Abstract
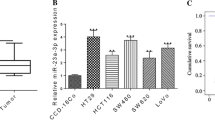
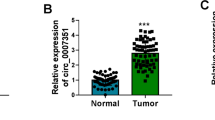
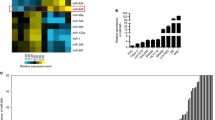
Studies have shown that the expression of CD133, leucine-rich-repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 (Lgr5), and ATP binding cassette (ABC)G2 proteins is associated with malignancy and poor prognosis in colon cancer. However, molecular regulation mechanism of the three proteins has not been elucidated. Here, we report that microRNA-142-3p (miR-142-3p) inhibits the expression of CD133, Lgr5, and ABCG2 in colon cancer cells by binding to both the 3′-untranslated region and the coding sequences of the three genes. The miR-142-3p was markedly decreased in colon cancer specimens, in which it was negatively correlated with the expression of CD133, Lgr5, and ABCG2. Reduction of miR-142-3p corresponds to poor differentiation and bigger tumor size in colon cancers. Moreover, miR-142-3p levels were reduced in cells that formed spheres compared to cells that were cultured in regular media. Transfection of miR-142-3p mimics in colon cancer cells downregulated cyclin D1 expression, induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest, and elevated the sensitivity of the cells to 5-fluorouracil. Furthermore, OCT4 suppressed miR-142-3p, and hypomethylation of the OCT4 promoter was associated with a reduction in miR-142-3p. Finally, the miR-142-3p inhibited the growth of colon cancer cells in vivo, which was accompanied by the downregulation of CD133, Lgr5, and ABCG2 in tumor tissues. Our results elucidate a novel regulation pathway in colon cancer cells and suggest a potential therapeutic approach for colon cancer therapy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127:2893–2917. doi:10.1002/ijc.25516
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E, Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C, De Maria R (2007) Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 445:111–115. doi:10.1038/nature05384
Kobayashi S, Yamada-Okabe H, Suzuki M, Natori O, Kato A, Matsubara K, Jau Chen Y, Yamazaki M, Funahashi S, Yoshida K et al (2012) LGR5-positive colon cancer stem cells interconvert with drug-resistant LGR5-negative cells and are capable of tumor reconstitution. Stem Cells 30:2631–2644. doi:10.1002/stem.1257
Zhu MM, Tong JL, Xu Q, Nie F, Xu XT, Xiao SD, Ran ZH (2012) Increased JNK1 signaling pathway is responsible for ABCG2-mediated multidrug resistance in human colon cancer. PLoS One 7:e41763. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041763
Marshman E, Booth C, Potten CS (2002) The intestinal epithelial stem cell. Bioessays 24:91–98. doi:10.1002/bies.10028
Yu X, Lin Y, Yan X, Tian Q, Li L, Lin EH (2011) CD133, stem cells, and cancer stem cells: myth or reality. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep 7:253–259. doi:10.1007/s11888-011-0106-1
O’Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S, Dick JE (2007) A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature 445:106–110. doi:10.1038/nature05372
Bruno S, Bussolati B, Grange C, Collino F, Graziano ME, Ferrando U, Camussi G (2006) CD133+ renal progenitor cells contribute to tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 169:2223–2235. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.060498
Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ et al (2007) Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 449:1003–1007. doi:10.1038/nature06196
Zeki SS, Graham TA, Wright NA (2011) Stem cells and their implications for colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:90–100. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2010.211
Walker F, Zhang HH, Odorizzi A, Burgess AW (2011) LGR5 is a negative regulator of tumourigenicity, antagonizes Wnt signalling and regulates cell adhesion in colorectal cancer cell lines. PLoS One 6:e22733. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022733
Ding XW, Wu JH, Jiang CP (2010) ABCG2: a potential marker of stem cells and novel target in stem cell and cancer therapy. Life Sci 86:631–637. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2010.02.012
Zhou S, Schuetz JD, Bunting KD, Colapietro AM, Sampath J, Morris JJ, Lagutina I, Grosveld GC, Osawa M, Nakauchi H et al (2001) The ABC transporter Bcrp1/ABCG2 is expressed in a wide variety of stem cells and is a molecular determinant of the side-population phenotype. Nat Med 7:1028–1034. doi:10.1038/nm0901-1028
Kanwar SS, Yu Y, Nautiyal J, Patel BB, Padhye S, Sarkar FH, Majumdar AP (2011) Difluorinated-curcumin (CDF): a novel curcumin analog is a potent inhibitor of colon cancer stem-like cells. Pharm Res 28:827–838. doi:10.1007/s11095-010-0336-y
Zhou S, Morris JJ, Barnes Y, Lan L, Schuetz JD, Sorrentino BP (2002) Bcrp1 gene expression is required for normal numbers of side population stem cells in mice, and confers relative protection to mitoxantrone in hematopoietic cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:12339–12344. doi:10.1073/pnas.192276999
Leal JA, Lleonart ME (2012) MicroRNAs and cancer stem cells: therapeutic approaches and future perspectives. Cancer Lett. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.04.020
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong C, Huang Y, Hu X, Su F, Lieberman J et al (2007) Let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 131:1109–1123. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.054
Xi Y, Formentini A, Chien M, Weir DB, Russo JJ, Ju J, Kornmann M (2006) Prognostic values of microRNAs in colorectal cancer. Biomark Insights 2:113–121
Cummins JM, He Y, Leary RJ, Pagliarini R, Diaz LA Jr, Sjoblom T, Barad O, Bentwich Z, Szafranska AE, Labourier E et al (2006) The colorectal microRNAome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:3687–3692. doi:10.1073/pnas.0511155103
Shen WW, Wu J, Cai L, Liu BY, Gao Y, Chen GQ, Fu GH (2007) Expression of anion exchanger 1 sequestrates p16 in the cytoplasm in gastric and colonic adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia 9:812–819
Yang YC, Wang SW, Hung HY, Chang CC, Wu IC, Huang YL, Lin TM, Tsai JL, Chen A, Kuo FC et al (2007) Isolation and characterization of human gastric cell lines with stem cell phenotypes. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22:1460–1468. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05031.x
Deb-Rinker P, Ly D, Jezierski A, Sikorska M, Walker PR (2005) Sequential DNA methylation of the Nanog and Oct-4 upstream regions in human NT2 cells during neuronal differentiation. J Biol Chem 280:6257–6260. doi:10.1074/jbc.C400479200
Faurez F, Dory D, Le Moigne V, Gravier R, Jestin A (2010) Biosafety of DNA vaccines: new generation of DNA vectors and current knowledge on the fate of plasmids after injection. Vaccine 28:3888–3895. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.03.040
Levy MY, Barron LG, Meyer KB, Szoka FC Jr (1996) Characterization of plasmid DNA transfer into mouse skeletal muscle: evaluation of uptake mechanism, expression and secretion of gene products into blood. Gene Ther 3:201–211
Suo WH, Zhang N, Wu PP, Zhao L, Song LJ, Shen WW, Zheng L, Tao J, Long XD, Fu GH (2012) Anti-tumour effects of small interfering RNA targeting anion exchanger 1 in experimental gastric cancer. Br J Pharmacol 165:135–147. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01521.x
Ernst A, Aigner M, Nakata S, Engel F, Schlotter M, Kloor M, Brand K, Schmitt S, Steinert G, Rahbari N et al (2011) A gene signature distinguishing CD133hi from CD133− colorectal cancer cells: essential role for EGR1 and downstream factors. Pathology 43:220–227. doi:10.1097/PAT.0b013e328344e391
Zhang L, Jin M, Margariti A, Wang G, Luo Z, Zampetaki A, Zeng L, Ye S, Zhu J, Xiao Q (2010) Sp1-dependent activation of HDAC7 is required for platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced smooth muscle cell differentiation from stem cells. J Biol Chem 285:38463–38472. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.153999
Sarkar S, Swiercz R, Kantara C, Hajjar KA, Singh P (2011) Annexin A2 mediates up-regulation of NF-kappaB, beta-catenin, and stem cell in response to progastrin in mice and HEK-293 cells. Gastroenterology 140(583–595):e584. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.08.054
Wierenga AT, Vellenga E, Schuringa JJ (2010) Down-regulation of GATA1 uncouples STAT5-induced erythroid differentiation from stem/progenitor cell proliferation. Blood 115:4367–4376. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-10-250894
Jia Y, Yao H, Zhou J, Chen L, Zeng Q, Yuan H, Shi L, Nan X, Wang Y, Yue W et al (2011) Role of epimorphin in bile duct formation of rat liver epithelial stem-like cells: involvement of small G protein RhoA and C/EBPbeta. J Cell Physiol 226:2807–2816. doi:10.1002/jcp.22625
Song B, Wang Y, Titmus MA, Botchkina G, Formentini A, Kornmann M, Ju J (2010) Molecular mechanism of chemoresistance by miR-215 in osteosarcoma and colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer 9:96. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-96
King CE, Wang L, Winograd R, Madison BB, Mongroo PS, Johnstone CN, Rustgi AK (2011) LIN28B fosters colon cancer migration, invasion and transformation through let-7-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Oncogene 30:4185–4193. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.131
Wang XY, Wu MH, Liu F, Li Y, Li N, Li GY, Shen SR (2010) Differential miRNA expression and their target genes between NGX6-positive and negative colon cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 345:283–290. doi:10.1007/s11010-010-0582-7
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO81101845), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (NO11YZ54), and Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau (NO2010Y006).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 53 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, WW., Zeng, Z., Zhu, WX. et al. MiR-142-3p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting CD133, ABCG2, and Lgr5 in colon cancer cells. J Mol Med 91, 989–1000 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1037-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1037-x