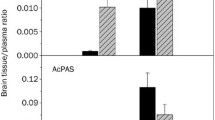
Results. RT-PCR and Western blot analyses revealed the expression of Mrp1 in isolated rat brain capillary; however, RT-PCR was unable to detect any expression of Mrp2. Significant elimination of E217βG was observed in wild-type mice at a rate constant of 0.007 min−1, which was significantly decreased (0.004 min−1) in Mrp1 knockout mice. In contrast, there was no difference in the efflux of E217βG from the brain in wild-type and Mdr1a/Mdr1b knockout mice and in normal and EHBR. No significant difference was observed in the accumulation of E217βG by brain slices prepared from wild-type and Mrp1 knockout mice.
Conclusion. Mrp1, but not Mrp2, is involved in the excretion of E217βG at the BBB and provides a barrier function by extruding conjugated metabolites into the blood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. M. Pardridge. CNS drug design based on principles of blood–brain barrier transport. J. Neurochemistry 70:1781–1792 (1998).
R. Spector. Drug transport in the mammalian central nervous system: multiple complex systems. A critical analysis and commentary. Pharmacology 60:58–73 (2000).
A. Minn, J. F. Ghersi–Egea, R. Perrin, B. Leininger, and G. Siest. Drug metabolizing enzymes in the brain and cerebral microvessels. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 16:65–82 (1991).
N. Strazielle and J. F. Ghersi–Egea. Demonstration of a coupled metabolism–efflux process at the choroid plexus as a mechanism of brain protection toward xenobiotics. J. Neurosci. 19:6275–6289 (1999).
H. Suzuki, T. Terasaki, and Y. Sugiyama. Role of efflux transport across the blood–brain barrier and blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier on the disposition of xenobiotics in the central nervous system. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 25:257–285 (1997).
H. Kusuhara and Y. Sugiyama. Efflux transport systems for drugs at the blood–brain barrier and blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier (Part 1). Drug Discov. Today 6:150–156 (2001).
G. Lee, S. Dallas, M. Hong, and R. Bendayan. Drug transporters in the central nervous system: brain barriers and brain parenchyma considerations. Pharmacol. Rev. 52:569–596 (2001).
B. Leininger, J. F. Ghersi–Egea, and G. Siest, and A. Minn. In vivo study of the elimination from rat brain of an intracerebrally formed xenobiotic metabolite, 1–naphthyl–β–D–glucuronide. J. Neurochem. 56:1163–1168 (1991).
J. F. Ghersi–Egea, A. Minn, and G. Siest. A new aspect of the protective functions of the blood–brain barrier: activities of four drug–metabolizing enzymes in isolated rat brain microvessels. Life Sci. 42:2515–2523 (1988).
B. Gao, B. Stieger, B. No, J. M. Fritschy, and P. J. Meier. Localization of the organic anion transporting polypeptide 2 (Oatp2) in capillary endothelium and choroid plexus epithelium of rat brain. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 47:1255–1264 (1999).
L. Li, P. J. Meier, and N. Ballatori. Oatp2 mediates bidirectional organic solute transport: a role for intracellular glutathione. Mol. Pharmacol. 58:335–340 (2000).
D. Sugiyama, H. Kusuhara, Y. Shitara, T. Abe, P. J. Meier, T. Sekine, H. Endou, H. Suzuki, and Y. Sugiyama. Characterization of the efflux transport of 17beta–estradiol–D–17beta–glucuronide from the brain across the blood–brain barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 298:316–322 (2001).
D. R. Hipfner, R. G. Deeley, and S. P. C. Cole. Structural, mechanistic and clinical aspects of MRP1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1461:359–376 (1998).
J. Renes, E. G. de Vries, P. L. Jansen, and M. Muller. The (patho) physiological functions of the MRP family. Drug Resist. Updat. 3:289–302 (2000).
P. Borst, R. Evers, M. Kool, and J. Wijnholds. A family of drug transporters: the multidrug resistance–associated proteins. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 92:1295–1302 (2000).
T. Ishikawa, M. T. Kuo, K. Furuta, and M. Suzuki. The human multidrug resistance–associated protein (MRP) gene family: from biological function to drug molecular design. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 38:893–897 (2000).
H. Kusuhara, H. Suzuki, M. Naito, T. Tsuruo, and Y. Sugiyama. Characterization of efflux transport of organic anions in a mouse brain capillary endothelial cell line. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 285:1260–1265 (1998).
M. Homma, H. Suzuki, H. Kusuhara, M. Naito, T. Tsuruo, and Y. Sugiyama. High–affinity efflux transport system for glutathione conjugates on the luminal membrane of a mouse brain capillary endothelial cell line (MBEC4). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 288:198–203 (1999).
A. Regina, A. Koman, M. Piciotti, B. El Hafny, M. S. Center, R. Bergmann, P. O. Couraud, and F. Roux. Mrp1 multidrug resistance–associated protein and P–glycoprotein expression in rat brain microvessel endothelial cells. J. Neurochem. 71:705–715 (1998).
Y. Zhang, H. Han, W. F. Elmquist, and D. W. Miller. Expression of various multidrug resistance–associated protein (MRP) homologues in brain microvessel endothelial cells. Brain Res. 876:148–153 (2000).
J. Wijnholds, E. C. deLange, G. L. Scheffer, D. J. van den Berg, C. A. Mol, M. van der Valk, A. H. Schinkel, R. J. Scheper, D. D. Breimer, and P. Borst. Multidrug resistance protein 1 protects the choroid plexus epithelium and contributes to the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. J. Clin. Invest. 105:279–285 (2000).
H. Sun, D. R. Johnson, R. A. Finch, A. C. Sartorelli, D. W. Miller, and W. F. Elmquist. Transport of fluorescein in MDCKII–MRP1 transfected cells and mrp1–knockout mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 284:863–869 (2001).
H. Suzuki and Y. Sugiyama. Excretion of GSSG and glutathione conjugates mediated by MRP1 and cMOAT/MRP2. Semin. Liver Dis. 18:359–376 (1998).
D. Keppler. Export pumps for glutathione S–conjugates. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 27:985–991 (1999).
M. Muller and P. L. Jansen. Molecular aspects of hepatobiliary transport. Am. J. Physiol. 272:G1285–G1303 (1997).
D. S. Miller, C. Graeff, L. Droulle, S. Fricker, and G. Fricker. Xenobiotic efflux pumps in isolated fish brain capillaries. Am. J. Physiol. 282:R191–R198 (2002).
L. Huang, T. Hoffman, and M. Vore. Adenosine triphosphate–dependent transport of estradiol–17beta(beta–D–glucuronide) in membrane vesicles by MDR1 expressed in insect cells. Hepatology 28:1371–1377 (1998).
R. J. Boado and M. M. Pardridge. A one–step procedure for isolation of poly(A)+ mRNA from isolated brain capillaries and endothelial cells in culture. J. Neurochem. 57:2136–2139 (1991).
A. Kakee, T. Terasaki, and Y. Sugiyama. Brain efflux index as a novel method of analyzing efflux transport at the blood–brain barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 277:1550–1559 (1996).
W. A. Banks, A. J. Kastin, H. M. Sam, V. T. Cao, B. King, L. M. Maness, and A. V. Schally. Saturable efflux of the peptides RC–160 and Tyr–MIF–1 by different parts of the blood–brain barrier. Brain Res. Bull. 35:179–182 (1994).
W. Slikker Jr., J. R. Bailey, D. Newport, G. W. Lipe, and D. E. Hill. Placental transfer and metabolism of 17 alpha–ethynylestradiol–17 beta and estradiol–17 beta in the rhesus monkey. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 223:483–489 (1982).
Z. S. Chen, K. Lee, and G. D. Kruh. Transport of cyclic nucleotides and estradiol 17–beta–D–glucuronide by multidrug resistance protein 4. Resistance to 6–mercaptopurine and 6–thioguanine. J. Biol. Chem. 276:33747–33754 (2001).
V. V. Rao, J. L. Dahlheimer, M. E. Bardgett, A. Z. Snyder, R. A. Finch, A. C. Sartorelli, and D. Piwnica–Worms. Choroid plexus epithelial expression of MDR1 P glycoprotein and multidrug resistance–associated protein contribute to the blood–cerebrospinal–fluid drug–permeability barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:3900–3905 (1999).
M. Sasaki, H. Suzuki, K. Ito, T. Abe, and Y. Sugiyama. Transcellular transport of organic anions across a double–transfected Madin–Darby canine kidney II cell monolayer expressing both human organic anion–transporting polypeptide (OATP2/SLC21A6) and multidrug resistance–associated protein 2 (MRP2/ABCC2). J. Biol. Chem. 277:6497–6503 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiyama, D., Kusuhara, H., Lee, YJ. et al. Involvement of Multidrug Resistance Associated Protein 1 (Mrp1) in the Efflux Transport of 17β Estradiol-D-17β-Glucuronide (E217βG) Across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Pharm Res 20, 1394–1400 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025749925541
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025749925541