Abstract
Rationale
Methadone maintenance treatment is complicated by the wide variability of efficacy among patients. The large interindividual variability of the plasma concentrations of methadone was previously thought to be responsible for the variable therapeutic efficacy. However, recent studies suggested that methadone may be a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). Therefore, the function of P-gp in blood–brain barrier (BBB) may affect the concentration of methadone at its site(s) of action in the central nervous system, thereby contributing to its therapeutic efficacy and/or adverse events.
Objective
To investigate the effect of P-gp on brain penetration of methadone (R)- and (S)-enantiomers and their major oxidative metabolite 2-ethylidene-1,5-dimethyl-3,3-diphenylpyrrolidine (EDDP).
Methods
We compared the tissue distribution of methadone (R)- and (S)-enantiomers and EDDP in the Abcb1a−/− gene knockout mice and the Abcb1a+/+ wild-type mice 1 h following intraperitoneal administration of 15 μg Rac-methadone/g mouse.
Results
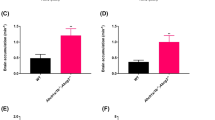
Plasma concentrations of (R)- and (S)-methadone were similar between the two animal groups. However, the brain concentrations of (R)- and (S)-methadone in the Abcb1a−/− mice were markedly higher (15- and 23-fold, respectively, P<0.0001) than those of the Abcb1a+/+ wild-type mice. No statistically significant difference was found for other organs between the mutants and controls. No organ difference was found for EDDP between the mutants and controls.
Conclusions
(R)- and (S)-methadone are substrates of P-gp. The P-gp in BBB greatly limits the brain entry of (R)- and (S)-methadone to their central nervous system acting sites. The interindividual variation in expression of P-gp in BBB may represent a source of variation for the access and effects of methadone in the brain.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aquilante CL, Letrent SP, Pollack GM, Brouwer KL (2000) Increased brain P-glycoprotein in morphine tolerant rats. Life Sci 64:47–51
Bell J, Bowron P, Lewis J, Batey R (1990) Serum levels of methadone in maintenance clients who persist in illicit drug use. Br J Addict 85:1599–1602
Bouer R, Barthe L, Philibert C, Tournaire C, Woodley J, Houin G (1999) The roles of P-glycoprotein and intracellular metabolism in the intestinal absorption of methadone: in vitro studies using the rat everted intestinal sac. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 13:494–500
Boulton DW, DeVane C (2000) Development and application of a chiral high-performance liquid chromatography assay for pharmacokinetic studies of methadone. Chirality 12:681–687
Boulton DW, Arnaud P, DeVane CL (2001) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methadone enantiomers after a single oral dose of racemate. Clin Pharmacol Ther 70:48–57
Choo EF, Leake B, Wandel C, Imamura H, Wood AJ, Wilkinson GR, Kim RB (2000) Pharmacological inhibition of P-glycoprotein transport enhances the distribution of HIV-1 protease inhibitors into brain and testes. Drug Metab Dispos 28:655–660
Cordon-Cardo C, O’Brien JP, Casals D, Rittman-Grauer L, Biedler JL, Melamed MR, Bertino JR (1989) Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood-brain barrier sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:695–698
Eap CB, Bourquin M, Martin J, Spagnoli J, Livoti S, Powell K, Baumann P, Deglon J (2000) Plasma concentrations of the enantiomers of methadone and therapeutic response in methadone maintenance treatment. Drug Alcohol Depend 61:47–54
Eap CB, Buclin T, Baumann P (2002) Interindividual variability of the clinical pharmacokinetics of methadone: implications for the treatment of opioid dependence. Clin Pharmacokinet 41:1153–1193
Farrell M, Ward J, Mattick R, Hall W, Stimson GV, des Jarlais D, Gossop M, Strang J (1994) Methadone maintenance treatment in opiate dependence: a review. BMJ 309:997–1001
Foster DJ, Somogyi AA, Bochner F (1999) Methadone N-demethylation in human liver microsomes: lack of stereoselectivity and involvement of CYP3A4. Br J Clin Pharmacol 47:403–412
Fromm MF (2000) P-glycoprotein: a defense mechanism limiting oral bioavailability and CNS accumulation of drugs. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 38:69–74
Garrido MJ, Troconiz IF (1999) Methadone: a review of its pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic properties. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 42:61–66
Hagen NA, Wasylenko E (1999) Methadone: outpatient titration and monitoring strategies in cancer patients. J Pain Symptom Manage 18:369–375
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmoller J, Johne A, Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Roots I, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U (2000) Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:3473–3478
Holash JA, Harik SI, Perry G, Stewart PA (1993) Barrier properties of testis microvessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:11069–11073
Johnson RE, Chutuape MA, Strain EC, Walsh SL, Stitzer ML, Bigelow GE (2000) A comparison of levomethadyl acetate, buprenorphine, and methadone for opioid dependence. N Engl J Med 343:1290–1297
Kim RB, Fromm MF, Wandel C, Leake B, Wood AJ, Roden DM, Wilkinson GR (1998) The drug transporter P-glycoprotein limits oral absorption and brain entry of HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J Clin Invest 101:289–294
Kreek MJ, Oratz M, Rothschild MA (1978) Hepatic extraction of long- and short-acting narcotics in the isolated perfused rabbit liver. Gastroenterology 75:88–94
Kristensen K, Christensen CB, Christrup LL (1995) The mu1, mu2, delta, kappa opioid receptor binding profiles of methadone stereoisomers and morphine. Life Sci 56:PL45–PL50
Kurata Y, Ieiri I, Kimura M, Morita T, Irie S, Urae A, Ohdo S, Ohtani H, Sawada Y, Higuchi S, Otsubo K (2002) Role of human MDR1 gene polymorphism in bioavailability and interaction of digoxin, a substrate of P-glycoprotein. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72:209–219
Letrent SP, Pollack GM, Brouwer KR, Brouwer KL (1999) Effects of a potent and specific P-glycoprotein inhibitor on the blood–brain barrier distribution and antinociceptive effect of morphine in the rat. Drug Metab Dispos 27:827–834
Lin JH, Yamazaki M (2003) Role of p-glycoprotein in pharmacokinetics: clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet 42:59–98
Ling W, Wesson DR, Charuvastra C, Klett CJ (1996) A controlled trial comparing buprenorphine and methadone maintenance in opioid dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:401–407
Loimer N, Schmid R, Grunberger J, Jagsch R, Linzmayer L, Presslich O (1991) Psychophysiological reactions in methadone maintenance patients do not correlate with methadone plasma levels. Psychopharmacology 103:538–540
Lotsch J, Schmidt R, Vetter G, Schmidt H, Niederberger E, Geisslinger G, Tegeder I (2002) Increased CNS uptake and enhanced antinociception of morphine-6-glucuronide in rats after inhibition of P-glycoprotein. J Neurochem 83:241–248
Mahar Doan KM, Humphreys JE, Webster LO, Wring SA, Shampine LJ, Serabjit-Singh CJ, Adkison KK, Polli JW (2002) Passive permeability and P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux differentiate central nervous system (CNS) and non-CNS marketed drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:1029–1037
Nakamura T, Sakaeda T, Horinouchi M, Tamura T, Aoyama N, Shirakawa T, Matsuo M, Kasuga M, Okumura K (2002) Effect of the mutation (C3435T) at exon 26 of the MDR1 gene on expression level of MDR1 messenger ribonucleic acid in duodenal enterocytes of healthy Japanese subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 71:297–303
Polli JW, Wring SA, Humphreys JE, Huang L, Morgan JB, Webster LO, Serabjit-Singh CS (2001) Rational use of in vitro P-glycoprotein assays in drug discovery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:620–628
Potschka H, Loscher W (2001) In vivo evidence for P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of phenytoin at the blood–brain barrier of rats. Epilepsia 42:1231–1240
Potschka H, Fedrowitz M, Loscher W (2001) P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein are involved in the regulation of extracellular levels of the major antiepileptic drug carbamazepine in the brain. Neuroreport 12:3557-3560
Potschka H, Fedrowitz M, Loscher W (2002) P-Glycoprotein-mediated efflux of phenobarbital, lamotrigine, and felbamate at the blood–brain barrier: evidence from microdialysis experiments in rats. Neurosci Lett 327:173-176
Preston KL, Umbricht A, Epstein DH (2000) Methadone dose increase and abstinence reinforcement for treatment of continued heroin use during methadone maintenance. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:395–404
Rhoades HM, Creson D, Elk R, Schmitz J, Grabowski J (1998) Retention, HIV risk, and illicit drug use during treatment: methadone dose and visit frequency. Am J Public Health 88:34–39
Riordan JR, Deuchars K, Kartner N, Alon N, Trent J, Ling V (1985) Amplification of P-glycoprotein genes in multidrug-resistant mammalian cell lines. Nature 316:817–819
Schinkel AH, Smit JJ, van Tellingen O, Beijnen JH, Wagenaar E, van Deemter L, Mol CA, van der Valk MA, Robanus-Maandag EC, te Riele HPJ, Berns AJM, Borst P (1994) Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood–brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell 77:491–502
Schinkel AH, Wagenaar E, Mol CA, van Deemter L (1996) P-glycoprotein in the blood–brain barrier of mice influences the brain penetration and pharmacological activity of many drugs. J Clin Invest 97:2517–2524
Schinkel AH, Mayer U, Wagenaar E, Mol CA, van Deemter L, Smit JJ, van der Valk MA, Voordouw AC, Spits H, van Tellingen O, Zijlmans JM, Fibbe WE, Borst P (1997) Normal viability and altered pharmacokinetics in mice lacking mdr1-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:4028–4033
Scott CC, Robbins EB, Chen KK (1948) Pharmacologic comparison of the optical isomers of methadone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 93:282–286
Shah NS, Donald AG, Bertolatus JA, Hixson B (1976) Tissue distribution of levo-methadone in nonpregnant and female and male mice: effect of SKF 525-A 1,2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199:103–116
Siddiqui A, Kerb R, Weale ME, Brinkmann U, Smith A, Goldstein DB, Wood NW, Sisodiya SM (2003) Association of multidrug resistance in epilepsy with a polymorphism in the drug-transporter gene ABCB1. N Engl J Med 348:1442–1448
Silverman JA (2000) P-glycoprotein. In: Levy R (ed) Metabolic drug interactions. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 135–144
Strain EC, Bigelow GE, Liebson IA, Stitzer ML (1999) Moderate- vs high-dose methadone in the treatment of opioid dependence: a randomized trial. JAMA 281:1000–1005
Sullivan HR, Due SL (1973) Urinary metabolites of dl-methadone in maintenance subjects. J Med Chem 16:909–913
Thompson SJ, Koszdin K, Bernards CM (2000) Opiate-induced analgesia is increased and prolonged in mice lacking P-glycoprotein. Anesthesiology 92:1392–1399
Uhr M, Grauer MT (2003) abcb1ab P-glycoprotein is involved in the uptake of citalopram and trimipramine into the brain of mice. J Psychiatr Res 37:179–185
Uhr M, Steckler T, Yassouridis A, Holsboer F (2000) Penetration of amitriptyline, but not of fluoxetine, into brain is enhanced in mice with blood–brain barrier deficiency due to mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene disruption. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:380–387
Uhr M, Holsboer F, Muller MB (2002) Penetration of endogenous steroid hormones corticosterone, cortisol, aldosterone and progesterone into the brain is enhanced in mice deficient for both mdr1a and mdr1b P-glycoproteins. J Neuroendocrinol 14:753–759
Umbenhauer DR, Lankas GR, Pippert TR, Wise LD, Cartwright ME, Hall SJ, Beare CM (1997) Identification of a P-glycoprotein-deficient subpopulation in the CF-1 mouse strain using a restriction fragment length polymorphism. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 146:88–94
Wang JS, DeVane CL (2003) Involvement of CYP3A4, CYP2C8, and CYP2D6 in the metabolism of (R)- and (S)-methadone in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos 31:742–747
Wang JS, Taylor R, Runa Y, Donovan LJ, Markowitz SJ, DeVane CL (2004) Olanzapine penetration into brain is greater in transgenic mdr1a p-glycoprotein deficient mice than FVB1 (wild type) animals. Neuropsychopharmacology (in press)
Yu DK (1999) The contribution of P-glycoprotein to pharmacokinetic drug–drug interactions. J Clin Pharmacol 39:1203–1211
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by Public Health Service grant DA-13027. None of the authors has conflicting interests that interfere with the integrity of the content of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JS., Ruan, Y., Taylor, R.M. et al. Brain penetration of methadone (R)- and (S)-enantiomers is greatly increased by P-glycoprotein deficiency in the blood–brain barrier of Abcb1a gene knockout mice. Psychopharmacology 173, 132–138 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1718-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1718-1