Abstract
Purpose
Hydroxylation of the antidepressant and smoking deterrent drug bupropion is a clinically important bioactivation and elimination pathway. Bupropion hydroxylation is catalyzed selectively by cytochrome P4502B6 (CYP2B6). CYP2B6-catalyzed bupropion hydroxylation has been used as an in vitro and in vivo phenotypic probe for CYP2B6 activity and CYP2B6 drug interactions. Bupropion is chiral, used clinically as a racemate, and disposition is stereoselective. Nevertheless, it is unknown whether CYP2B6-catalyzed bupropion hydroxylation is stereoselective.
Methods
Hydroxylation of racemic bupropion by recombinant CYP2B6 and human liver microsomes was evaluated using a stereoselective assay.
Results
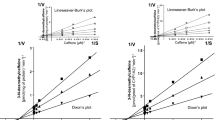
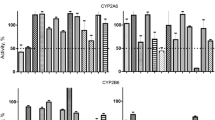
At therapeutic concentrations, hydroxylation of (S)-bupropion was threefold and 1.5-greater than (R)-bupropion, respectively, by recombinant CYP2B6 and human liver microsomes. In vitro intrinsic clearances were likewise different for bupropion enantiomers.
Conclusions
Stereoselective bupropion hydroxylation may have implications for the therapeutic efficacy of bupropion as an antidepressant or smoking cessation therapy, and for the use of bupropion as an in vivo phenotypic probe for CYP2B6 activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CYP2B6:
-
cytochrome P4502B6
- LC-MS/MS:
-
liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
References
A. A. Lai, and D.H. Schroeder. Clinical pharmacokinetics of bupropion: a review. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 44:82–84 (1983).
M. L. Bondarev, T. S. Bondareva, R. Young, and R. A. Glennon. Behavioral and biochemical investigations of bupropion metabolites. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 474:85–93 (2003).
M. I. Damaj, F. I. Carroll, J. B. Eaton, H. A. Navarro, B. E. Blough, S. Mirza, R. J. Lukas, and B. R. Martin. Enantioselective effects of hydroxy metabolites of bupropion on behavior and on function of monoamine transporters and nicotinic receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 66:675–682 (2004).
S. Palovaara, O. Pelkonen, J. Uusitalo, S. Lundgren, and K. Laine. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 2B6 activity by hormone replacement therapy and oral contraceptive as measured by bupropion hydroxylation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 74:326–333 (2003).
J. W. Jefferson, J. F. Pradko, and K. T. Muir. Bupropion for major depressive disorder: Pharmacokinetic and formulation considerations. Clin. Ther. 27:1685–1695 (2005).
R. F. Suckow, M. F. Zhang, and T. B. Cooper. Enantiomeric determination of the phenylmorpholinol metabolite of bupropion in human plasma using coupled achiral–chiral liquid chromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr. 11:174–179 (1997).
H. Xu, K. K. Loboz, A. S. Gross, and A. J. McLachlan. Stereoselective analysis of hydroxybupropion and application to drug interaction studies. Chirality 19:163–170 (2007).
R. Coles, and E. D. Kharasch. Stereoselective analysis of bupropion and hydroxybupropion in human plasma and urine by LC/MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B. 857:67–75 (2007).
L. M. Hesse, K. Venkatakrishnan, M. H. Court, L. L. von Moltke, S. X. Duan, R. I. Shader, and D. J. Greenblatt. CYP2B6 mediates the in vitro hydroxylation of bupropion: potential drug interactions with other antidepressants. Drug Metab. Dispos. 28:1176–1183 (2000).
S. R. Faucette, R. L. Hawke, E. L. Lecluyse, S. S. Shord, B. Yan, R. M. Laethem, and C. M. Lindley. Validation of bupropion hydroxylation as a selective marker of human cytochrome P450 2B6 catalytic activity. Drug Metab. Dispos. 28:1222–1230 (2000).
S. R. Faucette, R. L. Hawke, S. S. Shord, E. L. Lecluyse, and C. M. Lindley. Evaluation of the contribution of cytochrome P450 3A4 to human liver microsomal bupropion hydroxylation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 29:1123–1129 (2001).
A. M. Lee, C. Jepson, E. Hoffmann, L. Epstein, L. W. Hawk, C. Lerman, and R. F. Tyndale. CYP2B6 genotype alters abstinence rates in a bupropion smoking cessation trial. Biol. Psychiatry 62:635–641 (2007).
S. Ekins, and S. A. Wrighton. The role of CYP2B6 in human xenobiotic metabolism. Drug Metab. Rev. 31:719–754 (1999).
M. Turpeinen, H. Raunio, and O. Pelkonen. The functional role of CYP2B6 in human drug metabolism: substrates and inhibitors in vitro, in vivo and in silico. Curr. Drug Metab. 7:705–714 (2006).
C. Sridar, U. M. Kent, L. M. Notley, E. M. Gillam, and P. F. Hollenberg. Effect of tamoxifen on the enzymatic activity of human cytochrome CYP2B6. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301:945–952 (2002).
E. D. Kharasch, C. Hoffer, D. Whittington, and P. Sheffels. Role of hepatic and intestinal cytochrome CYP3A and CYP2B6 in the metabolism, disposition and miotic effects of methadone. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 76:250–269 (2004).
R. A. Totah, K. E. Allen, P. Sheffels, D. Whittington, and E. D. Kharasch. Enantiomeric metabolic interactions and stereoselective human methadone metabolism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 321:389–399 (2007).
D. Nolan, E. Phillips, and S. Mallal. Efavirenz and CYP2B6 polymorphism: implications for drug toxicity and resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 42:408–410 (2006).
U. M. Zanger, K. Klein, T. Saussele, J. Blievernicht, M. H. Hoffman, and M. Schwab. Polymorphic CYP2B6: molecular mechanisms and emerging clinical significance. Pharmacogenomics 8:743–759 (2007).
L. M. Hesse, Y. Sakai, D. Vishnuvardhan, A. P. Li, L. L. Von Moltke, and D. J. Greenblatt. Effect of bupropion on CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 catalytic activity, immunoreactive protein and mRNA levels in primary human hepatocytes: comparison with rifampicin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 55:1229–1239 (2003).
S. R. Faucette, H. Wang, G. A. Hamilton, S. L. Jolley, D. Gilbert, C. Lindley, B. Yan, M. Negishi, and E. L. LeCluyse. Regulation of CYP2B6 in primary human hepatocytes by prototypical inducers. Drug Metab. Dispos. 32:348–358 (2004).
K. K. Loboz, A. S. Gross, K. M. Williams, W. S. Liauw, R. O. Day, J. K. Blievernicht, U. M. Zanger, and A. J. McLachlan. Cytochrome P450 2B6 activity as measured by bupropion hydroxylation: Effect of induction by rifampin and ethnicity. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 80:75–84 (2006).
R. L. Walsky, A. V. Astuccio, and R. S. Obach. Evaluation of 227 drugs for in vitro inhibition of cytochrome P450 2B6. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 46:1426–1438 (2006).
M. Turpeinen, R. Nieminen, T. Juntunen, P. Taavitsainen, H. Raunio, and O. Pelkonen. Selective inhibition of CYP2B6-catalyzed bupropion hydroxylation in human liver microsomes in vitro. Drug Metab. Dispos. 32:626–631 (2004).
L. M. Hesse, P. He, S. Krishnaswamy, Q. Hao, K. Hogan, L. L. von Moltke, D. J. Greenblatt, and M. H. Court. Pharmacogenetic determinants of interindividual variability in bupropion hydroxylation by cytochrome P450 2B6 in human liver microsomes. Pharmacogenetics 14:225–238 (2004).
T. Richter, T. E. Murdter, G. Heinkele, J. Pleiss, S. Tatzel, M. Schwab, M. Eichelbaum, and U. M. Zanger. Potent mechanism-based inhibition of human CYP2B6 by clopidogrel and ticlopidine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 308:189–197 (2004).
M. Turpeinen, A. Tolonen, J. Uusitalo, J. Jalonen, O. Pelkonen, and K. Laine. Effect of clopidogrel and ticlopidine on cytochrome P450 2B6 activity as measured by bupropion hydroxylation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 77:553–559 (2005).
J. Kirchheiner, C. Klein, I. Meineke, J. Sasse, U. M. Zanger, T. E. Murdter, I. Roots, and J. Brockmöller. Bupropion and 4-OH-bupropion pharmacokinetics in relation to genetic polymorphisms in CYP2B6. Pharmacogenetics 13:619–626 (2003).
T. M. Klees, P. Sheffels, K. E. Thummel, and E. D. Kharasch. Pharmacogenetic determinants of human liver microsomal alfentanil metabolism and the role of cytochrome P450 3A5. Anesthesiology 102:550–556 (2005).
J. S. Munro, and T. A. Walker. Bupropion hydrochloride: the development of a chiral separation using an ovomucoid column. J. Chromatogr. A. 913:275–282 (2001).
R. L. Walsky, and R. S. Obach. Verification of the selectivity of (+)N-3-benzylnirvanol as a CYP2C19 inhibitor. Drug Metab. Dispos. 31:343 (2003).
A. Petsalo, M. Turpeinen, and A. Tolonen. Identification of bupropion urinary metabolites by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21:2547–2554 (2007).
Q. K. Fang, Z. Han, P. Grover, D. Kessler, C. H. Senanayake*, and S. A. Wald. Rapid access to enantiopure bupropion and its major metabolite by stereospecific nucleophilic substitution on an a-ketotriflate. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 11:3659–3663 (2000).
L. Gervot, B. Rochat, J. C. Gautier, F. Bohnenstengel, H. Kroemer, V. de Berardinis, H. Martin, P. Beaune, and I. de Waziers. Human CYP2B6: Expression, inducibility and catalytic activities. Pharmacogenetics 9:295–306 (1999).
S. Miksys, C. Lerman, P. G. Shields, D. C. Mash, and R. F. Tyndale. Smoking, alcoholism and genetic polymorphisms alter CYP2B6 levels in human brain. Neuropharmacology 45:122–132 (2003).
C. L. DeVane, S. C. Laizure, J. T. Stewart, B. E. Kolts, E. G. Ryerson, R. L. Miller, and A. A. Lai. Disposition of bupropion in healthy volunteers and subjects with alcoholic liver disease. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 10:328–332 (1990).
E. D. Kharasch, D. Mitchell, and R. Coles. Stereoselective bupropion hydroxylation as an in vivo phenotypic probe for CYP2B6 activity. J. Clin. Pharmacol. (in press) (2008).
Acknowledgements
Supported by NIH R01DA14211 and K24DA00417.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coles, R., Kharasch, E.D. Stereoselective Metabolism of Bupropion by Cytochrome P4502B6 (CYP2B6) and Human Liver Microsomes. Pharm Res 25, 1405–1411 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9535-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9535-1