Abstract
Purpose. MDR1 P-glycoprotein (P-gp) plays an important role in determining drug disposition. The purpose of the present study was to establish in vitro models to predict the in vivo function of P-gp.
Methods. As an in vitro method, the transcellular transport of 12 compounds across the monolayer of Caco-2- and MDR1-transfected cells was examined. The ability of these compounds to stimulate the ATP hydrolysis was also determined using the isolated membrane fraction expressing P-gp. As a parameter to describe the in vivo P-gp function, we calculated the brain-to-plasma concentration ratio of compounds in mdr1a/1b knockout mice divided by the same ratio in wild type mice.
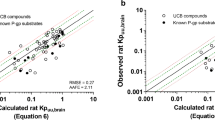
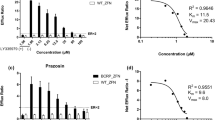
Results. A good correlation was observed between the in vitro flux ratio across the monolayer and in vivo P-gp function for 12 compounds. Although all compounds that stimulated ATP hydrolysis were significantly transported by P-gp, some compounds were transported by P-gp without significantly affecting ATP hydrolysis.
Conclusion. Collectively, the in vitro flux ratio across monolayers of P-gp-expressing cells may be used to predict in vivo P-gp function. The extent of ATP-hydrolysis in vitro may also be a useful parameter for in vivo prediction, particularly for eliminating P-gp substrates in high-throughput screening procedures.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. J. Chen, J. E. Chin, K. Ueda, D. P. Clark, I. Pastan, M. M. Gottesman, and I. B. Roninson. Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Cell 47:381-389 (1986).
K. Ueda, D. P. Clark, C. J. Chen, I. B. Roninson, M. M. Gottesman, and I. Pastan. The human multidrug resistance (mdr1) gene. cDNA cloning and transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 262:505-508 (1987).
S. V. Ambudkar, S. Dey, C. A. Hrycyna, M. Ramachandra, I. Pastan, and M. M. Gottesman. Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 39:361-398 (1999).
V. J. Wacher, J. A. Silverman, Y. Zhang, and L. Z. Benet. Role of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 3A in limiting oral absorption of peptides and peptidomimetics. J. Pharm. Sci. 87:1322-1330 (1998).
L. Z. Benet, T. Izumi, Y. Zhang, J. A. Silverman, and V. J. Wacher. Intestinal MDR transport proteins and P450 enzymes as barriers to oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 62:25-31 (1999).
A. H. Schinkel. Pharmacological insights from P-glycoprotein knockout mice. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 36:9-13 (1998).
S. Hoffmeyer, O. Burk, O. von Richter, H. P. Arnold, J. Brockmöller, A. Johne, I. Cascorbi, T. Gerloff, I. Roots, M. Eichelbaum, and U. Brinkmann. Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: Multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:3473-3478 (2000).
U. Mayer, E. Wagenaar, B. Dorobek, J. H. Beijnen, P. Borst, and A. H. Schinkel. Full blockade of intestinal P-glycoprotein and extensive inhibition of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein by oral treatment of mice with PSC833. J. Clin. Invest. 100:2430-2436 (1997).
H. Kusuhara, H. Suzuki, T. Terasaki, A. Kakee, M. Lemaire, and Y. Sugiyama. P-glycoprotein mediates the efflux of quinidine across the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283:574-580 (1997).
D. J. Edwards, M. E. Fitzsimmons, E. G. Schuetz, K. Yasuda, M. P. Ducharme, L. H. Warbasse, P. M. Woster, J. D. Schuetz, and P. Watkins. 6′,7′-Dihydroxybergamottin in grapefruit juice and Seville orange juice: Effects on cyclosporine disposition, enterocyte CYP3A4, and P-glycoprotein. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 65: 237-244 (1999).
H. Suzuki and Y. Sugiyama. Role of metabolic enzymes and efflux transporters in the absorption of drugs from the small intestine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 12:3-12 (2000).
D. K. Yu. The contribution of P-glycoprotein to pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 39:1203-1211 (1999).
M. Verschraagen, C. H. W. Koks, J. H. M. Schellens, and J. H. Beijnen. P-glycoprotein system as a determinant of drug interactions: The case of digoxin-verapamil. Pharmacol. Res. 40:301-306 (1999).
A. H. Schinkel, J. J. M. Smit, O. van Tellingen, J. H. Beijnen, E. Wagenaar, L. van Deemter, C. A. A. M. Mol, M. A. van der Valk, E. C. Robanus-Maandag, H. P. J. te Riele, A. J. M. Berns, and P. Borst. Disruption of the mouse moder1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell 77:491-502 (1994).
G. Y. Kwei, R. F. Alvaro, Q. Chen, H. J. Jenkins, C. E. A. C. Hop, C. A. Keohane, V. T. Ly, J. R. Strauss, R. W. Wang, Z. Wang, T. R. Pippert, and D. R. Umbenhauer. Disposition of ivermectin and cyclosporin A in CF-1 mice deficient in mdr1a P-glycoprotein. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27:581-587 (1999).
A. H. Schinkel, E. Wagenaar, L. van Deemter, C. A. A. M. Mol, and P. Borst. Absence for the mdr1a P-glycoprotein in mice affects tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone, digoxin, and cyclosporin A. J. Clin. Invest. 96:1698-1705 (1995).
A. H. Schinkel, E. Wagenaar, C. A. A. M. Mol, and L. van Deemter. P-glycoprotein in the blood-brain barrier of mice influences the brain penetration and pharmacological activity of many drugs. J. Clin. Invest. 97:2517-2524 (1996).
A. Tsuji, H. Takanaga, I. Tamai, and T. Terasaki. Transcellular transport of benzoic acid across Caco-2 cells by a pH-dependent and carrier-mediated transport mechanism. Pharm. Res. 11:30-37 (1994).
R. B. Kim, M. F. Fromm, C. Wandel, B. Leake, A. J. J. Wood, D. M. Roden, and G. R. Wilkinson. The drug transporter P-glycoprotein limits oral absorption and brain entry of HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 101:289-294 (1998).
B. Sarkadi, E. M. Price, R. C. Boucher, U. A. Germann, and G. A. Scarborough. Expression of the human multidrug resistance cDNA in insect cells generates a high activity Drug-stimulated membrane ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 267:4854-4858 (1992).
F. J. Sharom, Xiaohong Yu, Peihua Lu, Ronghua Liu, J. W. K Chu, K. Szabo, M. Muller, C. D. Hose, A. Monks, A. Varadi, J. Seprodi, and B. Sarkadi. Interaction of the P-glycoprotein Multidrug transporter (MDR1) with high affinity peptide chemosensitizers in isolated membranes, reconstituted system and intact cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 58:571-586 (1999).
J. W. Jonker, E. Wagenaar, L. van Deemter, R. Gottschlich, H. M. Bender, J. Dasenbrock, and A. H. Schinkel. Role of blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein in limiting brain accumulation and sedative side-effects of asimadoline, a peripherally acting analgaesic drug. Br. J. Pharmacol. 127:43-50 (1999).
C. F. Neville, S. Ninomiya, N. Shimada, T. Kamataki, S. Imaoka, and Y. Funae. Characterization of specific cytochrome P450 enzyme responsible for the metabolism of diazepam hepatic microsomes of adult male rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 45:59-65 (1993).
N. H. Hendrikse, A. H. Schinkel, E. G. E. De Vries, E. Fluks, W. T. A. Van der Graaf, A. T. M. Willemsen, W. Vaalburg, and E. J. F. Franssen. Complete in vivo reversal of P-glycoprotein pump function in the blood-drain barrier visualized with positron emission tomography. Br. J. Pharmacol. 124:1413-1418 (1998).
M. Yamazaki, W. E. Neway, T. Ohe, I. Chen, J. F. Rowe, J. H. Hochman, M. Chiba, and J. H. Lin. In vitro substrate identification studies for P-glycoprotein-mediated transport: species difference and predictability of in vivo results. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 296:723-735 (2001).
T. Litman, T. Zeuthen, T. Skovsgaard, and W. D. Stein. Structure-activity relationships of P-glycoprotein interacting drugs: kinetic characterization of their effects on ATPase activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1361:159-168 (1997).
E. Buxbaum. Co-operative binding sites for transported substrates in the multiple drug resistance transporter Mdr1. Eur. J. Biochem. 265:64-70 (1999).
S. Drori, G. D. Eytan, and Y. G. Assaraf. Potentiation of anticancer-drug cytotoxicity by multidrug-resistance chemosensitizers involves alterations in membrane fluidity leading to increased membrane permeability. Eur. J. Biochem. 228:1020-1029 (1995).
M. J. Borgnia, G. D. Eytan, and Y. G. Assaraf. Competition of hydrophobic peptides, cytotoxic drugs, and chemosensitizers on a common P-glycoprotein pharmacophore as revealed by Its ATPase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 271:3163-3171 (1996).
K. Ueda, A. Yoshida, and T. Amachi. Recent progress in P-glycoprotein research. Anti-Cancer Drug Design 14:115-121 (1999).
Z. E. Sauna and S. V. Ambudkar. Evidence for a requirement for ATP hydrolysis at two distinct steps during a single turnover of the catalytic cycle of human P-glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:2515-2520 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adachi, Y., Suzuki, H. & Sugiyama, Y. Comparative Studies on in Vitro Methods for Evaluating in Vivo Function of MDR1 P-Glycoprotein. Pharm Res 18, 1660–1668 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013358126640
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013358126640