Abstract
Purpose
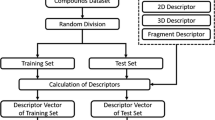
The goals of the present study were to apply a generalized regression model and support vector machine (SVM) models with Shape Signatures descriptors, to the domain of blood–brain barrier (BBB) modeling.
Materials and Methods
The Shape Signatures method is a novel computational tool that was used to generate molecular descriptors utilized with the SVM classification technique with various BBB datasets. For comparison purposes we have created a generalized linear regression model with eight MOE descriptors and these same descriptors were also used to create SVM models.
Results
The generalized regression model was tested on 100 molecules not in the model and resulted in a correlation r 2 = 0.65. SVM models with MOE descriptors were superior to regression models, while Shape Signatures SVM models were comparable or better than those with MOE descriptors. The best 2D shape signature models had 10-fold cross validation prediction accuracy between 80–83% and leave-20%-out testing prediction accuracy between 80–82% as well as correctly predicting 84% of BBB+ compounds (n = 95) in an external database of drugs.
Conclusions
Our data indicate that Shape Signatures descriptors can be used with SVM and these models may have utility for predicting blood–brain barrier permeation in drug discovery.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADME:
-
absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion
- BBB:
-
blood–brain barrier
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- MEP:
-
molecular electrostatic potential
- MOE:
-
molecular operating environment
- PCA:
-
principal component analysis
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- QSAR:
-
quantitative structure activity relationship
- RFE:
-
recursive feature elimination
- SAS:
-
solvent accessible surface
- SVM:
-
support vector machine
- TPSA:
-
topological polar surface area
- UFS:
-
unsupervised forward selection
References
S. Ekins, C. L. Waller, P. W. Swaan, G. Cruciani, S. A. Wrighton, and J. H. Wikel. Progress in predicting human ADME parameters in silico. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 44:251–272 (2000).
H. van de Waterbeemd, and E. Gifford. ADMET in silico modelling: towards prediction paradise? Nat. Rev. 2:192–204 (2003).
S. Ekins, and P. W. Swaan. Computational models for enzymes, transporters, channels and receptors relevant to ADME/TOX. Rev. Comp. Chem. 20:333–415 (2004).
R. Cecchelli, V. Berezowski, S. Lundquist, M. Culot, M. Renftel, M. P. Dehouck, and L. Fenart. Modelling of the blood–brain barrier in drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. 6:650–661 (2007).
A. George. The design and molecular modeling of CNS drugs. Curr. Opin. Drug. Disc. Dev. 2:286–292 (1999).
K. M. Mahar Doan, J. E. Humphreys, L. O. Webster, S. A. Wring, L. J. Shampine, C. J. Serabjit-Singh, K. K. Adkison, and J. W. Polli. Passive permeability and P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux differentiate central nervous system (CNS) and non-CNS marketed drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 303:1029–1037 (2002).
F. Lombardo, J. F. Blake, and W. J. Curatolo. Computation of brain–blood partitioning of organic solutes via free energy calculations. J. Med. Chem. 39:4750–4755 (1996).
U. Norinder, and M. Haeberlein. Computational approaches to the prediction of the blood–brain distribution. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 54:291–313 (2002).
D. E. Clark. In silico prediction of blood–brain barrier permeation. Drug Discov. Today. 8:927–933 (2003).
J. T. Goodwin, and D. E. Clark. In silico predictions of blood–brain barrier penetration: considerations to “keep in mind”. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 315:477–483 (2005).
M. Iyer, R. Mishru, Y. Han, and A. J. Hopfinger. Predicting blood–brain barrier partitioning of organic molecules using membrane-interaction QSAR analysis. Pharm. Res. 19:1611–1621 (2002).
M. Iyer, E. J. Reschly, and M. D. Krasowski. Functional evolution of the pregnane X receptor. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2:381–397 (2006).
M. Lobell, L. Molnar, and G. M. Keseru. Recent advances in the prediction of blood–brain partitioning from molecular structure. J. Pharm. Sci. 92:360–370 (2003).
F. Ooms, P. Weber, P. A. Carrupt, and B. Testa. A simple model to predict blood–brain barrier permeation from 3D molecular fields. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1587:118–125 (2002).
R. J. Zauhar, G. Moyna, L. Tian, Z. Li, and W. J. Welsh. Shape signatures: a new approach to computer-aided ligand- and receptor-based drug design. J. Med. Chem. 46:5674–5690 (2003).
K. Nagarajan, R. Zauhar, and W. J. Welsh. Enrichment of ligands for the serotonin receptor using the Shape Signatures approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 45:49–57 (2005).
C. Y. Wang, N. Ai, S. Arora, E. Erenrich, K. Nagarajan, R. Zauhar, D. Young, and W. J. Welsh. Identification of previously unrecognized antiestrogenic chemicals using a novel virtual screening approach. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 19:1595–1601 (2006).
S. Kortagere, and W. J. Welsh. Development and application of hybrid structure based method for efficient screening of ligands binding to G-protein coupled receptors. J. Comput-Aided Mol. Des. 20:789–802 (2006).
P. J. Meek, Z. Liu, L. Tian, C. Y. Wang, W. J. Welsh, and R. J. Zauhar. Shape signatures: speeding up computer aided drug discovery. Drug. Discov. Today 11:895–904 (2006).
P. Garg, and J. Verma. In silico prediction of blood brain barrier permeability: an artificial neural network model. J. Chem. Inf. Model 46:289–297 (2006).
T. J. Hou, and X. J. Xu. ADME evaluation in drug discovery. 3. Modeling blood–brain barrier partitioning using simple molecular descriptors. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 43:2137–2152 (2003).
D. A. Konovalov, D. Coomans, E. Deconinck, and Y. V. Heyden. Benchmarking of QSAR models for blood–brain barrier permeation. J. Chem. Inf. Model 47:1648–1656 (2007).
H. Li, C. W. Yap, C. Y. Ung, Y. Xue, Z. W. Cao, and Y. Z. Chen. Effect of selection of molecular descriptors on the prediction of blood–brain barrier penetrating and nonpenetrating agents by statistical learning methods. J. Chem. Inf. Model 45:1376–1384 (2005).
R. Liu, H. Sun, and S. S. So. Development of quantitative structure–property relationship models for early ADME evaluation in drug discovery. 2. Blood–brain barrier penetration. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 41:1623–1632 (2001).
G. Subramanian, and D. B. Kitchen. Computational models to predict blood–brain barrier permeation and CNS activity. J. Comput-Aided Mol. Des. 17:643–664 (2003).
L. Gomella, and S. Haist. Clinician’s pocket drug reference. McGraw-Hill, New York, 2004.
C. Chang, P. M. Bahadduri, J. E. Polli, P. W. Swaan, and S. Ekins. Rapid identification of P-glycoprotein substrates and inhibitors. Drug Metab. Dispos. 34:1976–1984 (2006).
S. Ekins, J. S. Johnston, P. Bahadduri, V. M. D’Souzza, A. Ray, C. Chang, and P. W. Swaan. In vitro and pharmacophore based discovery of novel hPEPT1 inhibitors. Pharm. Res. 22:512–517 (2005).
J. Gasteiger, and M. Marsili. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron. 36:3219–3228 (1980).
R. J. Zauhar. SMART: a solvent-accessible triangulated surface generator for molecular graphics and boundary element applications. J. Comput-Aided Mol. Des. 9:149–159 (1995).
D. S. Chekmarev, V. Kholodovych, K. V. Balakin, Y. Ivanenkov, S. Ekins, and W. J. Welsh. Shape signatures: new descriptors for predicting cardiotoxicity in silico. Chem. Res. Toxicol., in press (2008).
C. Cortes, and V. Vapnik. Support vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20:273–293 (1995).
V. Vapnik. Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York, 1998.
A. H. Fielding. Cluster and classification techniques for the biosciences. Cambridge University Press, New York, 2007.
D. Plewczynski, S. A. Spieser, and U. Koch. Assessing different classification methods for virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model 46:1098–1106 (2006).
M. Tobita, T. Nishikawa, and R. Nagashima. A discriminant model constructed by the support vector machine method for HERG potassium channel inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15:2886–2890 (2005).
Y. Xue, C.W. Yap, L. Z. Sun, Z. W. Cao, J. F. Wang, and Y. Z. Chen. Prediction of P-glycoprotein substrates by a support vector machine approach. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 44:1497–1505 (2004).
C. C. Chang, and C. J. Lin. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines, 2001.
C. Y. Ung, H. Li, C. W. Yap, and Y. Z. Chen. In silico prediction of pregnane X receptor activators by machine learning approaches. Mol. Pharmacol. 71:158–168 (2007).
B. W. Matthews. Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of T4 phage lysozyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 405:442–451 (1975).
D. C. Whitley, M. G. Ford, and D. J. Livingstone. Unsupervised forward selection: a method for eliminating redundant variables. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 40:1160–1168 (2000).
H. Van de Waterbeemd, and M. Kansy. Hydrogen-bonding capacity and brain penetration. Chimia. 46:5 (1992).
M. H. Abraham, H. S. Chadha, and R. C. Mitchell. Hydrogen-bonding. Part 36. Determination of blood brain distribution using octanol–water partition coefficients. Drug Des. Discov. 13:123–131 (1995).
D. E. Clark. Rapid calculation of polar molecular surface area and its application to the prediction of transport phenomena. 2. Prediction of blood–brain barrier penetration. J. Pharm. Sci. 88:815–821 (1999).
W. L. Jorgensen, and E. M. Duffy. Prediction of drug solubility from Monte Carlo simulations. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 10:1155–1158 (2000).
U. Norinder, P. Sjoberg, and T. Osterberg. Theoretical calculation and prediction of brain–blood partitioning of organic solutes using MolSurf parametrization and PLS statistics. J. Pharm. Sci. 87:952–959 (1998).
R. M. M. Kaliszan. Brain/blood distribution described by a combination of partition coefficient and molecular mass. Int. J. Pharm. 145:8 (1996).
X. C. Fu, C. X. Chen, W. Q. Liang, and Q. S. Yu. Predicting blood–brain barrier penetration of drugs by polar molecular surface area and molecular volume. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 22:663–668 (2001).
H. Sun. A universal molecular descriptor system for prediction of logP, logS, logBB, and absorption. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 44:748–757 (2004).
S. Van Damme, W. Langenaeker, and P. Bultinck. Prediction of blood–brain partitioning: a model based on ab initio calculated quantum chemical descriptors. J. Mol. Graph. Model., in press (2007).
S. Ekins, M. J. Embrechts, C. M. Breneman, K. Jim, and J.-P. Wery. Novel applications of Kernel-partial least squares to modeling a comprehensive array of properties for drug discovery. In S. Ekins (ed.), Computational toxicology: risk assessment for pharmaceutical and environmental chemicals, Wiley, Hoboken, 2007, pp. 403–432.
R. Todeschini, and V. Consonni. Handbook of molecular descriptors. Wiley, Weinheim, 2000.
Acknowledgments
Support for this work has been provided by the USEPA-funded Environmental Bioinformatics and Computational Toxicology Center (ebCTC), under STAR Grant number GAD R 832721-010. WJW gratefully acknowledges support for this work provided by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, under contract number HDTRA-BB07TAS020. This work was also funded in part by NIH R21-GM081394 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences and by NIH Integrated Advanced Information Management Systems (IAIMS) Grant # 2G08LM06230-03A1 from the National Library of Medicine. This work has not been reviewed by and does not represent the opinions of the funding agencies. The authors are sincerely grateful to Randy Zauhar, Ph.D., of the University of the Sciences in Philadelphia, for useful discussions on technical aspects of Shape Signatures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary materials.
Supplemental Table 1
Details the list of BBB datasets available in literature along with references. (DOC 134 KB)
Supplemental Table 2
Provides model predictions for the SCUT database and consensus scoring respectively. Both are available online along with the SDF files for the Li, Combined and SCUT datasets. (XLS 67.0 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kortagere, S., Chekmarev, D., Welsh, W.J. et al. New Predictive Models for Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability of Drug-like Molecules. Pharm Res 25, 1836–1845 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9584-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-008-9584-5