Abstract
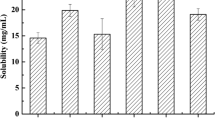
The objective of this work was to develop a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) for improving oral absorption of poorly water-soluble drug, silymarin. The pseudo-ternary phase diagrams were constructed using ethyl linoleate, Cremophor EL, ethyl alcohol, and normal saline to identify the efficient self-microemulsification region. The particle size and its distribution of the resultant microemulsions were determined using dynamic light scattering. The optimal formulation with the best self-microemulsifying and solubilization ability consisted of 10% (w/w) of ethyl linoleate, 30% of Cremophor EL, and 60% of ethyl alcohol. The release of silymarin from SMEDDS was significantly faster than that from the commercial silymarin preparation hard capsule (Legalon®). The bioavailability results indicated that the oral absorption of silymarin SMEDDS was enhanced about 2.2-fold compared with the hard capsule in fasted dogs. It could be concluded that SMEDDS would be a promising drug delivery system for poorly water-soluble drugs by the oral route.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pepping J. Milk thistle: silybum marianum. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1999;56:1195–7.
Barzaghi N, Crema F, Gatti G, Pifferi G, Perucca E. Pharmacokinetic studies on IdB 1016, a silybin–phosphatidylcholine complex, in healthy human subjects. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1990;15:333–8.
Schandalik R, Gatti G, Perucca E. Pharmacokinetics of silybin in bile following administration of silipide and silymarin in cholecystectomy patients. Arzneimittelforschung. 1992;42:964–8.
Chen W, Xia H, Wu W. Optimized preparation of silymarin dripping pills by a central composite design–response surface method. Chin Trad Herb Drug. 2005;36:679–83.
Xiao YY, Song YM, Chen ZP, Ping QN. Preparation of silymarin proliposome: a new way to increase oral bioavailability of silymarin in beagle dogs. Int J Pharm. 2006;319:162–8.
Woo JS, Kim TS, Park JH, Chi SC. Formulation and biopharmaceutical evaluation of silymarin using SMEDDS. Arch Pharm Res. 2007;30:82–9.
Wu W, Wang Y, Que L. Enhanced bioavailability of silymarin by self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2006;63:288–94.
Weyhenmeyer R, Mascher H, Birkmayer J. Study on dose-linearity of the pharmacokinetics of silibinin diastereomers using a new stereospecific assay. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1992;30:134–8.
Schulz HU, Schurer M, Krumbiegel G, Wachter W, Weyhenmeyer R, Seidel G. The solubility and bioequivalence of silymarin preparations. Arzneimittelforschung. 1995;45:61–4.
Pouton CW. Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;25:47–58.
Khoo SM, Humberstone AJ, Porter CJH, Edwards GA, Charman WN. Formulation design and bioavailability assessment of lipidic self-emulsifying formulations of halofantrine. Int J Pharm. 1998;167:155–64.
Kim HJ, Yoon KA, Hahn M, Park ES, Chi SC. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems containing idebenone. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000;26:523–9.
Pouton CW. Lipid formulation for oral administration of drugs: non-emulsifying, self-emulsifying and ‘self-microemulsifying’ drug delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2000;11:S93–8.
Kommuru TR, Gurley B, Khan MA, Reddy IK. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) of coenzyme Q10: formulation development and bioavailability assessment. Int J Pharm. 2001;212:233–46.
Itoh K, Matsui S, Tozuka Y, Oguchi T, Yamamoto K. Improvement of physicochemical properties of N-4472 Part II: characterization of N-4472 microemulsion and the enhanced oral absorption. Int J Pharm. 2002;246:75–83.
Holm R, Porter CJH, Edwards GA, Müllertz A, Kristensen HG, Charman WN. Examination of oral absorption and lymphatic transport of halofantrine in triple-cannulated canine model after administration in self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) containing structured triglycerides. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2003;20:91–7.
Grove M, Müllertz A, Nielsen JL, Pedersen GP. Bioavailability of seocalcitol II: development and characterisation of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) for oral administration containing medium and long chain triglycerides. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;28:233–42.
Cirri M, Mura P, Corvi Mora P. Liquid spray formulations of xibornol by using self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2007;340:84–91.
Kang BK, Lee JS, Chon SK, Jeong SY, Yuk SH, Khang G et al. Development of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) for oral bioavailability enhancement of simvastatin in beagle dogs. Int J Pharm. 2004;274:65–73.
Swenson ES, Curatolo WJ. Means to enhance penetration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1992;8:39–42.
Haus DJ, Mehta SC, Radebaugh GW. Targeting lymphatic transport and modified systemic distribution of CI-976, a lipophilic lipid-regulator drug, via a formulation approach. Int J Pharm. 1994;108:85–93.
Humberstone AJ, Charman WN. Lipid-based vehicles for the oral delivery of poorly water soluble drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;25:103–28.
O'Driscoll CM. Lipid-based formulations for intestinal lymphatic delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002;15:405–15.
Liu JB, Xiao YH, Allen C. Polymer-drug compatibility: a guide to the development of delivery systems for the anticancer agent, ellipticine. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93:132–43.
Philipoff W. Micelles and X-rays. J Colloid Sci. 1950;5:169–91.
Riegelman S, Allawala NA, Hrenoff MK, Srait LA. The ultraviolet absorption spectrum as a criterion of the type of solubilization. J Colloid Sci. 1958;13:208–17.
Folliad KJ, Berke NS. Properties of high-performance concrete containing shrinkage-reducing admixture. Cem Concr Res. 1997;27:1357–64.
Gershanik T, Benita S. Self-dispersing lipid formulations for improving oral absorption of lipophilic drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50:179–88.
Yuan Q, Li XR, Wang HJ, Li XY, Liu Y. The absorption kinetics of silymarin microemulsion in rat intestine. Acta Pharm Sin. 2004;39:631–4.
Charman WN, Stella VJ. Transport of lipophilic molecules by the intestinal lymphatic system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1991;7:1–14.
Sha XY, Yan GJ, Wu YJ, Li JC, Fang XL. Effect of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems containing Labrasol on tight junctions in Caco-2 cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;24:477–86.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Development of Significant New Drug (New Preparation and New Technology, Grant nos. 2009ZX09310-001) and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 program, no. 2009CB930300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Yuan, Q., Huang, Y. et al. Development of Silymarin Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System with Enhanced Oral Bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 11, 672–678 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-010-9432-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-010-9432-x