Abstract
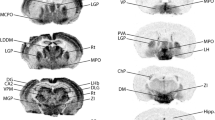
The signaling action of neuropeptides in the brain is terminated by breakdown through extracellular peptidases and subsequent removal of the peptide fragments from the extracellular fluid via specific transporter proteins. Here we describe the anatomical distribution in the rat nervous system of the recently isolated high affinity peptide transporter PEPT2. Using nonisotopic in situ hybridization we demonstrate that PEPT2 mRNA is expressed in brain by astrocytes, subependymal cells, ependymal cells and epithelial cells of choroid plexus. Furthermore, PEPT2 is expressed in retina by Müller cells and in dorsal root ganglia by satellite cells. The mRNA levels of PEPT2 in astrocytes are moderate and relatively homogenous throughout the brain except for an area in ventral forebrain where PEPT2 levels are below average. PEPT2 mRNA expression is weakly upregulated in reactive astrocytes that were stimulated through an injection of the glutamatergic neurotoxin quinolinic acid. These data suggest that removal of neuropeptide fragments from brain extracellular fluid occurs via PEPT2 expressed in astrocytes, ependymal cells and choroid plexus epithelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 26 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, U., Hediger, M. Distribution of peptide transporter PEPT2 mRNA in the rat nervous system. Anat Embryol 199, 439–449 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004290050242
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004290050242