Abstract
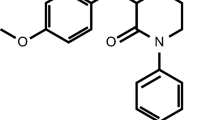
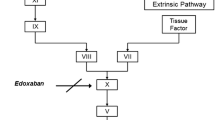
Apixaban is a potent, highly selective, reversible, oral, direct factor Xa (fXa) inhibitor in development for thrombosis prevention and treatment. The preclinical pharmacokinetic (PK) attributes of apixaban feature small volume of distribution (Vd), low systemic clearance (CL), and good oral bioavailability. Apixaban is well absorbed in rat, dog, and chimpanzee, with absolute oral bioavailability of approximately 50% or greater. The steady-state Vd of apixaban is approximately 0.5, 0.2, and 0.17 l/kg in rats, dogs, and chimpanzees, while CL is approximately 0.9, 0.04, and 0.018 l/h/kg, respectively. In vitro metabolic clearance of apixaban is also low. Renal clearance comprises approximately 10–30% of systemic clearance in rat, dog, and chimpanzee. Anti-fXa activity, prothrombin time (PT), and HEPTEST® clotting time (HCT) prolongation correlated well with plasma apixaban concentration in rat, dog and chimpanzee. There was no lag time between apixaban plasma concentration and the pharmacodynamic (PD) markers, suggesting a rapid onset of action of apixaban. The PK/PD analyses were performed using an inhibitory E max model for anti-fXa assay and a linear model for PT and HCT assays. The IC50 values for anti-fXa activity were 0.73 ± 0.03 and 1.5 ± 0.15 μM for rat and dog, respectively. The apparent K i values for PT were approximately 1.7, 6.6, and 4.8 μM for rat, dog and chimpanzee, respectively. The apparent K i for HCT was approximately 1.3 μM for dog. Apixaban exhibits desirable PK and PD properties for clinical development with good oral bioavailability, small Vd, low CL, and direct, predictable, concentration-dependent PD responses.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α1-AGP:
-
α1-Acid glycoprotein
- AUCinf :
-
Area under concentration–time curve from 0 to infinity
- AUC(0–24h) :
-
Area under concentration–time curve from 0 to 24 h
- CL:
-
Clearance
- CLint :
-
Intrinsic clearance
- C max :
-
Maximum concentration
- F :
-
Absolute bioavailability
- fXa:
-
Factor Xa
- HCT:
-
HEPTEST® clotting time
- HSA:
-
Human serum albumin
- IC50 :
-
Concentration required for 50% inhibition
- K i :
-
Inhibition constant
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- MRT:
-
Mean residence time
- PD:
-
Pharmacodynamics
- PK:
-
Pharmacokinetics
- PT:
-
Prothrombin time
- t 1/2 :
-
Half-life
- T max :
-
Time to maximum concentration
- Vdss :
-
Volume of distribution at steady state
References
Davies B, Morris T (1993) Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharm Res 10(7):1093–1095
Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Rosencher N, Kurth AA, Van Dijk CN, Frostick SP, Kälebo P, Christiansen AV, Hantel S, Hettiarachchi R, Schnee J, Büller HR, for the Re-Model Study Group (2007a) Oral dabigatran etexilate vs. subcutaneous enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total knee replacement: the RE-MODEL randomized trial. J Thromb Haemost 5(11):2178–2185
Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Rosencher N, Kurth AA, van Dijk CN, Frostick SP, Prins MH, Hettiarachchi R, Hantel S, Schnee J, Büller HR (2007b) Dabigatran etexilate versus enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement: a randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 370(9591):949–956
Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ, Haas S, Huisman MV, Kakkar AK, Bandel TJ, Beckmann H, Muehlhofer E, Misselwitz F, Geerts W (2008) Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty. N Engl J Med 358(26):2765–2775
Hara T, Yokoyama A, Morishima Y, Kunitada S (1995) Species differences in anticoagulant and anti-Xa activity of DX-9065a, a highly selective factor Xa inhibitor. Thromb Res 80(1):99–104
Harder S, Thürmann P (1996) Clinically important drug interactions with anticoagulants: an update. Clin Pharmacokinet 30(6):416–444
Hauptmann J, Stürzebecher J (1999) Synthetic inhibitors of thrombin and factor Xa: from bench to bedside. Thromb Res 93(5):203–241
Hemker H, Vermeer C, Govers-Riemslag J (1977) Kinetic aspects of the interaction of blood clotting enzymes. VII. The relation between clotting time and prothrombin concentration. Thromb Haemost 37(1):81–85
Kakkar AK, Brenner B, Dahl OE, Eriksson BI, Mouret P, Muntz J, Soglian AG, Pap ÁF, Misselwitz F, Haas S (2008) Extended duration rivaroxaban versus short-term enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 372(9632):31–39
Kimmel SE (2008) Warfarin therapy: in need of improvement after all these years. Expert Opin Pharmacother 9(5):677–686
Kubitza D, Becka M, Voith B, Zuehlsdorf M, Wensing G (2005) Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of single doses of BAY 59–7939, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78(4):412–421
Lam PYS, Clark CG, Li R, Pinto DJP, Orwat MJ, Galemmo RA, Fevig JM, Teleha CA, Alexander RS, Smallwood AM, Rossi KA, Wright MR, Bai SA, He K, Luettgen JM, Wong PC, Knabb RM, Wexler RR (2003) Structure-based design of novel guanidine/benzamidine mimics: potent and orally bioavailable factor Xa inhibitors as novel anticoagulants. J Med Chem 46(21):4405–4418
Lassen MR, Ageno W, Borris LC, Lieberman JR, Rosencher N, Bandel TJ, Misselwitz F, Turpie AGG (2008) Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty. N Engl J Med 358(26):2776–2786
Lassen MR, Raskob GE, Gallus A, Pineo G, Chen D, Hornick P (2010a) Apixaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after knee replacement (ADVANCE-2): a randomised double-blind trial. Lancet 375(9717):807–815
Lassen MR, Gallus A, Raskob GE, Pineo G, Chen D, Ramirez LM (2010b) Apixaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip replacement. N Engl J Med 363(26):2487–2498
Leadley R (2001) Coagulation factor Xa inhibition: biological background and rationale. Curr Top Med Chem 1(2):151–159
Lin JH, Cocchetto DM, Duggan DE (1987) Protein binding as a primary determinant of the clinical pharmacokinetic properties of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet 12(6):402–432
Luettgen JM, Knabb RM, He K, Pinto DJP, Rendina AR (2011) Apixaban inhibition of factor Xa: microscopic rate constants and inhibition mechanism in purified protein systems and in human plasma. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. doi:10.3109/14756366.2010.535793
Obach RS, Baxter JG, Liston TE, Silber BM, Jones BC, Macintyre F, Rance DJ, Wastall P (1997) The prediction of human pharmacokinetic parameters from preclinical and in vitro metabolism data. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283(1):46–58
Paccaly A, Frick A, Ozoux M-L, Chu V, Rosenburg R, Hinder M, Shukla U, Jensen BK (2006) Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationships for otamixaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 46(1):45–51
Pinto DJP, Orwat MJ, Wang S, Fevig JM, Quan ML, Amparo E, Cacciola J, Rossi KA, Alexander RS, Smallwood AM, Luettgen JM, Liang L, Aungst BJ, Wright MR, Knabb RM, Wong PC, Wexler RR, Lam PYS (2001) Discovery of 1-[3-(aminomethyl)phenyl]-N-[3-fluoro-2′-(methylsulfonyl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamide (DPC423), a highly potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. J Med Chem 44(4):566–578
Pinto DJP, Orwat MJ, Koch S, Rossi KA, Alexander RS, Smallwood A, Wong PC, Rendina AR, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM, He K, Xin B, Wexler RR, Lam PYS (2007) Discovery of 1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide (apixaban, BMS-562247), a highly potent, selective, efficacious, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. J Med Chem 50(22):5339–5356
Qiao JX, Wang TC, Wang GZ, Cheney DL, He K, Rendina AR, Xin B, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM, Wexler RR, Lam PYS (2007) Enantiopure five-membered cyclicdiamine derivatives as potent and selective inhibitors of factor Xa. Improving in vitro metabolic stability via core modifications. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17(18):5041–5048
Quan ML, Wexler RR (2001) The design and synthesis of noncovalent factor Xa inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem 1(2):137–149
Quan ML, Lam PYS, Han Q, Pinto DJP, He MY, Li R, Ellis CD, Clark CG, Teleha CA, Sun J-H, Alexander RS, Bai S, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM, Wong PC, Wexler RR (2005) Discovery of 1-(3′-aminobenzisoxazol-5′-yl)-3-trifluoromethyl-N-[2-fluoro-4-[(2′-dimethylaminomethyl)imidazol-1-yl]phenyl]-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxyamide hydrochloride (razaxaban), a highly potent, selective, and orally bioavailable factor Xa inhibitor. J Med Chem 48(6):1729–1744
Raghavan N, Frost CE, Yu Z, He K, Zhang H, Humphreys WG, Pinto D, Chen S, Bonacorsi S, Wong PC, Zhang D (2009) Apixaban metabolism and pharmacokinetics after oral administration to humans. Drug Metab Disp 37(1):74–81
Segel IH (1993) Enzyme kinetics: behavior and analysis of rapid equilibrium and steady-state enzyme systems. Wiley and Sons, New York
Stangier J, Rathgen K, Stähle H, Gansser D, Roth W (2007) The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of dabigatran etexilate, a new oral direct thrombin inhibitor, in healthy male subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 64(3):292–303
Svensson CK, Woodruff MN, Baxter JG, Lalka D (1986) Free drug concentration monitoring in clinical practice: rationale and current status. Clin Pharmacokinet 11(6):450–469
Tobu M, Iqbal O, Hoppensteadt DA, Shultz C, Jeske W, Fareed J (2002) Effects of a synthetic factor Xa inhibitor (JTV-803) on various laboratory tests. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 8(4):325–336
Turpie AGG (2004) Fondaparinux: a Factor Xa inhibitor for antithrombotic therapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 5(6):1373–1384
Walenga JM, Hoppensteadt DA (2004) Monitoring the new antithrombotic drugs. Semin Thromb Hemost 30(6):683–695
Wang L, Zhang D, Raghavan N, Yao M, Ma L, Frost CA, Maxwell BD, Chen S-Y, He K, Goosen TC, Griffith WH, Grossman SJ (2010) In vitro assessment of metabolic drug-drug interaction potential of apixaban through cytochrome P450 phenotyping, inhibition, and induction studies. Drug Metab Disp 38(3):448–458
Weitz JI (2006) Emerging anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost 96(3):274–284
Wong PC, Crain EJ, Watson CA, Zaspel AM, Wright MR, Lam PY, Pinto DJP, Wexler RR, Knabb RM (2002) Nonpeptide factor Xa inhibitors III: effects of DPC423, an orally-active pyrazole antithrombotic agent, on arterial thrombosis in rabbits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303(3):993–1000
Wong H, Grossman SJ, Bai SA, Diamond S, Wright MR, Grace JE, Qian M, He K, Yeleswaram K, Christ DD (2004) The chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) as a pharmacokinetic model for selection of drug candidates: model characterization and application. Drug Metab Disp 32(12):1359–1369
Wong PC, Crain EJ, Xin B, Wexler RR, Lam PYS, Pinto DJ, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM (2008) Apixaban, an oral, direct and highly selective factor Xa inhibitor: in vitro, antithrombotic and antihemostatic studies. J Thromb Haemost 6(5):820–829
Zhang D, He K, Raghavan N, Wang L, Mitroka J, Maxwell BD, Knabb RM, Frost C, Schuster A, Hao F, Gu Z, Humphreys WG, Grossman SJ (2009) Comparative metabolism of 14C-labeled apixaban in mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, and humans. Drug Metab Disp 37(8):1738–1748
Conflict of interest
The authors are current or former employees of Bristol-Myers Squibb. This study was sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, K., Luettgen, J.M., Zhang, D. et al. Preclinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of apixaban, a potent and selective factor Xa inhibitor. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 36, 129–139 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-011-0037-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-011-0037-x