Abstract
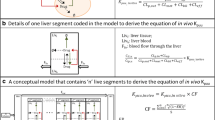
The metabolic sequence of drug, D,to its primary (MI)and terminal (MII)metabolites as mediated by enzymes Aand B,respectively, was chosen to illustrate metabolizing activities among hepatocytes in different regions of the liver lobule. Six models of distributions of the hepatocellular activities (intrinsic clearances for A and B) were defined with respect to the flow path in liver, and the concentrations D, MI,and MIIin the liver were simulated. The extent of sequential metabolism of the primary metabolite was compared for these six models of enzymic distributions. It was found that when the average hepatic intrinsic clearances of Aand Bwere high (almost complete extraction of both drug and primary metabolite during their single passage through the liver), the distributions of Aand Bwere not important determinants of metabolite kinetics. By contrast, when the average hepatic intrinsic clearances of A and Bwere both low,the distributions of Aand Bexerted profound effects on metabolite kinetics. The sensitivity to enzymic distribution in this region, however, was difficult to assess due to difficulties in detecting low levels of MIand MIIThe effects of enzymic distributions on metabolite disposition would be better detected in compounds (drug and metabolite) with intermediate extraction ratios.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. S. Ketty. Theory and applications of the exchange of inert gas at the lungs and tissues.Pharmacol. Rev. 3:1–41 (1951).
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier.Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed. Marcel Dekker, New York, 1981.
K. B. Bischoff and R. L. Dedrick. Thiopental kinetics.J. Pharm. Sci. 57:1346–1351 (1968).
K. B. Bischoff, R. L. Dedrick, D. S. Zaharko, and J. A. Longstreth. Methotrexate pharmacokinetics.J. Pharm. Sci. 60:1128–1133 (1971).
N. Benowitz, R. P. Forsyth, K. L. Melmon, and M. Rowland. Lidocaine disposition kinetics in monkey and man. I. Prediction by a perfusion model.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16:84–98 (1974).
K. Winkler, S. Keiding, and N. Tygstrup. Clearance as a quantitive measure of liver and function. In P. Paumgartner and R. Presig (eds.),The Liver: Quantitative Aspects of Structure and Functions, Karger, Basel, pp. 144–155.
M. Rowland, L. Z. Benet, and G. G. Graham. Clearance concepts in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:123–136 (1973).
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs. II. Experimental evidence for acceptance of the “well-stirred” model over the “parallel tube” model using lidocaine in the perfused rat liverin situ preparation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:655–680 (1977).
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs III. Additional experimental evidence for the acceptance of the “well-stirred” model using metabolite (MEGX) data generated from lidocaine under varying hepatic blood flows in the rat liver perfusedin situ preparation.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:681–699 (1977).
D. G. Shand, D. M. Kornhauser, and G. R. Wilkinson. Effects of routes of administration and blood flow on hepatic elimination.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 195:424–432 (1975).
S. Keiding, S. Johansen, K. Winkler, K. Tonnesen, and N. Tygstrup. Michaelis-Menten kinetics of galactose elimination in the isolated perfused pig liver.Am. J. Physiol. 230:1302–1313 (1976).
S. Keiding and E. Chiarantini. Effect of sinusoidal perfusion on galactose elimination kinetics in perfused rat liver.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 205:465–470 (1978).
S. Keiding, S. Johansen, I. Midtbll, A. Rabol, and L. Christiansen. Ethanol elimination kinetics in human liver and pig liverin vivo.Am. J. Physiol. 237:E316-E324 (1979).
K. S. Pang and J. R. Gillette. Kinetics of metabolite formation and elimination in the perfused rat liver preparation: differences between the elimination of preformed acetaminophen and acetaminophen formed from phenacetin.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 207:178–194 (1978).
K. S. Pang and J. R. Gillette. Sequential first-pass elimination of a metabolite derived from its precursor.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7:275–290 (1979).
K. S. Pang and J. A. Terrell. Retrogade perfusion to probe the heterogeneous distributions of hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes in the rat.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 216:339–346 (1981).
L. W. Wattenberg and J. L. Leong. Histochemical demonstration of reduced pyridine nucleotide dependent polycyclic hydrocarbon metabolizing systems.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10:412–420 (1962).
J. Baron, J. A. Redick, and F. P. Guengerich. Immunohistochemical localization of cytochromes P-450 in rat liver.Life Sci. 23:2627–2632 (1978).
J. H. Dees, B. S. S. Masters, U. Muller-Eberhard, and E. F. Johnson. Effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and phenobarbital on the occurrence and distribution of four cytochrome P-450 isozymes in rabbit kidney, lung and liver.Cancer Res. 42:1423–1432 (1982).
A. E. M. McLean, E. McLean, and J. E. Judah. Cellular necrosis in the liver induced and modified by drugs.Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol 4:125–157 (1965).
J. H. N. Meerman, A. B. van Doom, and G. J. Mulder. Inhibition of sulfate conjugation of N-hydroxy-2-acetylaminofluorene in isolated perfused rat liver and in the ratin vivo by pentachlorophenol and low sulfate.Cancer Res. 40:3772–3779 (1980).
K. S. Pang, L. Waller, K. K. Chan, and M. G. Horning. Metabolite kinetics: formation of acetaminophen from deuterated and non-deuterated phenacetin and acetanilide on acetaminophen sulfation kinetics in the perfused rate liver preparation.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 222:14–19 (1982).
K. S. Pang, P. Kong, J. A. Terrell, and R. E. Billings. Disposition of acetaminophen and phenacetin by isolated rat hepatocytes—a system in which the spatial organization inherent of an intact organ is disrupted, submitted for publication.
J. R. Gillette. Factors affecting drug metabolism.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 179:43–46 (1971).
G. R. Wilkinson and D. G. Shand. Commentary: A physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 18:377–390 (1975).
A. A. B. Pritsker.The GASP IV Simulation Package. Wiley, New York, 1974.
K. S. Pang, H. Koster, I. C. M. Halsema, E. Scholtens, G. J. Mulder, and R. N. Stillwell. Normal and retrograde perfusion to probe the zonal distribution of sulfation and glucuronidation activities of harmol in the perfused rat liver preparation.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 224:647–653 (1983).
J. G. Conway, F. C. Kauffman, S. Ji, and R. G. Thurman. Ratio of sulfation and glucuronidation of 7-hydroxyxoumarin in periportal and pericentral regions of the liver lobule.Mol. Pharmacol. 22:509–516 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by USPHS Grants GM-27323; by a Research Career Development Award AM-01028; by the Medical Research Council of Canada; Faculty Development Award, DG-262, 263 & 264 (KSP); and by a USPHS Grant GM-13901 (RNS).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, K.S., Stillwell, R.N. An understanding of the role of enzyme localization of the liver on metabolite kinetics: A computer simulation. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 11, 451–468 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062205
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062205