Summary
The ability of a fatty-alcohol matrix, slow-release tablet of nifedipine 60 mg to maintain a 24-hour antiischaemic action in the fixed dose of 60 mg once daily has been investigated in a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial.
12 normotensive patients with angiographically proven coronary artery disease (stenosis of at least one major vessel ≥ 70%) were studied. The anti-ischaemic response was assessed over a period of 4 days as changes in the exercise-induced ST-segment depression 6 h and 24 h postdose, and ST segment changes in 24-h ambulatory ECGs.
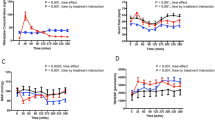
A measurable anti-ischaemic response was observed in 8 of the 12 patients. Exercise-induced ST-segment depression 6 h after the administration of nifedipine was reduced by 30% compared to placebo, and there was still a measurable anti-ischaemic response 24-h post-dosing. Both responses were independent of changes in exercise blood pressure. In 7 patients with ischaemic episodes in the 24-h ECGs, nifedipine treatment had only a minor effect on the intensity and duration of ischaemia.
It is concluded that a significant anti-ischaemic effect lasting 24 h could be demonstrated using effort-induced ST-segment changes in patients with angiographically proven coronary heart disease, who were treated once daily with nifedipine 60 mg as a fatty-alcohol slow release tablet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moskowitz RM, Piccini PA, Nacarelli GV, Zelis R (1979) Nifedipine therapy for stable angina pectoris: preliminary results of effects on angina frequency and treadmill exercise response. Am J Cardiol 44:811–816
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, van de Linde JA, Voogd PJ, Breimer DD (1984) Nifedipine: Kinetics and dynamics in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 35:742–749
Vetrovec GW, Parker VE, Cole S, Procacci PM, Tabatznik B, Terry R (1987) Nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system in stable angina pectoris. Am J Med 83 [Suppl 6B]: 24–29
Woodcock BG, Menke G, Fischer A, Köhne H, Rietbrock N (1988) Drug input rate from the GI-tract. Michaelis-Menten kinetics and the bioavailability of slow release verapamil and nifedipine. Drug Design Delivery 2: 298–309
Raftery EB, Brigden G, Woodcock BG (1990) 24-Stunden Blutdruckprofile eines langwirkenden Nifedipinpräparates unter Anwendung intraarterieller Blutdruckmessungen. In: Deutsche Liga zur Bekämpfung des Bluthochdrucks (ed) Abstracts der 3. Nationalen Blutdruck-Konferenz, Heidelberg, S 81
Feris JV, McHenry PL, Morris SN (1978) Concepts and applications of treadmill exercise testing and the exercise electrocardiogram. Am Heart J 95: 102–114
Kaltenbach M, Klepzig H, Tschirdewahn B (1964) Die Kletterstufe, eine einfache Vorrichtung für exakt meβbare und reproduzierbare Belastungsuntersuchungen. Med Klin 59: 248–254
Thürmann P, Odenthal HJ, Reitbrock N (1991) Converting enzyme inhibition in coronary artery disease: A randomised placebo-controlled trial with benazepril. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17: 718–723
Nayler WG (1988) Calcium Antagonists. Academic Press, London San Diego, pp 177–192
Vetrovec GW (1989) Once-daily therapy for angina pectoris with nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system. Am J Med 86 [Suppl 1A]: 29–32
Deanfield J, Wright C, Fox K (1983) Treatment of angina pectoris with nifedipine: importance of dose titration. Br Med J 286: 1467–1470
Bacracheva N, Thürmann P, Rietbrock N (1990) Dose adjustment of nifedipine in hypertensive patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 38: 17–20
Caitman BR, Wagniart P, Pasternac A, Brevers G, Scholl JM, Lam J, Methe M, Ferguson RJ, Bourassa MG (1984) Improved exercise tolerance after propranolol, diltiazem or nifedipine in angina pectoris: comparison at 1, 3 and 8 hours and correlation with plasma drug concentration. Am J Cardiol 53: 1–9
Ardissino D, De Servi S, Salerno JA, Specchia G, Prevital M, Mussini A, Bobba P (1983) Efficacy, duration and mechanism of action of nifedipine in stable exercise-induced angina pectoris. Eur Heart J 4: 873–881
Khurmi NS, Raftery EB (1988) Lack of diurnal variation in maximal symptom e-limited exercise test response in chronic stable angina. Am J Cardiol 61: 38–42
Mulcahy D, Keegan J, Crean P, Quyyumi A, Shapiro L, Wright C, Fox K (1988) Silent myocardial ischaemia in chronic stable angina: a study of its frequency and characteristics in 150 patients. Br Heart J 60: 417–423
Fox KM, Mulcahy DA (1990) Circadian variation of the total ischemic burden and influence byβ-blocking agents. J Cardiovase Pharmacol 16 [Suppl 5]: S100–104
Shell WE, Dobson D (1990) Dissociaton of exercise tolerance and total myocardial ischemic burden in chronic stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 66: 42–48
von Arnim T (1987) Influence of isosorbide-5-mononitrate 20 mg, sustained-release 50 mg and sustained-release nifedipine 20 mg on ischaemic ST segment changes during holter monitoring. Cardiology 74 [Suppl 1]: 40–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woodcock, B.G., Thürmann, P.A., Pfleiderer, S. et al. 24-hour anti-ischaemic action with once daily nifedipine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 43, 587–590 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02284955
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02284955