Summary
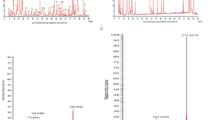
Guanfu base A is a novel arrhythmic drug candidate isolated from the tuber of a traditional Chinese herb. Phase I and Phase II metabolites of Guanfu base A (GFA) Hydrochloride were studied in human urine by means of liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC/MSD) and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). For phase I metabolites, Guanfu base I (GFI) was separated by HPLC and identified by comparison with authentic reference for their retention times, molecular ion peaks, fragment ions, and UV spectra. GFA oxide was also indicate to exist in human urine. For phase II metabolites, after human urine was treated either with glucuronidase or sulfatase, GFA occured in the chromatograms. It was suggested that there were GFA glucuronide and GFA sulfate in human urine. Further more, positive molecular ions, m/z 606 and m/z 510, of the two conjugates were detected in human urine by LC/MSD. In addition, characteristic ion of m/z 606 was identified as the precursor ion of m/z 177 [Glucuronic acid+H]+ by using MS/MS. Characteristic ion of m/z 430 [GFA+H]+ was also identified as a product ion of m/z 606 [GFA glucuronide+H]+. It was concluded that there were GFI, GFA oxide, GFA glucuronide and GFA sulfate in human urine.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GFA:
-
guanfu base A
- GFI:
-
guanfu base I
- AA:
-
guanfu alcohol amine
- LC/MSD:
-
liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
- ESI:
-
electrospray ionization
- CID:
-
collision-induced dissociation
- TIC:
-
total ion chromatogram
- MS/MS:
-
tandem mass spectrometry
References
Liu J.H., Wang H.C., Gao Y.L., Zhu R.H., (1981): The study of Chinese Aconitum coreanum (Levl.) Raipaics XVI. A new alkaloid in the tuber of Aconitum coreanum. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 12: 1–2.
Hou D.H., Li L., Wang Q.J., Liu J.H., (1981): The effect of guanfu base A on experimental cardiac arrhythmias. J Nanjing Pharm Coll 17: 68–74.
Dong Y.L., Chen W.Z., (1995): Effects of guanfu base A on experimental cardiac arrhythmias and myocardial contractility. Acta Pharm Sin 30: 577–582.
Chen W.Z., Dong Y.L., Zhang Y.F., Ding G.S., (1983): Anti-arrhythmic effects of guanfu base A. Acta Pharmacol Sin 4: 247–250.
Wang Y.P., Chen W.Z., Gu P.K., (1990): Effects of guan-fu base A on spontaneous rate of isolated sinoatrial node of guinea pig. Acta Pharmacol Sin 11: 502–505.
Chen H.Z., Chen W.Z., Gu P.K., Zhang L., Jin Z.J., (1989): Effects of guan-fu base A on fact response action potentials of papillary muscles of guinea pigs. Acta Pharmacol Sin 10: 399–401.
Zhang L., Gu P.K., Zhao W.B., Chen Y.L., Zhang J.X., Jin Z.J., (1986): Effect of guan-fu base A on action potential of canine Purkinje fibers. Acta Pharmacol Sin 7: 234–236.
AJ.Y., Wang G.J., Wu M.S. and Liu J.H., (2002): Identification of guanfu base A hydrochloride phase I and phase II metabolites in rat bile by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Acta Pharmacol Sin 23: 1045–1050.
A J.Y., Wang G.J., Liu X.Q., Jiang D.Y. and Liu J.H., (2002): Studies on metabolites of guanfu base A hydrochloride in rat urine by liquid chromatography-mass spectrum. Acta Pharm Sin 37: 283–287.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
A J. Y., Wang, G.J., Sun, J.G. et al. Identification of Phase I and Phase II metabolites of Guanfu base a Hydrochloride in human urine. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 28, 265–272 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220178
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220178