Abstract
Purpose. To examine the changes in expression levels of CYP3A4 and efflux transporters in CYP3A4-transfected Caco-2 (colon carcinoma) cells in the presence of the inducers sodium butyrate (NaB) and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). To characterize the transport of [3H]-digoxin and the metabolism of midazolam in the cells under different inducing conditions.
Methods. CYP3A4-Caco-2 cells were seeded onto cell culture inserts and were grown for 13-14 days. Transport and metabolism studies were performed on cells induced with NaB and/or TPA for 24 h. The expression and localization of P-gp, MRP1, MRP2, and CYP3A4 were examined by Western blot and confocal microscopy.
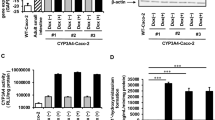
Results. In the presence of both inducers, CYP3A4 protein levels were increased 40-fold over uninduced cells, MRP2 expression was decreased by 90%, and P-gp and MRP1 expression were unchanged. Midazolam 1-OH formation exhibited a rank order correlation with increased CYP3A4 protein, whereas [3H]-digoxin transport (a measure of P-gp activity) was unchanged with induction. P-gp and MRP2 were found on the apical membrane, whereas MRP1 was found peri-nuclear within the cell. CYP3A4 displayed a punctate pattern of expression consistent with endoplasmic reticulum localization and exhibited preferential polarization towards the apical side of the cell.
Conclusions. The present study characterized CYP3A4-Caco-2 cell monolayers when induced for 24 h in the presence of both NaB and TPA. These conditions provide intact cells with significant CYP3A4 and P-gp expression suitable for the concurrent study of transport and metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
P. Artursson and R. T. Borchardt. Intestinal drug absorption and metabolism in cell cultures: Caco-2 and beyond. Pharm. Res. 14:1655-1658 (1997).
P. Artursson and J. Karlsson. Correlation between oral drug absorption in humans and apparent drug permeability coefficients in human intestinal epithelial (caco-2) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 175:880-885 (1991).
S. Yee. In vitro permeability across caco-2 cells (colonic) can predict in vivo (small intestinal) absorption in man: Fact or myth. Pharm. Res. 14:763-766 (1997).
A. Tsuji and I. Tamai. Carrier-meditated intestinal transport of drugs. Pharm. Res. 13:963-977 (1996).
H. Gutmann, G. Fricker, M. Török, S. Michael, C. Beglinger, and J. Drewe. Evidence for different ABC-transporters in caco-2 cells modulating drug uptake. Pharm. Res. 16:402-407 (1999).
T. Hirohashi, H. Suzuki, X.-Y. Chu, I. Tamai, A. Tsuji, and Y. Sugiyama. Function and expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein family in human colon adenocarcinoma cells (caco-2). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 292:265-270 (2000).
M. F. Paine, D. D. Shen, K. L. Kunze, J. D. Perkins, C. L. Marsh, J. P. McVicar, D. M. Barr, B. S. Gillies, and K. E. Thummel. First-pass metabolism of midazolam by the human intestine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 60:14-24 (1996).
C.-Y. Wu, L. Z. Benet, M. F. Hebert, S. K. Gupta, M. Rowland, D. Y. Gomez, and V. J. Wacher. Differentiation of absorption and first-pass gut and hepatic metabolism in humans: Studies with cyclosporine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 58:492-497 (1995).
P. Schmiedlin-Ren, K. E. Thummel, J. M. Fisher, M. F. Paine, K. S. Lown, and P. B. Watkins. Expression of enzymatically active CYP3A4 by caco-2 cells grown on extracellular matrix-coated permeable supports in the presence of 1α,25-dihydroxy-vitamin-D3. Mol. Pharmacol. 51:741-754 (1997).
C. L. Crespi, B. W. Penman, and M. Hu. Development of caco-2 cells expressing high levels of cDNA-derived cytochrome P4503A4. Pharm. Res. 13:1635-1641 (1996).
J. H. Hochman, M. Chiba, J. Nishime, M. Yamazaki, and J. H. Lin. Influence of p-glycoprotein on the transport and metabolism of indinavir in caco-2 cells expressing cytochrome P-450 3A4. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 292:310-318 (2000).
M. Hu, Y. Li, C. M. Davitt, S.-M. Huang, K. E. Thummel, B. W. Penman, and C. L. Crespi. Transport and metabolic characterization of caco-2 cells expressing CYP3A4 and CYP3A4 plus oxidoreductase. Pharm. Res. 16:1352-1359 (1999).
M. Kool, M. de Haas, G. L. Scheffer, R. J. Scheper, M. J. T. van Eijk, J. A. Juijn, F. Baas, and P. Borst. Analysis of expression of cMOAT(MRP2), MRP3, MRP4, and MRP5, homologues of the multi-drug resistance-associated protein gene (MRP1), in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 57:3537-3547 (1997).
J. M. Fisher, S. A. Wrighton, P. B. Watkins, P. Schmiedlin-Ren, J. C. Calamia, D. D. Shen, K. L. Kunze, and K. E. Thummel. First-pass midazolam metabolism catalyzed by 1α,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3-modified caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 289:1134-1142 (1999).
J. Hunter, M. A. Jepson, T. Tsuruo, N. L. Simmons, and B. H. Hirst. Functional expression of p-glycoprotein in apical membranes of human intestinal caco-2 cells: Kinetics of vinblastine secretion and interaction with modulators. J. Biol. Chem. 268:14991-14997 (1993).
P. Anderle, E. Niederer, W. Rubas, C. Hilgendorf, H. Spahn-Langguth, H. Wunderli-Allenspach, H. P. Merkle, and P. Langguth. P-glycoprotein (p-gp) mediated efflux in caco-2 monolayers: The influence of culturing conditions and drug exposure on p-gp expression levels. J. Pharm. Sci. 87:757-762 (1998).
R. Evers, G. J. R. Zaman, L. van Deemter, H. Jansen, J. Calafat, L. C. J. M. Oomen, R. P. J. Oude Elferink, P. Borst, and A. H. Schinkel. Basolateral localization and export activity of the human multidrug resistance-associated protein in polarized pig kidney cells. J. Clin. Invest. 97:1211-1218 (1996).
R. Evers, M. Kool, L. van Deemter, H. Janssen, J. Calafat, L. C. J.M. Oomen, C. C. Paulusma, R. P. J. Oude Elferink, F. Baas, A. H. Schinkel, and P. Borst. Drug export activity of the human canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter in polarized kidney MDCK cells expressing cMOAT (MRP2) cDNA. J. Clin. Invest. 101:1310-1319 (1998).
P. B. Watkins, S. A. Wrighton, E. G. Schuetz, D. T. Molowa, and P. S. Guzelian. Identification of glucocorticoid-inducible cytochromes P-450 in the intestinal mucosa of rats and man. J. Clin. Invest. 80:1029-1036 (1987).
L. Z. Benet, D. L. Kroetz, and L. B. Sheiner. Pharmacokinetics: The dynamics of drug absorption, distribution, and elimination. In J. G. Hardman, L. E. Limbird, P. B. Molinoff, R. W. Ruddon, and A. G. Gilman (eds.), Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, McGraw-Hill, New York 1996 pp. 3-28.
K. Hosoya, K.-J. Kim, and V. H. L. Lee. Age-dependent expression of p-glycoprotein gp170 in caco-2 cell monolayers. Pharm. Res. 13:885-890 (1996).
P. Artursson, A.-L. Ungell, and J.-E. Löfroth. Selective paracellular permeability in two models of intestinal absorption: Cultured monolayers of human intestinal epithelial cells and rat intestinal segments. Pharm. Res. 10:1123-1129 (1993).
V. D. Makhey, A. Guo, D. A. Norris, P. Hu, J. Yan, and P. J. Sinko. Characterization of the regional intestinal kinetics of drug efflux in rat and human intestine and in caco-2 cells. Pharm. Res. 15:1160-1167 (1998).
U. K. Walle, A. Galijatovic, and T. Walle. Transport of the flavonoid chrysin and its conjugated metabolites by the human intestinal cell line caco-2. Biochem. Pharmacol. 58:431-438 (1999).
R. A. Walgren, K. J. Karnaky, Jr., G. E. Lindenmayer, and T. Walle. Efflux of dietary flavonoid quercetin 4′-β-glucoside across human intestinal caco-2 cell monolayers by apical multi-drug resistance-associated protein-2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 294:830-836 (2000).
G. L. Scheffer, M. Kool, M. Heijn, M. de Haas, A. C. L. M. Pijnenborg, J. Wijnholds, A. van Helvoort, M. C. de Jong, J. H. Hooijberg, C. A. A. M. Mol, M. van der Linden, J. M. L. de Vree, P. van der Valk, R. P. J. Oude Elferink, P. Borst, and R. J. Scheper. Specific detection of multidrug resistance proteins MRP1, MRP2, MRP3, MRP5, and MDR3 p-glycoprotein with a panel of monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 60:5269-5277 (2000).
M. J. Flens, G. J. R. Zaman, P. van der Valk, M. A. Izquierdo, A. B. Schroeijers, G. L. Scheffer, P. van der Groep, M. de Haas, C. J. L. M. Meijer, and R. J. Scheper. Tissue distribution of the multi-drug resistance protein. Am. J. Pathol. 148:1237-1247 (1996).
M. J. Flens, M. A. Izquierdo, G. L. Scheffer, J. M. Fritz, C. L. M. Meijer, R. J. Scheper, and G. J. R. Zaman. Immunochemical detection of the multidrug resistance-associated protein MRP in human multidrug-resistant tumor cells by monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 54:4557-4563 (1994).
A. D. Mottino, T. Hoffman, L. Jennes, and M. Vore. Expression and localization of multidrug resistant protein mrp2 in rat small intestine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 293:717-723 (2000).
R. A. M. H. Van Aubel, A. Hartog, R. J. M. Bindels, C. H. Van Os, and F. G. M. Russel. Expression and immunolocalization of multidrug resistance protein 2 in rabbit small intestine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 400:195-198 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cummins, C.L., Mangravite, L.M. & Benet, L.Z. Characterizing the Expression of CYP3A4 and Efflux Transporters (P-gp, MRP1, and MRP2) in CYP3A4-Transfected Caco-2 Cells After Induction with Sodium Butyrate and the Phorbol Ester 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate. Pharm Res 18, 1102–1109 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010914624111
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010914624111