Abstract
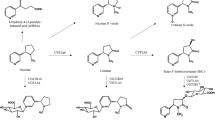
Human cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2A6 metabolizes nicotine to cotinine. Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2A6 contribute to the interindividual variability of nicotine metabolism. We encountered some subjects possessing two copies of the CYP2A6 gene, although they were genotyped as heterozygotes of the CYP2A6*4A allele (entire CYP2A6 gene deleted allele). From the subjects, we found CYP2A7 polymorphic alleles (CYP2A7*1B, CYP2A7*1C, and CYP2A7*1D) in which the sequences in the 3′-flanking region were converted to the corresponding CYP2A6 sequences, being confused with the CYP2A6*4A. These allele frequencies in European-Americans (n=187) were 1.3, 2.1, 0.3%, respectively, but these were very rare in African-Americans (n=176), Japanese (n=184), and Koreans (n=209). By an improved genotyping method, the allele frequency of CYP2A6*4A of 3.7% in European-Americans was corrected to 0%. The comprehensible and reliable genotyping method developed in this study would be useful to evaluate associations between the genotype and phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Nakajima M, Yamamoto T, Nunoya K-I, Yokoi T, Nagashima K, Inoue K et al. Role of human cytochrome P4502A6 in C-oxidation of nicotine. Drug Metab Dispos 1996; 24: 1212–1217.
Yamano S, Tatsuno J, Gonzalez FJ . The CYP2A3 gene product catalyzes coumarin 7-hydroxylation in human liver microsomes. Biochemistry 1990; 29: 1322–1329.
Komatsu T, Yamazaki H, Shimada N, Nakajima M, Yokoi T . Roles of cytochrome P450 1A2, 2A6 and 2C8 in 5-fluorouracil formation from tegafur, an anticancer prodrug, in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 2000; 28: 1457–1463.
Torchin CD, McNeilly PJ, Kapetanovic IM, Strong JM, Kupferberg HJ . Stereoselective metabolism of a new anticonvulsant drug candidate, losigamone, by human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 1996; 24: 1002–1008.
Yamazaki H, Murai K, Kawai Y, Kamataki T . Effect of the CYP2A6 polymorphisms on letrozole oxidation in human liver microsomes. Abstracts of the 125th Meeting of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, Vol. 3. Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, Tokyo, 2005 p 117.
Tiano HF, Hosokawa M, Chulada PC, Smith PB, Wang RL, Gonzalez FJ et al. Retroviral mediated expression of human cytochrome P450 2A6 in C3H/10T1/2 cells confers transformability by 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK). Carcinogenesis 1993; 14: 1421–1427.
Ding S, Lake BG, Friedberg T, Wolf CR . Expression and alternative splicing of the cytochrome P-450 CYP2A7. Biochem J 1995; 306: 161–166.
Oscarson M, McLellan RA, Gullstén H, Yue QY, Lang MA, Bernal ML et al. Characterization and PCR-based detection of a CYP2A6 gene deletion found at a high frequency in a Chinese population. FEBS Lett 1999; 448: 105–110.
Nunoya K, Yokoi T, Takahashi Y, Kimura K, Kinoshita M, Kamataki T . Homologous unequal cross-over within the human CYP2A gene cluster as a mechanism for the deletion of the entire CYP2A6 gene associated with the poor metabolizer phenotype. J Biochem 1999; 126: 402–407.
Ariyoshi N, Sekine H, Nakayama K, Saito K, Miyamoto A, Kamataki T . Identification of deletion-junction site of CYP2A6*4B allele lacking entire coding region of CYP2A6 in Japanese. Pharmacogenetics 2004; 14: 701–705.
Oscarson M, McLellan RA, Gullstén H, Yue QY, Lang MA, Bernal ML et al. Identification and characterization of novel polymorphisms in the CYP2A locus: implications for nicotine metabolism. FEBS Lett 1999; 460: 321–327.
Rao Y, Hoffmann E, Zia M, Bodin L, Zeman M, Sellers EM et al. Duplications and defects in the CYP2A6 gene: identification, genotyping, and in vivo effects on smoking. Mol Pharmacol 2000; 58: 747–755.
Oscarson M, McLellan RA, Asp V, Ledesma M, Ruiz MLB, Sinues B et al. Characterization of a novel CYP2A7/CYP2A6 hybrid allele (CYP2A6*12) that causes reduced CYP2A6 activity. Hum Mutat 2002; 20: 275–283.
Nakajima M, Yoshida R, Fukami T, McLeod HL, Yokoi T . Novel human CYP2A6 alleles confound gene deletion analysis. FEBS Lett 2004; 569: 75–81.
Ariyoshi N, Takahashi Y, Miyamoto M, Umetsu Y, Daigo S, Tateishi T et al. Structural characterization of a new variant of the CYP2A6 gene (CYP2A6*1B) apparently diagnosed as heterozygotes of CYP2A6*1A and CYP2A6*4C. Pharmacogenetics 2000; 10: 687–693.
Loriot MA, Rebuissou S, Oscarson M, Cenée S, Miyamoto M, Ariyohi N et al. Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 2A6 in a case–control study on lung cancer in a French population. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 39–44.
Goodz SD, Tyndale RF . Genotyping human CYP2A6 variants. Methods Enzymol 2002; 357: 59–69.
Schoedel KA, Hoffmann EB, Rao Y, Seller EM, Tyndale RF . Ethnic variation in CYP2A6 and association of genetically slow nicotine metabolism and smoking in adult Caucasians. Pharmacogenetics 2004; 14: 615–626.
Nakajima M, Kwon J-T, Tanaka N, Zenta T, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto H et al. Relationship between interindividual differences in nicotine metabolism and CYP2A6 genetic polymorphism in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2001; 68: 72–78.
Kwon JT, Nakajima M, Chai S, Yom YK, Kim HK, Yamazaki H, Sohn DR et al. Nicotine metabolism and CYP2A6 allele frequencies in Koreans. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 317–323.
Miyamoto M, Umetsu Y, Dosaka-Akita H, Sawamura Y, Yokota J, Kunitoh H et al. CYP2A6 gene deletion reduces susceptibility to lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1999; 261: 658–660.
Ariyoshi N, Miyamoto M, Umetsu Y, Kunitoh H, Dosaka-Akita H, Sawamura Y et al. Genetic polymorphism of CYP2A6 gene and tobacco-induced lung cancer risk in male smokers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2002; 11: 890–894.
Fujieda M, Yamazaki H, Saito T, Kiyotani K, Gyamfi MA, Sakurai M et al. Evaluation of CYP2A6 genetic polymorphisms as determinants of smoking behavior and tobacco-related lung cancer risk in male Japanese smokers. Carcinogenesis 2004; 25: 2451–2458.
Tan W, Chen GF, Ding DY, Song CY, Kadlubar FF, Lin DX . Frequency of CYP2A6 gene deletion and its relation to risk of lung and esophageal cancer in the Chinese population. Int J Cancer 2001; 95: 96–101.
Wang H, Tan W, Hao B, Miao X, Zhou G, He F et al. Substantial reduction in risk of lung adenocarcinoma associated with genetic polymorphism in CYP2A13, the most active cytochrome P450 for the metabolic activation of tobacco-specific carcinogen NNK. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 8057–8061.
Yoshida R, Nakajima M, Watanabe Y, Kwon J-T, Yokoi T . Genetic polymorphisms in human CYP2A6 gene causing impaired nicotine metabolism. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2002; 54: 511–517.
Nakajima M, Yamagishi S, Yamamoto H, Yamamoto T, Kuroiwa Y, Yokoi T . Deficient cotinine formation from nicotine is attributed to the whole deletion of the CYP2A6 gene in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2000; 67: 57–69.
Yoshida R, Nakajima M, Nishimura K, Tokudome S, Kwon J-T, Yokoi T . Effects of polymorphism in promoter region of human CYP2A6 gene (CYP2A6*9) on expression level of messenger ribonucleic acid and enzymatic activity in vivo and in vitro. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2003; 74: 69–76.
Fukami T, Nakajima M, Higashi E, Yamanaka H, Sakai H, McLeod HL et al. Characterization of novel CYP2A6 polymorphic alleles (CYP2A6*18 and CYP2A6*19) that affect enzymatic activity. Drug Metab Dispos 2005; 33: 1202–1210.
Fukami T, Nakajima M, Yoshida R, Tsuchiya Y, Fujiki Y, Katoh M et al. A novel polymorphism of human CYP2A6 gene CYP2A6*17 has an amino acid substitution (V365M) that decreases enzymatic activity in vitro and in vivo. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004; 76: 519–527.
Fukami T, Nakajima M, Higashi E, Yamanaka H, McLeod HL, Yokoi T . A novel CYP2A6*20 allele found in African-American population produces a truncated protein lacking enzymatic activity. Biochem Pharmacol 2005; 70: 801–808.
Nakajima M, Yamamoto T, Kuroiwa Y, Yokoi T . Improved highly sensitive method for determination of nicotine and cotinine in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 2000; 742: 211–215.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Japan Health Sciences Foundation with the Research on Health Science Focusing on Drug Innovation, by an SRF Grant for Biomedical Research in Japan and by Philip Morris Incorporated. The enthusiasm and research support of Tracy Jones, RN, Arnita Pitts, RN, Phyllis Klein, RN, and Ladonna Gaines, Washington University Center for Clinical Studies, and Margaret Ameyaw, MD are greatly appreciated. We acknowledge Mr Brent Bell for reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
DUALITY OF INTEREST
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukami, T., Nakajima, M., Sakai, H. et al. CYP2A7 polymorphic alleles confound the genotyping of CYP2A6*4A allele. Pharmacogenomics J 6, 401–412 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500390
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500390
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Relationship Between Amounts of Daily Cigarette Consumption and Abdominal Obesity Moderated by CYP2A6 Genotypes in Chinese Male Current Smokers
Annals of Behavioral Medicine (2012)
-
Genetic Variation in Nicotine Metabolism Predicts the Efficacy of Extended-Duration Transdermal Nicotine Therapy
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2010)
-
Identification of Novel CYP2A6*1B Variants: The CYP2A6*1B Allele is Associated With Faster In Vivo Nicotine Metabolism
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics (2008)