Abstract
We used the intestinal segregated flow model (SFM) versus the traditional model (TM), nested within physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) models, to describe the biliary and urinary excretion of morphine 3β-glucuronide (MG) after intravenous and intraduodenal dosing of morphine in rats in vivo. The SFM model describes a partial (5%–30%) intestinal blood flow perfusing the transporter- and enzyme-rich enterocyte region, whereas the TM describes 100% flow perfusing the intestine as a whole. For the SFM, drugs entering from the circulation are expected to be metabolized to lesser extents by the intestine due to the segregated flow, reflecting the phenomenon of shunting and route-dependent intestinal metabolism. The poor permeability of MG crossing the liver or intestinal basolateral membranes mandates that most of MG that is excreted into bile is hepatically formed, whereas MG that is excreted into urine originates from both intestine and liver metabolism, since MG is effluxed back to blood. The ratio of MG amounts in urine/bile 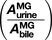 for intraduodenal/intravenous dosing is expected to exceed unity for the SFM but approximates unity for the TM. Compartmental analysis of morphine and MG data, without consideration of the permeability of MG and where MG is formed, suggests the ratio to be 1 and failed to describe the kinetics of MG. The observed intraduodenal/intravenous ratio of
for intraduodenal/intravenous dosing is expected to exceed unity for the SFM but approximates unity for the TM. Compartmental analysis of morphine and MG data, without consideration of the permeability of MG and where MG is formed, suggests the ratio to be 1 and failed to describe the kinetics of MG. The observed intraduodenal/intravenous ratio of  (2.55 at 4 hours) was better predicted by the SFM-PBPK (2.59 at 4 hours) and not the TM-PBPK (1.0), supporting the view that the SFM is superior for the description of intestinal-liver metabolism of morphine to MG. The SFM-PBPK model predicts an appreciable contribution of the intestine to first pass M metabolism.
(2.55 at 4 hours) was better predicted by the SFM-PBPK (2.59 at 4 hours) and not the TM-PBPK (1.0), supporting the view that the SFM is superior for the description of intestinal-liver metabolism of morphine to MG. The SFM-PBPK model predicts an appreciable contribution of the intestine to first pass M metabolism.
Footnotes
- Received January 16, 2016.
- Accepted April 19, 2016.
Q.J.Y. and J.F. are co-first authors.
↵1 Current affiliation: Office of Generic Drugs, Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, Maryland.
↵2 Current affiliation: Apotex Inc., Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
↵3 Current affiliation: Bristol Myers Squibb, Princeton, New Jersey.
This research was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research [(to K.S.P.)] and the Ontario Graduate Scholarship Program [(to Q.J.Y.)].
- Copyright © 2016 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
DMD articles become freely available 12 months after publication, and remain freely available for 5 years.Non-open access articles that fall outside this five year window are available only to institutional subscribers and current ASPET members, or through the article purchase feature at the bottom of the page.
|






