Abstract
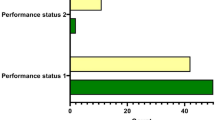
The effect of a SNP in exon 10 of CYP19 on tumor mRNA levels and splice variants were studied and correlated with clinical parameters and risk of breast cancer. In the vast majority of breast cancers, the estrogen levels modulate the tumor growth and depend on the activity of CYP19. Patients (n=481) and controls (n=236) were genotyped by T-tracks in a single sequencing reaction (SSR). The frequency of TT genotypes was significantly higher in patients versus controls (P=0.007) particularly among those with stage III and IV disease (P=0.004) and with tumors larger than 5 cm (P=0.001). A significant association between presence of the T allele and the level of aromatase mRNA in the tumors was observed (P=0.018), as well as with a switch from adipose promoter to ovary promoter (P=0.004). Previously, we reported a rare polymorphic allele of CYP19 (repeat (TTTA)12) to be significantly more frequent in breast cancer patients than in controls. Here we describe another polymorphism, a C–T substitution in exon 10 of the CYP19 gene which is in strong linkage disequilibrium with the (TTTA)n polymorphism but with higher frequency of the variant allele. Our data suggest that the T-allele of the CYP19 gene is associated with a ‘high activity’ phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burak Jr WE, Quinn AL, Farrar WB and Brueggemeier RW . 1997 Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 44: 57–64
Durgam VR, Easton JA, Surya R and Tekmal RR . 1995 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1263: 89–92
Fisher CR, Graves KH, Parlow AF and Simpson ER . 1998 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 6965–6970
Hankinson SE, Willet WC, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL and Speizer FE . 1998 J Nat Cancer Inst 90: 1292–1299
Harada N, Ogawa H, Shozu M and Yamada K . 1992 Am J Hum Genet 51: 666–672
Harada N, Utsumi T and Takagi Y . 1993 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 11312–11316
Harada N, Utsumi T and Tagaki Y . 1995 Pharmacogenetics 5: 59–64
Kristensen VN, Andersen TI, Lindblom A, Nesland J, Olsen A and Børresen-Dale AL . 1998a Pharmacogenetics 8: 43–48
Kristensen T, Nedelcheva Kristensen V and Børresen-Dale AL . 1998b BioTechniques 24: 832–835
Mahendroo MS, Mendelson CR and Simpson ER . 1993 J Biol Chem 268: 19463–19470
Means GD, Mahendroo MS, Corbin CJ, Mathis JM, Powell FE, Mendelson CR and Simpson ER . 1989 J Biol Chem 264: 19386–19391
Michael MD, Michael LF and Simpson ER . 1997 Mol Cell Endocrinol 134: 147–156
Pike MC, Spicer DV, Dagmoush L and Press MF . 1993 Epidemiol Rev 15: 17–35
Simpson ER, Mahendroo MS, Nichols JE and Bulun SE . 1994 Int J Fertil 39: 75–83
Sourdaine P, Parker MG, Telford J and Miller WR . 1994 J Mol Endocrinol 13: 331–337
Thomas HV, Key TJ, Allen DS, Moore JW, Dowsett M, Fentiman IS and Wang DY . 1997 Brit J Cancer 75: 1075–1079
Toda K, Terashima M, Mitsuuchi Y, Yamazaki Y, Yokoyama Y, Nojima S, Ushiro H, Maeda T, Yamamoto Y, Sagara Y and Shizuta Y . 1989 FEBS Lett 247: 371–376
Walter AE, Turner J, Kim MH, Lyttle P, Mueller P, Mathews DH and Zuker M . 1994 Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 9218–9222
Zhao Y, Agarwal VR, Mendelson CR and Simson ER . 1997 J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 61: 203–210
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Norwegian Cancer Society and the Norwegian Council for Science and Humanities. The authors would like to thank Professor Zuker, Institute for Biomedical Computing, Washington University for his comments on the RNA folding model.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kristensen, V., Harada, N., Yoshimura, N. et al. Genetic variants of CYP19 (aromatase) and breast cancer risk. Oncogene 19, 1329–1333 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203425
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203425
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Elevated Aromatase (CYP19A1) Expression Is Associated with a Poor Survival of Patients with Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
Hormones and Cancer (2018)
-
Alcohol-related breast cancer in postmenopausal women – effect of CYP19A1, PPARG and PPARGC1A polymorphisms on female sex-hormone levels and interaction with alcohol consumption and NSAID usage in a nested case-control study and a randomised controlled trial
BMC Cancer (2016)
-
Genetics of androgen metabolism in women with infertility and hypoandrogenism
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2015)
-
Role of cytochrome P450 genes in breast cancer etiology and treatment: effects on estrogen biosynthesis, metabolism, and response to endocrine therapy
Cancer Causes & Control (2015)
-
Germline variants in the CYP19A1 gene are related to specific adverse events in aromatase inhibitor users: a substudy of Dutch patients in the TEAM trial
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2014)