Abstract
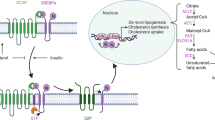
Peroxisomes in liver parenchymal cells proliferate in response to structurally diverse nonmutagenic compounds designated as peroxisome proliferators (PP). Sustained induction of peroxisome proliferation and peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation system in rats and mice leads to the development of liver tumors. Two mechanistic issues are important for consideration: elucidation of the upstream events responsible for the tissue and species specific induction of the characteristic pleiotropic responses by PPs; and delineation of the downstream events associated with peroxisome proliferation, and their role in the development of liver tumors in species that are sensitive to the induction of peroxisome proliferation. The induction of peroxisome proliferation is mediated by PP-activated receptor α (PPARα), a member of a group of transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes associated with lipid metabolism and adipocyte differentiation. Three isotypes of this family of nuclear receptors, namely PPARα, PPARγ, and PPARδ (also called β), have been identified as products of separate genes. Although PPARα is responsible for the PP-induced pleiotropic responses, PPARγ seems to be involved in adipogenesis and differentiation, but the events associated with PPARγ do not directly involve peroxisomes and peroxisome proliferation. PPARs heterodimerize with 9-cis retinoic acid receptor (RXR), and bind to PP response element(s) (PPREs) on the target gene promoter to initiate inducible transcriptional activity. Tissue and species responses to PPs depend on pharmacokinetics, relative abundance of PPAR isotypes, nature of PPRE in the upstream regions of target genes, the extent of competition or cross-talk among nuclear transcription factors for PPAR heterodimerization partner retinoid X receptor and the modulating role of coactivators and corepressors on ligand-dependent transcription of PPARs. Using PPAR as bait in the yeast two-hybrid system, the authors recently cloned mouse steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) and PPAR-binding protein (PBP), and identified them as PPAR coactivators. Both SRC-1 and PBP contain LXXLL signature motifs, considered necessary and sufficient for the binding of coactivators to nuclear receptors. A multifaceted approach, which includes the identification of additional coactivators that may be responsible for cell specific transcriptional activation of PPAR-mediated target genes, and generation of genetically modified animals (transgenic and gene disrupted), will be necessary to gain more insight into the upstream and downstream targets responsible for the induction of early and delayed PP-induced pleiotropic responses. In this context, it is important to note that mice deficient in fatty acyl-CoA oxidase, the first and rate-limiting enzyme of the peroxisomal β-oxidation system, revealed that this enzyme is indispensable for the physiological regulation of PPARα, and the absence of this enzyme leads to sustained transcriptional activation of genes regulated by this receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeDuve, C. and Baudhuin, P. (1966) Microbodies (peroxisomes) and related particles. Physiol. Rev. 46, 323–357.
Tolbert, N. E. (1981) Metabolic pathways in peroxisomes and glyoxysomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 50, 133–57.
Reddy J. K. and Mannaerts, G. P. (1994) Peroxisomal lipid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 14, 343–370.
Reddy, J. K. and Krishnakantha, T. P. (1975) Hepatic peroxisome proliferation: Induction by two novel compounds structurally unrelated to clofibrate. Science 200, 787–789.
Reddy, J. K. and Lalwani, N. D. (1983) Carcinogenesis by hepatic peroxisome proliferators: evaluation of the risk of hypolipidemic drugs and industrial plasticizers to human. CRC Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 12, 1–58.
Reddy, J. K., Rao, M. S., and Moody, D. E. (1976) Hepatocellular carcinomas in acatalasemic mice treated with nafenopin, a hypolipidemic peroxisome proliferator. Cancer Res. 36, 1211.
Reddy, J. K., Azarnoff, D. L., and Hignite, C. F. (1980) Hypolipidaemic hepatic peroxisome proliferators form a novel class of chemical carcinogens. Nature 283, 397–398.
Reddy, J. K., Goel, S. K., Nemali, M. R., Carrino, J. J., Laffler, T. G., Reddy, M. K., et al. (1986) Transcriptional regulation of peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA oxidase and enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase in rat liver by peroxisome proliferators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 1747–1751.
Aoyama, T., Hardwick, J. P., Imaoka, S., Funae, Y., Gelboin, H. V., and Gonzalez, F. J. (1990) Clofibrate-inducible rat hepatic P450IVA1 and IVA3 catalyze the omega- and (omega-1)-hydroxylation of fatty acids and the omega-hydroxylation of prostaglandins E1 and F2α. J. Lipid Res. 31, 1477–1482.
Muerhoff, A. S., Griffin, K. J., and Johnson E. F. (1992) The peroxisome proliferator activated receptor mediates the induction of CYP4A6, a cytochrome P450 fatty acid omegahydroxylase, by clofibric acid. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 19051–19053.
Kaikaus, R. M., Chan, W. K., Lysenko, N., Ray, R., Ortiz de Montellano, P. R., and Bass, N. M. (1993) Induction of peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation and liver fatty acid-binding protein by peroxisome proliferators: mediation via the cytochrome P-450IVA1 ω-hydroxylase pathway., J. Biol. Chem. 268, 9593–9603.
Gulick, T., Cresci, S., Caira, T., Moore, D. D., and Kelly, D. P. (1994) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor regulates mitochondrial fatty acid oxidative enzyme gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 11012–11016.
Reddy, J. K. and Rao, M. S. (1986) Peroxisome proliferators and cancer; mechanisms and implications. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 7, 438–443.
Reddy, J. K. and Rao, M. S. (1987) Peroxisome proliferation-related oxidative stress and hepatocarcinogenesis, in Anticarcinogenesis and Radiation Protection (Cerutti, P. A., Nygaard, O. F., Simic, M. G., eds.) Plenum, New York, pp. 85–91.
Lalwani, N. D., Fahl, W. E., and Reddy, J. K. (1983) Detection of nafenopin binding protein in rat liver cytosol associated with the induction of peroxisome proliferation by hypolipidemic compounds. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 116, 388–393.
Lalwani, N. D., Alvares K., Reddy, M. K., Reddy, M. N., Parikh, I., and Reddy, J. K. (1987) Peroxisome proliferator binding protein: identification and partial characterization of nafenopin, clofibric acid and ciprofibrate binding proteins from rat liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 5142–5246.
Alvares, K, Carrillo, A., Yuan, P. M., Kawano, H., Morimoto, R. I., and Reddy, J. K. (1990) Identification of peroxisome proliferator binding protein as a member of HSP70 protein family, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 5293–5297.
Issemann, I. and Green, S. (1990) Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature 347, 645–650.
Dreyer, C., Krey, G., Keller, H., Givel, F., Helftenbein, G., and Wahli, W. (1992) Control of the peroxisomal β-oxidation pathway by a novel family of nuclear hormone receptors. Cell 68, 879–887.
Zhu, Y., Alvares, K., Huang, Q., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1993) Cloning of a new member of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gene family from mouse, liver. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 26817–26820.
Sher, T., Yi, H. F., McBride, W., and Gonzalez F. J. (1993) cDNA cloning, chromosomal mapping, and functional characterization of the human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor. Biochemistry 32, 5598–5604.
Kliewer, S. A., Forman, B. M., Blumberg, B., Ong, E. S., Borgmeyer, U., Mangelsdorf, D. J., Umesono, K., and Evans, R. M. (1994) Differential expression and activation of a family of murine peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 7355–7359.
Lee, S. S.-T. Pineau, T., Drago, J., Lee, E. J., Owens, J. W., Kroetz, D. L., et al. (1995) Targeted disruption of the isoform of the peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor gene in mice results in abolishment of the pleiotropic effects of peroxisome proliferators. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 3012–3022.
Chatterjee, B., Demyan, W. F., Lalwani, N. D., Reddy, J. K., and Roy, A. K. (1983) Reversible alteration of hepatic messenger RNAs for peroxisomal and non-peroxisomal proteins induced by hypolipidemic drug Wy-14,643. Biochem. J. 241, 879–883.
Huang, Q., Alvares, K., Chu, R., Bradfield, C. A., and Reddy, J. K. (1994) Association of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor and HSP72. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 8493–8497.
Mangelsdorf, D. J., Thummel, C., Beato, M., Herrlich, P., Schutz, G., Umesono, K., et al. (1995) The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell 83, 835–839.
Tontonoz, P., Hu, E., Graves, R. A., Budavari, A. I., and Spiegelman, B. M. (1994) mPPAR gamma 2: tissue-specific regulator of an adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev. 8, 1224–1234.
Zhu, Y., Qi, C., Korenberg, J. R., Chen, Z.-N., Noya, D., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1995) Structural organization of mouse peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorγ (mPPARγ) gene: alternative promoter use and different splicing yield two mPPARγ isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7921–7925.
Danielian, P. S., White, R., Lees, J. A., and Parker, M. G. (1992) Identification of a conserved region required for hormone-dependent transcriptional activation by steroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 11, 1025–1033.
Kliewer, S. A., Umesono, K., Noonan, D. J., Heyman, R. A., and Evans, R. M. (1992) Convergence of 9-cis-retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature (London) 358, 771–774.
Palmer, C. N. A., Hsu, M.-H., Griffin, K. J., Johnson, and Johnson,E. F. (1995) Novel sequence determinants in peroxisome proliferator signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 16114–16121.
Reddy, J. K. and Chu, R. (1996) Peroxisome proliferator-induced pleiotropic responses: Pursuit of a phenomenon. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 804, 176–201.
Chu, R., Lin, Y., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1995) Cooperative formation of higher order peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor and retinoid X receptor complexes on the peroxisome proliferator responsive element of the rat hydratase-dehydrogenase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 29636–29639.
Nemali, M. R., Reddy M. K., Usuda, N., Reddy, P. G., Comeau, L. D., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1989) Differential induction and regulation of peroxisomal enzymes: predictive value of peroxisomal proliferation in identifying certain nonmutagenic carcinogens. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 97, 72–87.
Krey, G., Braissant, O., L'Horset, F., Kalkhoven, E., Perroud, M., Parker, M. G., and Wahli, W. (1997) Fatty acids, eicosanoids, and hypolipidemic agents identified as ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors by coactivator-dependent receptor ligand assay. Endocrinology 11, 779–791.
Forman, B. M., Chen, J., and Evans, R. M. (1997) Hypolipidemic drugs, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and eicosanoids are ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α and β. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 4312–4317.
Kliewer, S. A., Sundseth, S. S. Jones, S. A., Brown, P. J., Wisely, G. B., Koble, C. S., et al. (1997) Fatty acids and eicosanoids regulate gene expression through direct interactions with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α and γ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 4318–4323.
Fan, C.-Y., Pan, J., Usuda, N., Yeldandi, A. V., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1998) Steatohepatitis, spontaneous peroxisome proliferation and liver tumors in mice lacking peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 15639–15645.
Mosser, J., Lutz, Y., Stoeckel, M. E., Sarde, C. O., Kretz, C., Douar, A. M., Lopez, J., Aubourg, P., and Mandel J. L. (1994) The gene responsible for adrenoleukodystrophy encodes a peroxisomal membrane protein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2, 285–271.
Lu, J.-F., Lawler, A. M., Watkins, P. A., Powers, J. M., Moser, A. B., Moser, H. W., and Smith, K. D. (1997) A mouse model for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 9366–9371.
Kobayashi, T., Shinonoh, N., Kondo, A., and Yamada, T. (1997) Adrenoleukodystrophy protein deficient mice represent abnormality of very long chain fatty acid metabolism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 232, 631–636.
Tontonoz, P., Hu, E., and Spiegelman, B. M. (1994) Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR_2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell 79, 1147–1156.
Mansen, A., Guardiola-Diaz, H., Rafter, J., Branting, C., and Gustafsson, J.-A. (1996) Expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in the mouse colonic mucosa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 222, 844–851.
Braissant, O., Foufelle, F., Scotto, C., Dauca, M., and Wahli, W. (1996) Differential expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs): Tissue distribution of PPAR-α,-β, and-γ in the adult rat. Endocrinology 137, 354–366.
Jain, S., Pulikuri, S., Zhu, Y., Qi, C., Kanwar, Y. S., Yeldandi, A. V., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1998) Differential expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorγ (PPARα) and its coactivators steroid receptor coactivator-1 and PPAR-binding protein PBP in the brown fat, urinary bladder, colon, and breast of the mouse. Amer. J. Pathol. 153, 349–354.
Guan, Y., Zhang, Y., Davis, L., and Breyer, M. D. (1997) Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in urinary tract of rabbits and humans. Am. J. Physiol. 273, F1013-F1022.
Gottlicher, M., Widmark, K., Li, Q., and Gustafsson, J. A. (1992) Fatty acids activate chimera of the clofibric acid-activated receptor and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 4653–4657.
Forman, B. M., Tontonoz, P., Chen, J., Brun, R. P., Spiegelman, B. M, and Evans, R. M. (1995) 15-Deoxy-12,14-prostaglandin J2 is a ligand for the adipocyte determination factor PPAR. Cell 83, 803–812.
Kliewer, S. A., Lenhard, J. M., Willson, T. M., Patel, I., Morris, D. C., and Lehmann, J. M. (1995) A prostaglandin J2 metabolite binds peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Cell 83, 813–819.
Lehmann, J. M., Lenhard, J. M., Oliver, B. B., Ringold, G. M., and Kliewer, S. A. (1997) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma are activated by indomethacin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 3406–3410.
Huang, Q., Yeldandi, A. V., Alvares, K., Ide, H., Reddy, J. K., and Rao, M. S. (1995) Localization of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in mouse and rat tissues and demonstration of its nuclear translocation in transfected CV-1 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 6, 307–312.
Tontonoz, P., Singer, S., Forman, B., Sarraf, P., Fletcher, J., Fletcher, C. D. M., et al. (1997) Terminal differentiation of human liposarcoma cells induced by ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and the retinoid X receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94, 237–241.
Sarraf, P., Mueller, E., Jones, D., King, F. J., DeAngelo, D. J., Partridge, J. B., et al. (1998) Differentiation and reversal of malignant changes in colon cancer through PPARγ. Nature Med. 4, 1046–1052.
Glass, C. K., Rose, D. W., and Rosenfeld, M. G. (1997) Nuclear receptor coactivators. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 222–232.
Onate, S. A., Tsai, S. Y., Tsai, M.-J., and O'Malley, B. W. (1995) Sequence and characterization of a coactivator for the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science 270, 1354–1357.
Voegel, J. J., Heine, M. J. S., Zechel, C., Chambon, P., and Gronemeyer, H. (1996) TIF2, a 160 kDa transcriptional mediator for the ligand-dependent activation function AF-2 of nuclear receptors. EMBO J. 15, 3667–3675.
Torchia, J., Rose, D. W., Inostroza, J., Kamei, Y., Westin, S., Glass, C. K., and Rosenfeld, M. G. (1997) The transcriptional co-activator p/CIP binds CBP and mediates nuclear-receptor function. Nature 387, 677–684.
Hong, H., Kohli, K., Trivedi, A., Johnson, D. L., and Stallcup, M. R. (1996) GRIP1, a novel mouse protein that serves as a transcriptional coactivator in yeast for the hormone binding domains of steroid receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4948–4952.
Chen, H., Lin, R. J., Schiltz, R. L., Chakravarti, D., Nash, A., Nagy, L., et al. (1997) Nuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300. Cell 90, 569–580.
Anzick, S. L., Kononen, J., Walker, R. L., Azorsa, D. O., Tanner, M. M., Guan, X. Y., et al. (1997) AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277, 965–968.
Li, H., Gomes, P. J., and Chen, J. D. (1997) RAC3, a steroid/nuclear receptor-associated coactivator that is related to SRC-1 and TIF2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 8479–8484.
Kamei, Y., Xu, L., Heinzel, T., Torchia, J., Kurokawa, R., Gloss, B., et al. (1996) A CBP integrator complex mediates transcriptional activation and AP-1 inhibition by nuclear receptors. Cell 85, 403–414.
Zhu, Y., Qi, C., Jain, S., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1997) Isolation and characterization of PBP, a protein that interacts with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 25,500–25,506.
Yuan, C.-X., Ito, M., Fondell, J. D., Fu, Z.-Y., and Roeder, R. G. (1998) The TRAP220 component of a thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein (TRAP) coactivator complex interacts directly with nuclear receptors in a ligand-dependent fashion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7939–7944.
Puigserver, P., Wu, Z., Park, C. W., Graves, R., Wright, M., and Spiegelman, B. M. (1998) A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell 92, 829–839.
Yeh, S. and Chang, C. (1997) Cloning and characterization of a specific coactivator, ARA70, for the androgen receptor in human prostate cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 5517–5521.
Zhu, Y., Qi, C., Calandra, C., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1996) Cloning and identification of mouse steroid receptor coactivator-1 (mSRC-1), as a coactivator of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. Gene Express. 6, 185–195.
Yao, T.-P., Ku, G., Zhou, N., Scully, R., and Livingston, D. M. (1996) The nuclear hormone receptor coactivator SRC-1 is a specific target of p300. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 10626–10631.
Takeshita, A., Yen, P. M., Misiti, S., Cardona, G. R., Liu, Y., and Chin, W. W. (1996) Molecular cloning and properties of a full-length putative thyroid hormone receptor coactivator. Endocrinology 137, 3594–3597.
Heery, D. M., Kalkhoven, E., Hoare, S., and Parker, M. G. (1997) A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates binding to nuclear receptors. Nature 387, 733–736.
Ogryzko, V. V., Schiltz, R. L., Russanova, V., Howard, B. H., and Nakatani, Y. (1996) The transcriptional coactivators p300 and CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell 87, 953–959.
Brownell, J. E. and Allis, C. D. (1996) Special HATs for special occasions: Linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 6, 176–184.
Chakravarti, D., LaMorte, V. J., Nelson, M. C., Nakajima, T., Schulman, I. G., Juguilon, H., Montminy, M., and Evans, R. M. (1996) Role of CBP/P300 in nuclear receptor signalling. Nature 383, 99–102.
Dowell, P., Ishmael, J. E., Avram, D., Peterson, V. J., Nevrivy, D. J., and Leid, M. (1997) p300 Functions as a coactivator for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 33435–33443.
Mizukami, J. and Taniguchi, T. (1997) The antidiabetic agent thiazolidinedione stimulates the interaction between PPAR and CBP. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 240, 61–64.
Cavailles, V., Dauvois, S., L'Horset, F., Lopez, G., Hoare, S., Kushner, P. J., and Parker, M. G. (1995) Nuclear factor RIP140 modulates transcriptional activation by the estrogen receptor. EMBO J. 14, 3741–3751.
Treuter, E., Albrektsen, T., Johnasson, L., Leers, J., and Gustafsson, J.-A. (1998) A regulator role for RIP140 in nuclear receptor activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 12, 864–881.
Chu, R., Lin, Y., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1996) Cloning and identification of rat deoxyuridine triphosphatase as an inhibitor of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 27670–27675.
Brun, R. P., Kim, J. B., Hu, E., and Spiegelman, B. M. (1997) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and the control of adipogenesis. Curr. Opin. Lipid. 8, 212–218.
Schoonjans, K., Staels, B., and Auwerx, J. (1996) The peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARs) and their effects on lipid metabolism and adipocyte differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1302, 93–109.
Hashimoto, T. (1982) Individual peroxisomal β-oxidation enzymes. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 386, 5–12.
Martin, G., Schoonjans, K., Lefebvre, A.-M., Staels, B., and Auwerx, J. (1997) Coordinate regulation of the expression of the fatty acid transport protein and acyl-CoA synthetase genes by PPARα and PPARγ activators. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 28210–28217.
Ren, B., Thelen, A. P., Peters, J. M., Gonzalez, F. J., and Jump, D. B. (1997) Polyunsaturated fatty acid suppression of hepatic fatty acid synthase and S14 gene expression does not require peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26827–26832.
Warren, J. R., Simmon, V. F., and Reddy, J. K. (1980) Properties of hypolipidemic peroxisome proliferators in the lymphocyte [3H]-thymidine and salmonella mutagenesis assays. Cancer Res. 40, 36–41.
Rao, M. S. and Reddy, J. K. (1996) Hepatocarcinogenicity of peroxisome proliferators. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 804, 573–587, 1996.
Ashby, J., Brady, A., Elcombe, C. R., Elliot, B. M., Ishmael, J., Odum, J., Tugwood, J. M., Kettle, S., and L. F. H. Purchase. (1994) Mechanistically-based human hazard assessment of peroxisome proliferator-induced hepatocar-cinogenesis. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 13(Suppl. 2), S1-S117.
Rao, M. S. and Reddy, J. K. (1987) Peroxisome proliferation and hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 8, 631–636.
Lazarow, P. B. and deDuve, C. (1976) A fatty acyl-CoA oxidizing system in rat liver peroxisomes: Enhancement by clofibrate, a hypolipidemic drug. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73, 2043–2046.
Chu, S., Huang, Q., Alvares, K., Yeldandi, A. V., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1995) Transformation of mammalian cells by overexpressing H2O2-generating peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA oxidase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7080–7084.
Dadras, S. S., Thorgeirsson, S. S., Rao, M. S., and Reddy, J. K. (1998) Implication of hydrogen peroxide generation and apoptosis in the neoplastic transformation of mouse fibroblasts overexpressing peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA oxidase. Int. J. Oncol. 12, 37–44.
Okamoto, M., Reddy, J. K., and Oyasu, R. (1997) Tumorigenic conversion of a nontumorigenic rat urothelial cell line by overexpression of H2O2-generating peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA oxidase. Int. J. Cancer 70, 716–721.
Chu, R., Madison, L. D., Lin, Y., Kopp, P., Rao, M. S., Jameson, J. L., and Reddy, J. K. (1995) Thyroid hormone (T3) inhibits ciprofibrate-induced transcription of genes encoding β-oxidation enzymes: cross talk between peroxisome proliferator and T3 signaling pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 11593–11597.
Juge-Aubry, C. E., Gorla-Bajszczak, A., Pernin, A., Lemberger, T., Wahli, W., Burger, A. G., and Meier, C. A. (1995) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor mediates cross-talk with thyroid hormone receptor by competition for retinoid X receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 18,117–18,122.
Ricote, M., Li, A. C., Willson, T. M., Kelly, C. J., and Glass, C. K. (1998) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ is a negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature 391, 79–82.
Nagy, L., Tontonoz, P., Alvarez, J. G. A., Chen, H., and Evans, R. M. (1998) Oxidized LDL regulates macrophage gene expression through ligand activation of PPARγ. Cell 93, 229–240.
Tontonoz, P., Nagy, L., Alvarez, J. G. A., Thomazy, V. A., and Evans, R. M. (1998) PPARγ promotes monocyte/macrophage differentiation and uptake of oxidized LDL. Cell 93, 241–252.
Wu, Z., Xie, Y., Bucher, N. L., and Farmer, S. R. (1995) Conditional ectopic expression of C/EBP beta in NIH-3T3 cells induces PPAR gamma and stimulates adipogenesis. Genes Dev 9, 2350–2363.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, C., Zhu, Y. & Reddy, J.K. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, coactivators, and downstream targets. Cell Biochem Biophys 32, 187–204 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:32:1-3:187
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:32:1-3:187