Abstract
Purpose
To characterize the uptake mechanism of zidovudine (AZT), a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, in syncytiotrophoblast cells using the TR-TBT 18d-1 cell line previously established by our group.
Materials and Methods
The effects of several transporter inhibitors on the initial and steady-state apical uptake of AZT by TR-TBT 18d-1 were characterized, in order to identify the transporter(s) involved.
Results
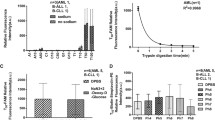
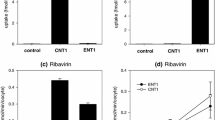
Initial uptake of AZT was sodium-independent and saturable; the K m value was about 16 μM. Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR), probenecid and cimetidine each had little effect on the saturable AZT uptake, indicating that well characterized transporters, such as organic anion transporters (OATs and OATPs), organic cation transporters (OCTs) and equilibrative nucleoside transporters (ENTs), are not involved. However, thymidine and 2′-deoxyuridine strongly inhibited AZT uptake. These results suggest that an unidentified nucleoside uptake transporter is responsible for the uptake of AZT. Cyclosporin A, Ko143 and probenecid had little effect on AZT accumulation by TR-TBT 18d-1 cells, suggesting that transporter-mediated efflux of AZT is not substantial.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that saturable AZT uptake into TR-TBT 18d-1 is mediated by a so-far-unidentified transporter.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AZT:
-
3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine
- BCRP:
-
breast cancer resistance protein
- CNT:
-
concentrative nucleoside transporter
- DHEAS:
-
dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate
- ENT:
-
equilibrative nucleoside transporter
- MRP:
-
multidrug resistance protein
- NMBPR:
-
nitrobenzylthioinosine
- OAT:
-
organic anion transporter
- OATP:
-
organic anion transporting polypeptide
- OCT:
-
organic cation transporter
- PAH:
-
-aminohippuric acid
- P-gp:
-
p-glycoprotein
References
K. Takata, and H. Hirano. Mechanism of glucose transport across the human and rat placental barrier: a review. Microsc. Res. Tech. 38:145–152 (1997).
T. Kitano, H. Iizasa, T. Terasaki, T. Asashima, N. Matsunaga, N. Utoguchi, Y. Watanabe, M. Obinata, M. Ueda, and E. Nakashima. Polarized glucose transporters and mRNA expression properties in newly developed rat syncytiotrophoblast cell lines, TR-TBTs. J. Cell Physiol. 193:208–218 (2002).
T. Kitano, H. Iizasa, I. W. Hwang, Y. Hirose, T. Morita, T. Maeda, and E. Nakashima. Conditionally immortalized syncytiotrophoblast cell lines as new tools for study of the blood-placenta barrier. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 27:753–759 (2004).
G. G. Briggs, R. K. Freeman, and S. J. Yaffe. Drugs in pregnancy and lactation. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, (2005).
M. J. O’Sullivan, P. J. Boyer, G. B. Scott, W. P. Parks, S. Weller, M. R. Blum, J. Balsley, and Y. J. Bryson. The pharmacokinetics and safety of zidovudine in the third trimester of pregnancy for women infected with human immunodeficiency virus and their infants: phase I acquired immunodeficiency syndrome clinical trials group study (protocol 082). Zidovudine Collaborative Working Group. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 168:1510–1516 (1993).
T. Chishu, Y. Sai, T. Nishimura, K. Sato, N. Kose, and E. Nakashima. Potential of various drugs to inhibit nucleoside uptake in rat syncytiotrophoblast cell line, TR-TBT 18d-1. Placenta, in press (2008).
L. Liebes, S. Mendoza, D. Wilson, and J. Dancis. Transfer of zidovudine (AZT) by human placenta. J. Infect. Dis. 161:203–207 (1990).
S. Schenker, R. F. Johnson, T. S. King, R. S. Schenken, and G. I. Henderson. Azidothymidine (zidovudine) transport by the human placenta. Am. J. Med. Sci. 299:16–20 (1990).
J. Dancis, J. Lee, S. Mendoza, and L. Liebes. Nucleoside transport by perfused human placenta. Placenta. 14:547–554 (1993).
S. Y. Yao, C. E. Cass, and J. D. Young. Transport of the antiviral nucleoside analogs 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine and 2′,3′-dideoxycytidine by a recombinant nucleoside transporter (rCNT) expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 50:388–393 (1996).
M. W. Ritzel, A. M. Ng, S. Y. Yao, K. Graham, S. K. Loewen, K. M. Smith, R. J. Hyde, E. Karpinski, C. E. Cass, S. A. Baldwin, and J. D. Young. Recent molecular advances in studies of the concentrative Na+-dependent nucleoside transporter (CNT) family: identification and characterization of novel human and mouse proteins (hCNT3 and mCNT3) broadly selective for purine and pyrimidine nucleosides (system cib). Mol. Membr. Biol. 18:65–72 (2001).
S. Y. Yao, A. M. Ng, M. Sundaram, C. E. Cass, S. A. Baldwin, and J. D. Young. Transport of antiviral 3′-deoxy-nucleoside drugs by recombinant human and rat equilibrative, nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)-insensitive (ENT2) nucleoside transporter proteins produced in Xenopus oocytes. Mol. Membr. Biol. 18:161–167 (2001).
S. Wada, M. Tsuda, T. Sekine, S. H. Cha, M. Kimura, Y. Kanai, and H. Endou. Rat multispecific organic anion transporter 1 (rOAT1) transports zidovudine, acyclovir, and other antiviral nucleoside analogs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 294:844–849 (2000).
N. Morita, H. Kusuhara, T. Sekine, H. Endou, and Y. Sugiyama. Functional characterization of rat organic anion transporter 2 in LLC-PK1 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 298:1179–1184 (2001).
M. Takeda, S. Khamdang, S. Narikawa, H. Kimura, Y. Kobayashi, T. Yamamoto, S. H. Cha, T. Sekine, and H. Endou. Human organic anion transporters and human organic cation transporters mediate renal antiviral transport. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 300:918–924 (2002).
M. Hasegawa, H. Kusuhara, H. Endou, and Y. Sugiyama. Contribution of organic anion transporters to the renal uptake of anionic compounds and nucleoside derivatives in rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 305:1087–1097 (2003).
R. Chen, and J. A. Nelson. Role of organic cation transporters in the renal secretion of nucleosides. Biochem. Pharmacol. 60:215–219 (2000).
A. Takeuchi, S. Masuda, H. Saito, T. Abe, and K. Inui. Multispecific substrate recognition of kidney-specific organic anion transporters OAT-K1 and OAT-K2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 299:261–267 (2001).
G. Antonelli, O. Turriziani, M. Cianfriglia, E. Riva, G. Dong, A. Fattorossi, and F. Dianzani. Resistance of HIV-1 to AZT might also involve the cellular expression of multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 8:1839–1844 (1992).
X. Wang, T. Nitanda, M. Shi, M. Okamoto, T. Furukawa, Y. Sugimoto, S. Akiyama, and M. Baba. Induction of cellular resistance to nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors by the wild-type breast cancer resistance protein. Biochem. Pharmacol. 68:1363–1370 (2004).
G. Pan, N. Giri, and W. F. Elmquist. Abcg2/Bcrp1 mediates the polarized transport of antiretroviral nucleosides abacavir and zidovudine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 35:1165–1173 (2007).
J. D. Schuetz, M. C. Connelly, D. Sun, S. G. Paibir, P. M. Flynn, R. V. Srinivas, A. Kumar, and A. Fridland. MRP4: A previously unidentified factor in resistance to nucleoside-based antiviral drugs. Nat. Med. 5:1048–1051 (1999).
K. Takasawa, T. Terasaki, H. Suzuki, and Y. Sugiyama. In vivo evidence for carrier-mediated efflux transport of 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine and 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine across the blood-brain barrier via a probenecid-sensitive transport system. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 281:369–375 (1997).
C. Cordon-Cardo, J. P. O’Brien, D. Casals, L. Rittman-Grauer, J. L. Biedler, M. R. Melamed, and J. R. Bertino. Multidrug-resistance gene (P-glycoprotein) is expressed by endothelial cells at blood–brain barrier sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 86:695–698 (1989).
M. Maliepaard, G. L. Scheffer, I. F. Faneyte, M. A. van Gastelen, A. C. Pijnenborg, A. H. Schinkel, M. J. van De Vijver, R. J. Scheper, and J. H. Schellens. Subcellular localization and distribution of the breast cancer resistance protein transporter in normal human tissues. Cancer Res. 61:3458–3464 (2001).
T. Litman, U. Jensen, A. Hansen, K. M. Covitz, Z. Zhan, P. Fetsch, A. Abati, P. R. Hansen, T. Horn, T. Skovsgaard, and S. E. Bates. Use of peptide antibodies to probe for the mitoxantrone resistance-associated protein MXR/BCRP/ABCP/ABCG2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1565:6–16 (2002).
M. Nishimura, and S. Naito. Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporter superfamilies. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 20:452–477 (2005).
T. Asashima, S. Hori, S. Ohtsuki, M. Tachikawa, M. Watanabe, C. Mukai, S. Kitagaki, N. Miyakoshi, and T. Terasaki. ATP-binding cassette transporter G2 mediates the efflux of phototoxins on the luminal membrane of retinal capillary endothelial cells. Pharm. Res. 23:1235–1242 (2006).
J. Wang, S. F. Su, M. J. Dresser, M. E. Schaner, C. B. Washington, and K. M. Giacomini. Na(+)-dependent purine nucleoside transporter from human kidney: cloning and functional characterization. Am. J. Physiol. 273:F1058–F1065 (1997).
S. A. Baldwin, P. R. Beal, S. Y. Yao, A. E. King, C. E. Cass, and J. D. Young. The equilibrative nucleoside transporter family, SLC29. Pflugers Arch. 447:735–743 (2004).
T. Sekine, S. H. Cha, M. Tsuda, N. Apiwattanakul, N. Nakajima, Y. Kanai, and H. Endou. Identification of multispecific organic anion transporter 2 expressed predominantly in the liver. FEBS Lett. 429:179–182 (1998).
T. Sekine, N. Watanabe, M. Hosoyamada, Y. Kanai, and H. Endou. Expression cloning and characterization of a novel multispecific organic anion transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 272:18526–18529 (1997).
H. Kusuhara, T. Sekine, N. Utsunomiya-Tate, M. Tsuda, R. Kojima, S. H. Cha, Y. Sugiyama, Y. Kanai, and H. Endou. Molecular cloning and characterization of a new multispecific organic anion transporter from rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 274:13675–13680 (1999).
H. Koepsell, and H. Endou. The SLC22 drug transporter family. Pflugers Arch. 447:666–676 (2004).
S. Y. Yao, A. M. Ng, W. R. Muzyka, M. Griffiths, C. E. Cass, S. A. Baldwin, and J. D. Young. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)-sensitive (es) and NBMPR-insensitive (ei) equilibrative nucleoside transporter proteins (rENT1 and rENT2) from rat tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 272:28423–28430 (1997).
Y. Urakami, M. Okuda, S. Masuda, H. Saito, and K. I. Inui. Functional characteristics and membrane localization of rat multispecific organic cation transporters, OCT1 and OCT2, mediating tubular secretion of cationic drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 287:800–805 (1998).
I. Tamai, T. Nozawa, M. Koshida, J. Nezu, Y. Sai, and A. Tsuji. Functional characterization of human organic anion transporting polypeptide B (OATP-B) in comparison with liver-specific OATP-C. Pharm. Res. 18:1262–1269 (2001).
M. Grube, K. Kock, S. Karner, S. Reuther, C. A. Ritter, G. Jedlitschky, and H. K. Kroemer. Modification of OATP2B1-mediated transport by steroid hormones. Mol. Pharmacol. 70:1735–1741 (2006).
S. Ekins, W. J. Crumb, R. D. Sarazan, J. H. Wikel, and S. A. Wrighton. Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship for inhibition of human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channel. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301:427–434 (2002).
Acknowledgement
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan, a grant from the “High-Tech Research Center” and “Open Research Center” Project for Private Universities matching fund subsidy, the Science Research Promotion Fund from the Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan, and a grant from the Joint Research Project under the Japan-Korea Basic Scientific Cooperation Program of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) and Korea Science & Engineering Foundation (KOSEF), and the SRC program (R 11-2005-017) of the KOSEF/MOST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sai, Y., Nishimura, T., Shimpo, S. et al. Characterization of the Mechanism of Zidovudine Uptake by Rat Conditionally Immortalized Syncytiotrophoblast Cell Line TR-TBT. Pharm Res 25, 1647–1653 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9564-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9564-9