Abstract
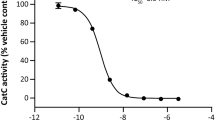
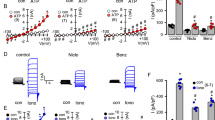
Nucleoside di- and triphosphates and adenosine regulate several components of the mucocilairy clearance process (MCC) that protects the lung against infections, via activation of epithelial purinergic receptors. However, assessing the contribution of individual nucleotides to MCC functions remains difficult due to the complexity of the mechanisms of nucleotide release and metabolism. Enzymatic activities involved in the metabolism of extracellular nucleotides include ecto-ATPases and secreted nucleoside diphosphokinase (NDPK) and adenyl kinase, but potent and selective inhibitors of these activities are sparse. In the present study, we discovered that ebselen markedly reduced NDPK activity while having negligible effect on ecto-ATPase and adenyl kinase activities. Addition of radiotracer [γ 32P]ATP to human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells resulted in rapid and robust accumulation of [32P]-inorganic phosphate (32Pi). Inclusion of UDP in the incubation medium resulted in conversion of [γ 32P]ATP to [32P]UTP, while inclusion of AMP resulted in conversion of [γ 32P]ATP to [32P]ADP. Ebselen markedly reduced [32P]UTP formation but displayed negligible effect on 32Pi or [32P]ADP accumulations. Incubation of HBE cells with unlabeled UTP and ADP resulted in robust ebselen-sensitive formation of ATP (IC50 = 6.9 ± 2 μM). This NDPK activity was largely recovered in HBE cell secretions and supernatants from lung epithelial A549 cells. Kinetic analysis of NDPK activity indicated that ebselen reduced the V max of the reaction (K i = 7.6 ± 3 μM), having negligible effect on K M values. Our study demonstrates that ebselen is a potent non-competitive inhibitor of extracellular NDPK.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boucher RC (2003) Regulation of airway surface liquid volume by human airway epithelia. Pflugers Arch 445:495–498
Davis CW, Lazarowski E (2008) Coupling of airway ciliary activity and mucin secretion to mechanical stresses by purinergic signaling. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 163:208–213
Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC (2009) Purinergic receptors in airway epithelia. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:262–267
Boucher RC (2002) An overview of the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis lung disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:1359–1371
Morse DM, Smullen JL, Davis CW (2001) Differential effects of UTP, ATP, and adenosine on ciliary activity of human nasal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:C1485–C1497
Rooney SA (2001) Regulation of surfactant secretion. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 129:233–243
Factor P, Mutlu GM, Chen L, Mohameed J, Akhmedov AT, Meng FJ, Jilling T, Lewis ER, Johnson MD, Xu A, Kass D, Martino JM, Bellmeyer A, Albazi JS, Emala C, Lee HT, Dobbs LG, Matalon S (2007) Adenosine regulation of alveolar fluid clearance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:4083–4088
Davis IC, Sullender WM, Hickman-Davis JM, Lindsey JR, Matalon S (2004) Nucleotide-mediated inhibition of alveolar fluid clearance in BALB/c mice after respiratory syncytial virus infection. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286:L112–L120
Blackburn MR, Lee CG, Young HW, Zhu Z, Chunn JL, Kang MJ, Banerjee SK, Elias JA (2003) Adenosine mediates IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling in the lung and interacts in an IL-13-adenosine amplification pathway. J Clin Invest 112:332–344
Sun CX, Zhong H, Mohsenin A, Morschl E, Chunn JL, Molina JG, Belardinelli L, Zeng D, Blackburn MR (2006) Role of A2B adenosine receptor signaling in adenosine-dependent pulmonary inflammation and injury. J Clin Invest 116:2173–2182
Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC, Harden TK (2000) Constitutive release of ATP and evidence for major contribution of ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase and nucleoside diphosphokinase to extracellular nucleotide concentrations. J Biol Chem 275:31061–31068
Watt WC, Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC (1998) Cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator-independent release of ATP—its implications for the regulation of P2Y(2) receptors in airway epithelia. J Biol Chem 273:14053–14058
Lazarowski ER, Tarran R, Grubb BR, van Heusden CA, Okada S, Boucher RC (2004) Nucleotide release provides a mechanism for airway surface liquid homeostasis. J Biol Chem 279:36855–36864
Picher M, Burch LH, Boucher RC (2004) Metabolism of P2 receptor agonists in human airways: Implications for mucociliary clearance and cystic fibrosis. J Biol Chem 279:20234–20241
Picher M, Burch LH, Hirsh AJ, Spychala J, Boucher RC (2003) Ecto 5′-nucleotidase and non-specific alkaline phosphatase: two AMP-hydrolyzing ectoenzymes with distinct roles in human airways. J Biol Chem 278:13468–13479
Donaldson SH, Picher M, Boucher RC (2002) Secreted and cell-associated adenylate kinase and nucleoside diphosphokinase contribute to extracellular nucleotide metabolism on human airway surfaces. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 26:209–215
Picher M, Boucher RC (2003) Human Airway Ecto-adenylate Kinase. A mechanism to propagate atp signaling on airway surfaces. J Biol Chem 278:11256–11264
Zuo P, Picher M, Okada SF, Lazarowski ER, Button B, Boucher RC, Elston TC (2008) Mathematical model of nucleotide regulation on airway epithelia. Implications for airway homeostasis. J Biol Chem 283:26805–26819
Kreda SM, Seminario-Vidal L, van Heusden CA, O’Neal W, Jones L, Boucher RC, Lazarowski ER (2010) Receptor-promoted exocytosis of airway epithelial mucin granules containing a spectrum of adenine nucleotides. J Physiol 588:2255–2267
Sesma JI, Esther CR Jr, Kreda SM, Jones L, O’Neal W, Nishihara S, Nicholas RA, Lazarowski ER (2009) ER/golgi nucelotide sugar transporters contribute to the cellular release of UDP-sugar signaling molecules. J Biol Chem 284:12572–12583
Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC, Harden TK (2003) Mechanisms of release of nucleotides and integration of their action as P2X- and P2Y-receptor activating molecules. Mol Pharmacol 64:785–795
Tatur S, Kreda S, Lazarowski E, Grygorczyk R (2008) Calcium-dependent release of adenosine and uridine nucleotides from A549 cells. Purinergic Signal 4:139–146
Donaldson SH, Lazarowski ER, Picher M, Knowles MR, Stutts MJ, Boucher RC (2000) Basal nucleotide levels, release, and metabolism in normal and cystic fibrosis airways. Mol Med 6:969–982
Huang PB, Lazarowski ER, Tarran R, Milgram SL, Boucher RC, Stutts MJ (2001) Compartmentalized autocrine signaling to cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator at the apical membrane of airway epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14120–14125
Okada SF, Nicholas RA, Kreda SM, Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC (2006) Physiological regulation of ATP release at the apical surface of human airway epithelia. J Biol Chem 281:22992–23002
Tarran R, Button B, Picher M, Paradiso AM, Ribeiro CM, Lazarowski ER, Zhang L, Collins PL, Pickles RJ, Fredburg JJ, Boucher RC (2005) Normal and cystic fbrosis airway surface liquid homeostasis: the effects of phasic shear stress and viral infections. J Biol Chem 280:35751–35759
Lazarowski ER, Paradiso AM, Watt WC, Harden TK, Boucher RC (1997) UDP activates a mucosal-restricted receptor on human nasal epithelial cells that is distinct from the P2Y(2) receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2599–2603
Furstenau CR, Spier AP, Rucker B, Luisa BS, Battastini AM, Sarkis JJ (2004) The effect of ebselen on adenine nucleotide hydrolysis by platelets from adult rats. Chem Biol Interact 148:93–99
Mishra B, Priyadarsini KI, Mohan H, Mugesh G (2006) Horseradish peroxidase inhibition and antioxidant activity of ebselen and related organoselenium compounds. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:5334–5338
Seminario-Vidal L, Kreda S, Jones L, O’Neal W, Trejo J, Boucher RC, Lazarowski ER (2009) Thrombin promotes release of ATP from lung epithelial cells through coordinated activation of Rho- and Ca2+-dependent signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 284:20638–20648
Lazarowski ER, Homolya L, Boucher RC, Harden TK (1997) Identification of an ecto-nucleoside diphosphokinase and its contribution to interconversion of P2 receptor agonists. J Biol Chem 272:20402–20407
Segel IH (1993) Enzyme Kinetics. Behavior and analysis of rapid equilibirum and steady-state enzyme systems. Wiley, New York
Buxton IL, Kaiser RA, Oxhorn BC, Cheek DJ (2001) Evidence supporting the Nucleotide Axis Hypothesis: ATP release and metabolism by coronary endothelium. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H1657–H1666
Buckley KA, Golding SL, Rice JM, Dillon JP, Gallagher JA (2003) Release and interconversion of P2 receptor agonists by human osteoblast-like cells. FASEB J 17:1401–1410
Burrell HE, Wlodarski B, Foster BJ, Buckley KA, Sharpe GR, Quayle JM, Simpson AW, Gallagher JA (2005) Human keratinocytes release ATP and utilize three mechanisms for nucleotide interconversion at the cell surface. J Biol Chem 280:29667–29676
Ostrom RS, Gregorian C, Insel PA (2000) Cellular release of and response to ATP as key determinants of the set-point of signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem 275:11735–11739
Cotrina ML, Lin JH, Alves-Rodrigues A, Liu S, Li J, Azmi-Ghadimi H, Kang J, Naus CC, Nedergaard M (1998) Connexins regulate calcium signaling by controlling ATP release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15735–15740
Zembowicz A, Hatchett RJ, Radziszewski W, Gryglewski RJ (1993) Inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by ebselen. Prevention by thiols suggests the inactivation by ebselen of a critical thiol essential for the catalytic activity of nitric oxide synthase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:1112–1118
Schewe C, Schewe T, Wendel A (1994) Strong inhibition of mammalian lipoxygenases by the antiinflammatory seleno-organic compound ebselen in the absence of glutathione. Biochem Pharmacol 48:65–74
Cotgreave IA, Duddy SK, Kass GE, Thompson D, Moldeus P (1989) Studies on the anti-inflammatory activity of ebselen. Ebselen interferes with granulocyte oxidative burst by dual inhibition of NADPH oxidase and protein kinase C? Biochem Pharmacol 38:649–656
Wetli HA, Buckett PD, Wessling-Resnick M (2006) Small-molecule screening identifies the selanazal drug ebselen as a potent inhibitor of DMT1-mediated iron uptake. Chem Biol 13:965–972
Soteropoulos P, Vaz T, Santangelo R, Paderu P, Huang DY, Tamas MJ, Perlin DS (2000) Molecular characterization of the plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase, an antifungal target in Cryptococcus neoformans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:2349–2355
Chan G, Hardej D, Santoro M, Lau-Cam C, Billack B (2007) Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of ebselen: role of the yeast plasma membrane H+-ATPase. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 21:252–264
Abdo M, Liu S, Zhou B, Walls CD, Wu L, Knapp S, Zhang ZY (2008) Seleninate in place of phosphate: irreversible inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatases. J Am Chem Soc 130:13196–13197
Song EJ, Kim YS, Chung JY, Kim E, Chae SK, Lee KJ (2000) Oxidative modification of nucleoside diphosphate kinase and its identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 39:10090–10097
Rosengard AM, Krutzsch HC, Shearn A, Biggs JR, Barker E, Margulies IM, King CR, Liotta LA, Steeg PS (1989) Reduced Nm23/Awd protein in tumour metastasis and aberrant Drosophila development. Nature 342:177–180
Stahl JA, Leone A, Rosengard AM, Porter L, King CR, Steeg PS (1991) Identification of a second human nm23 gene, nm23-H2. Cancer Res 51:445–449
Venturelli D, Martinez R, Melotti P, Casella I, Peschle C, Cucco C, Spampinato G, Darzynkiewicz Z, Calabretta B (1995) Overexpression of DR-nm23, a protein encoded by a member of the nm23 gene family, inhibits granulocyte differentiation and induces apoptosis in 32Dc13 myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7435–7439
Milon L, Rousseau-Merck MF, Munier A, Erent M, Lascu I, Capeau J, Lacombe ML (1997) nm23-H4, a new member of the family of human nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase genes localised on chromosome 16p13. Hum Genet 99:550–557
Munier A, Feral C, Milon L, Pinon VP, Gyapay G, Capeau J, Guellaen G, Lacombe ML (1998) A new human nm23 homologue (nm23-H5) specifically expressed in testis germinal cells. FEBS Lett 434:289–294
Tsuiki H, Nitta M, Furuya A, Hanai N, Fujiwara T, Inagaki M, Kochi M, Ushio Y, Saya H, Nakamura H (1999) A novel human nucleoside diphosphate (NDP) kinase, Nm23-H6, localizes in mitochondria and affects cytokinesis. J Cell Biochem 76:254–269
Rumjahn SM, Javed MA, Wong N, Law WE, Buxton IL (2007) Purinergic regulation of angiogenesis by human breast carcinoma-secreted nucleoside diphosphate kinase. Br J Cancer 97:1372–1380
Lazarowski ER, Homolya L, Boucher RC, Harden TK (1997) Direct demonstration of mechanically induced release of cellular UTP and its implication for uridine nucleotide receptor activation. J Biol Chem 272:24348–24354
Anciaux K, VanDommelen K, Willems R, Roymans D, Slegers H (1997) Inhibition of nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK/nm23) by cAMP analogues. FEBS Lett 400:75–79
Buxton IL (2008) Inhibition of Nm23H2 gene product (NDPK-B) by angiostatin, polyphenols and nucleoside analogs. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 51:30–34
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Scott Randell for providing primary cultures of HBE cells. We are indebted to Lisa Brown for editorial assistance with the manuscript. This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant P01-HL034322 (ERL, CH) and Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Grant CFF-SEMINA08FO (LS-V). GM was supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11302-011-9230-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semianrio-Vidal, L., van Hesuden, C., Mugesh, G. et al. Ebselen is a potent non-competitive inhibitor of extracellular nucleoside diphosphokinase. Purinergic Signalling 6, 383–391 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-010-9203-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-010-9203-x