Summary
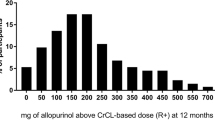
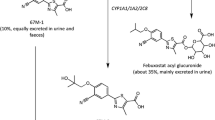
Allopurinol is a widely used drug in the management of hyperuricaemia. It is rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. The major and active metabolite, oxypurinol, is detected in the circulation within 15 minutes of allopurinol administration. Oxypurinol concentrations are higher than those of the parent drug and accumulation occurs during long term administration. Up to 80% of allopurinol is recovered in the urine within 24 hours, mainly in the form of oxypurinol. Allopurinol is negligibly absorbed after rectal administration.
In animals, allopurinol is found in highest concentrations in vascular tissue, blood, liver, intestine and heart. It is negligibly bound to plasma proteins. Oxypurinol is eliminated by the kidney and has a much longer elimination half-life than allopurinol. Oxypurinol accumulates in patients with renal dysfunction; hence allopurinol dosages should be adjusted in such patients. Allopurinol inhibits the metabolism of 6-mercaptopurine and azathioprine, which require dosage modifications. The interaction of allopurinol with oral anticoagulants and phenytoin has not been clearly established in clinical practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelbaum SJ, Mayersohn M, Dorr RT, Perrier D. Allopurinol kinetics and bioavailability. Intravenous, oral and rectal administration. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 14: 789, 1982
Benezra SA, Bennett TR. In Florey K (Ed.) Analytical profiles of drug substances, Vol. 7, pp. 1–17, Academic Press, New York, 1978
Berlinger WG, Park DG, Spector R. The effect of dietary protein on the clearance of allopurinol and oxypurinol. New England Journal of Medicine 313: 771–776, 1985
Betz AL. Identification of hypoxanthine transport and xanthine oxidase activity in brain capillaries. Journal of Neurochemistry 44: 574–579, 1985
Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program. Allopurinol and cytotoxic drugs. Laboratory Investigation 227: 1036, 1974
Caskey CT, Ashton DM, Wyngaarden JB. The enzymology of feedback inhibition of glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase by purine nucleotides. Journal of Biological Chemistry 239: 2570–2579, 1964
Chang S, Kramer WG, Feldman S, Ballentine R, Frankel LS. Bioavailability of allopurinol oral and rectal dosage forms. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 38: 365–368, 1981
Edwards NL, Recker D, Airozo D, Fox IH. Enhanced purine salvage during allopurinol therapy: an important pharmacologic property in humans. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 98: 673–683, 1981
Elion GB, Benezra FM, Beardmore TD, Kelley WN. Studies with allopurinol in patients with impaired renal function. Advances in Experimental Biology and Medicine 1224: 263–267, 1980
Elion GB, Kovensky A, Hitchings GH, Metz E, Rundles RW. Metabolic studies of allopurinol, an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Biochemical Pharmacology 15: 836–880, 1966
Elion GB, Yu TF, Gutman GB, Hitchings GH. Renal clearance of oxypurinol, the chief metabolite of allopurinol. American Journal of Medicine 45: 69–77, 1968
Endele R, Lettenbauer G. Hochdruckflussigchromatographische bestimmung von allopurinol und oxypurinol in serum. Journal of Chromatography 115: 228, 1975
Glogner P, Heni N. Panztopenie nach kombinationsbehandlung mit allopurinol und azothioprin. Medizinische Welt 27: 1545, 1976
Hande KR, Chabner BA. A competitive protein binding assay for allopurinol and oxipurinol. Analytical Biochemistry 101: 26–33, 1980
Hande KR, Noore RM, Stone WJ. Severe allopurinol toxicity. Description and guidelines for patients with renal insufficiency. American Journal of Medicine 76: 47–56, 1984
Hande K, Reed E, Chabner B. Allopurinol kinetics. Clinical Pharmacology 23: 598–605, 1978
Hornbeck CL, Floyd RA, Byfield JE, Griffiths JC, Frankel S, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid versus serum concentrations of 3-FU, allopurinol, and oxipurinol during treatment of metastatic brain cancer with 5-FU infusion, allopurinol, and radiation. Cancer Treatment Reports 66: 571–573, 1982
Jaeger VH, Russman D, Rasper J, Blome J. Vergleichende prufung der bioverfugbarkeit und des pharmakodynamischen effektes von funf allopurinol-zubereitungen. Arzneimittel-Forschung 32: 438–442, 1982
Jarasch ED, Grund C, Bruder G, Heid HW, Keenan TW, et al. Localisation of xanthine oxidase in mammary-gland epithelium and capillary endothelium. Cell 20: 67–82, 1981
Kelley WM, Beardmore TD. Allopurinol: alteration in pyrimidine metabolism in man. Science 169: 338–390, 1970
Kramer WG, Feldman S. Apparent metabolism of allopurinol by blood. Research Communications in Chemical Pathology and Pharmacology 18: 781–784, 1977
Marcus M, Tse FLS, Kleinberg SI. The bioavailability of two commercial preparations of allopurinol tablets. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 20: 302–305, 1982
Mertz DP, Eichhorn R. Does benzbromarone in therapeutic doses raise renal excretion of oxipurinol? Klinische Wochenschrift 62: 1170–1172, 1984
Nelson DJ, Bugge CJL, Krasny HC, Elion GB. Formation of nucleotides of [614C]allopurinol and [614C]oxipurinol in rat tissues and effects on uridine nucleotide pool. Biochemical Pharmacology 22: 2003–2022, 1973
Patel VS, Kramer WG. Allopurinol absorption from different sites of the rat gastrointestinal tract. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 75: 275–277, 1986
Petitpierre B, Perrin L, Rudhart M, Herrera A, Fabre J. Behaviour of chlorpropamide in renal insufficiency and under the effects of associated drug therapy. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 6: 120, 1972
Ragab AH, Gilkerson E, Myers M. The effect of 6-mercaptopurine and allopurinol on granulopoiesis. Cancer Research 34: 2246, 1974
Rundles GH, Wyngaarden JB, Hutchings GH, Elion GB, Silberman HR. Effects of xanthine oxidase inhibition of thiopurine metabolism, hyperuricemia and gout. Transactions of Association of American Physicians 76: 126–140, 1963
Simmonds HA, Levin B, Cameron JS. Variations in allopurinol metabolism by xanthinuric subjects. Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine 47: 173–178, 1974
Sved S, Wilson DL. Analysis of allopurinol and oxypurinol in plasma and its application to metabolic studies. Biopharmaceutics and Drug Disposition 1(3): 111–117, 1980
Sweetman L, Nyhan WL. Quantitation of oxypurines and allopurinol metabolites in biological fluids by cation exchange chromatography. Analytical Biochemistry 31: 358–365, 1969
Vesell ES, Passananti GT, Greene EF. Impairment of drug metabolism in man by allopurinol and nortriptyline. New England Journal of Medicine 283: 1484, 1970
Vogler WR, Bain JA, Huguley CM, Palmer HG, Lowrey ME. Metabolic and therapeutic effects of allopurinol in patients with leukaemia and gout. American Journal of Medicine 40: 548, 1966
Walter-Sack VI, Grobner W, Zollner N. Verlauf der oxipurinolspeigel im plasma nach akuter und chronischer gabe von allopurinol in verschiedenen zubereitunger. Arzneimittel-Forschung 29: 839–842, 1979
Wood MH, O’Sullivan WJ, Wilson M, Tiller DJ. Potentiation of an effect of allopurinol on pyrimidine metabolism by chlorothiazide in man. Clinical Experiments in Pharmacology and Physiology 1: 53, 1974
Yokochi K, Yokochi A, Chiba K, Ishizaki T. Phenytoin-allopurinol interaction: Michaelis-Menten kinetic parameters of phenytoin with and without allopurinol in a child with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 4: 353–357, 1982
Young JL, Boswell RB, Nies AS. Severe allopurinol sensitivity: association with thiazides and prior renal compromise. Archives of Internal Medicine 134: 553, 1974
Zimm S, Collins JM, O’Neill D, Chabner BA, Poplack DG. Inhibition of first pass metabolism in cancer chemotherapy: interaction of 6-mercaptopurine and allopurinol. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 34: 810–817, 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murrell, G.A.C., Rapeport, W.G. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Allopurinol. Clin-Pharmacokinet 11, 343–353 (1986). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-198611050-00001
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-198611050-00001